|
Hispanic Studies
Hispanism (sometimes referred to as Hispanic studies or Spanish studies) is the study of the literature and culture of the Spanish-speaking world, principally that of Spain and Hispanic America. It can also entail studying Spanish language and culture in the United States and in other presently or formerly Spanish-speaking countries in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific, such as the Philippines and Equatorial Guinea. A hispanist is a scholar specializing in Hispanicism. It was used in an article by Miguel de Unamuno in 1908 referring to 'el hispanista italiano Farinelli', and was discussed at length for the U.S. by Hispanist Richard L. Kagan of Johns Hopkins University. The work carried out by Hispanists includes translations of literature and they may specialize in certain genres, authors or historical periods of the Iberian Peninsula, Hispanic America, and the Spanish Philippines. Origins During the 16th century, Spain was a motor of innovation in Europe, given its links to new ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hispanic
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, Spanish culture, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad. The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to Viceroyalty, viceroyalties formerly part of the Spanish Empire following the Spanish colonization of the Americas, parts of the Spanish East Indies, Asia-Pacific region and Hispanic Africa , Africa. Outside of Spain, the Spanish language is a predominant or official language in the countries of Hispanic America and Equatorial Guinea. Further, the cultures of these countries were influenced by Spain to different degrees, combined with the local pre-Hispanic culture or other foreign influences. Former Spanish colonies elsewhere, namely the Spanish East Indies (the Philippines, Marianas, etc.) and Spanish Sahara (Western Sahara), were also influenced by Spanish culture, however Spanish is not a predominant language in these regions. Hispanic cul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (), ** * Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica'' ** ** * french: Péninsule Ibérique * mwl, Península Eibérica * eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defining the westernmost edge of Eurasia. It is principally divided between Spain and Portugal, comprising most of their territory, as well as a small area of Southern France, Andorra, and Gibraltar. With an area of approximately , and a population of roughly 53 million, it is the second largest European peninsula by area, after the Scandinavian Peninsula. Name Greek name The word ''Iberia'' is a noun adapted from the Latin word "Hiberia" originating in the Ancient Greek word Ἰβηρία ('), used by Greek geographers under the rule of the Roman Empire to refer to what is known today in English as the Iberian Peninsula. At that time, the name did not describe a single geographical entity or a distinct population; the same name was us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Doergangk
Heinrich Doergangk (Cologne, second half of the 16th century - before 1626) was a German Hispanist and grammarian. An advocate of Roman Catholicism, he wrote in Latin a Spanish grammar titled ''Institutiones in linguam hispanicam, admodum faciles, quales antehac nunquam visae'' (Coloniae, 1614), where he attacks Protestantism Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b .... References Writers from Cologne German Hispanists Grammarians from Germany Linguists of Spanish 16th-century philologists 17th-century philologists {{Germany-linguist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean Doujat
Jean Doujat (1609, in Toulouse – 27 October 1688, in Paris) was a French lawyer, '' juris consultus'', professor of canon law at the Collège royal, docteur-régent at the faculté de droit de Paris, preceptor of the Dauphin and historian. His works include histories of the reign of Louis XIV , house = Bourbon , father = Louis XIII , mother = Anne of Austria , birth_date = , birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France , death_date = , death_place = Palace of Ver .... He wrote an important ''Grammaire espagnole abrégée''. References 1609 births 1688 deaths Writers from Toulouse 17th-century French lawyers Collège de France faculty 17th-century French historians French translators Latin–French translators French legal writers French Hispanists Grammarians from France Linguists of Spanish Members of the Académie Française French male non-fiction writers 17th-century French tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Minsheu
John Minsheu (or Minshew) (1560–1627) was an English linguist and lexicographer. Biography He was born and died in London. Little is known about his life. He published some of the earliest dictionaries and grammars of the Spanish language for speakers of English. His major work was the ''Ductor in linguas'' (''Guide into tongues''), an eleven-language dictionary. With his ''Ductor in linguas'' he is also one of the first known inventors of the use of subscription as a method of funding publication of a book. He also expanded Richard Percivale's Spanish dictionary. Works * ''Joyful Newes out of the Newe Founde Worlde'' (1577) * ''Spanish Grammar'' (1599) * ''Dictionarie in Spanish and English'' (1599 & 1623), an augmented version of ''Bibliotheca Hispanica'' (1591) by Richard Percyvall (1993 reprint: ) * ''Ductor in linguas'' (''The Guide into Tongues'') (1617) ** including ''Vocabularium Hispanicolatinum et Anglicum copiossissimum'' (''A Most Copious Spanish Dictionarie wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Percivale
Sir Richard Percivale (''alias'' Perceval etc.) (1550 – 4 September 1620) of Sydenham, near Bridgwater, Somerset, was an English administrator and politician, also known as a Hispanist and lexicographer. He wrote a Spanish grammar for English readers, ''A Spanish Grammar'', and a dictionary, both included in his ''Bibliotheca Hispanica'' (1591); this work was later enlarged by John Minsheu in ''A dictionarie in Spanish and English'' (London: Edmund Bollifant, 1599; London: printed by John Haviland for various booksellers, including William Aspley, Matthew Lownes, and George Latham, 1623). Origins He was the eldest son and heir of George Perceval (c1532–1601) (''alias'' Percival, etc.) of Sydenham, near Bridgwater, Somerset, by his wife Elizabeth Bampfylde, a daughter of Sir Edward Bampfylde (d.1528) of Poltimore, Devon and Elizabeth Wadham. His family had inherited the manor of Sydenham by marriage to the heiress of the prominent Westcountry Sydenham family, which had origina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Miranda
Giovanni Miranda was an Italian Hispanist and grammar In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structure, structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clause (linguistics), clauses, phrases, and words. The term can also refer to the study of such constraint ...ian from the 16th century. He wrote the important ''Osservationi della lingua castigliana... diuise in quatro libri: ne’ quali s’insegna con gran facilità la perfetta lingua spagnuola. Con due tauole: l’vna de’ capi essentiali, & l’altra delle cose notabile'' (Venice: Gabriel Giolito de Ferrari, 1566; modern edition of Juan M. Lope Blanch, Mexico: UNAM, 1998), partially inspired by the work of Giovanni Mario Alessandri. References Italian Hispanists Grammarians from Italy Linguists of Spanish 16th-century Italian writers {{Italy-linguist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giovanni Mario Alessandri
Giovanni Mario Alessandri was an Italian Hispanist and grammarian from the 16th century. He spent a time at the Spanish royal court and he wrote the first Spanish grammar for Italians, ''Il Paragone della Lingua Toscana et Castigliana'' (Nápoles: Mattia Cancer, 1560). There he is particularly careful with phonetics. This work was inspirational for Giovanni Miranda Giovanni Miranda was an Italian Hispanist and grammar In linguistics, the grammar of a natural language is its set of structure, structural constraints on speakers' or writers' composition of clause (linguistics), clauses, phrases, and words ...'s ''Osservationi de la lingua castigliana''. References Italian Hispanists Grammarians from Italy Linguists of Spanish 16th-century Italian writers {{Italy-linguist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
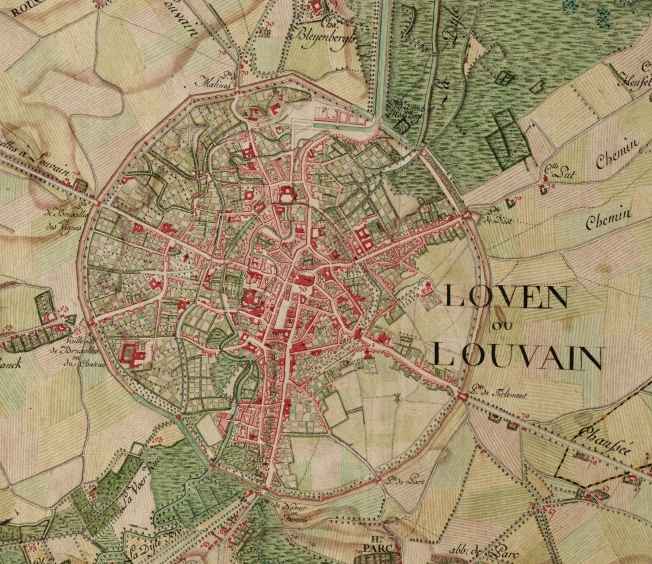
Leuven
Leuven (, ) or Louvain (, , ; german: link=no, Löwen ) is the capital and largest city of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is located about east of Brussels. The municipality itself comprises the historic city and the former neighbouring municipalities of Heverlee, Kessel-Lo, a part of Korbeek-Lo, Wilsele and Wijgmaal. It is the eighth largest city in Belgium, with more than 100,244 inhabitants. KU Leuven, Belgium's largest university, has its flagship campus in Leuven, which has been a university city since 1425. This makes it the oldest university city in the Low Countries. The city is home of the headquarters of Anheuser-Busch InBev, the world's largest beer brewer and sixth-largest fast-moving consumer goods company. History Middle Ages The earliest mention of Leuven (''Loven'') dates from 891, when a Viking army was defeated by the Frankish king Arnulf of Carinthia (see: Battle of Leuven). According to a legend, the city's red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cristóbal De Villalón
Cristóbal de Villalón ( – ) was a Spanish professor and humanist. He was probably a native of Villalón de Campos. He obtained a bachelor of arts degree from the University of Alcalá in 1525 and a licentiate in logic from the University of Salamanca in 1529 or 1530. From 1530 to 1545, he was a professor of logic at the University of Valladolid. In 1532–1534, he was a private tutor in Latin and rhetoric to the family of the Counts of Lemos. He won a lawsuit against the countess for back wages. In 1545, he obtained a degree in theology from Valladolid. He may have become a priest around this time. He retired to , where he died.José Miguel Martínez Torrejón and Pedro Schwartz Girón"Villalón, Cristóbal de" '' Diccionario biográfico español'' (Real Academia de la Historia, 2018). Works *''Tragedia de Mirra'', written while a student and published at Medina del Campo in 1536 *''Ingeniosa comparación entre lo antiguo y lo presente'', written while a student and published at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |