|
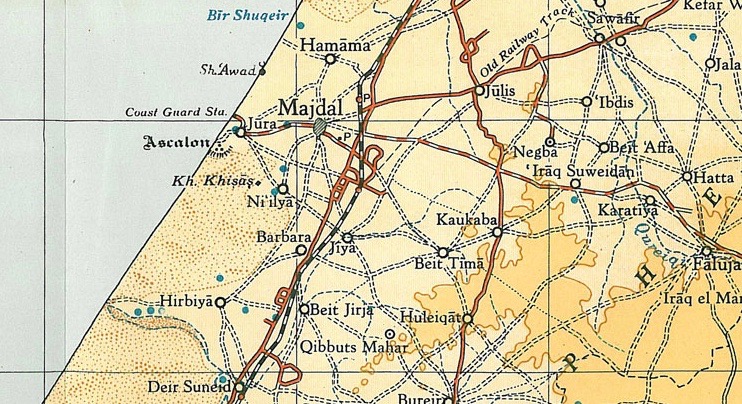
Hiribya
Hirbiya ( ar, هربيا) was a Palestinian Arab village in the Gaza Subdistrict, located northeast of Gaza along the southern coastal plain of Palestine. Situated where the Battle of La Forbie took place in 1244, it was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.Khalidi, 1992, p.101. History Settlement at the site of Hirbiya dates back to the Canaanite period. It was known as "Forbie" to the Crusaders. In 1226, the Syrian geographer Yaqut al-Hamawi called it "Firbiya" (or "Farbaya") and noted that it was within the administrative jurisdiction of Ascalon. The village was the site of a crucial battle, called the Battle of La Forbie, between the Crusaders and the Ayyubids, which ended in a decisive Ayyubid victory. Historians consider it second in strategic significance only to the Battle of Hattin in 1187. A circular well, made of masonry, and the foundations of a small tower was still found there in the late 19th century. Ottoman era Hirbiya was incorporated into the Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiribya 1931
Hirbiya ( ar, هربيا) was a Palestinian Arab village in the Gaza Subdistrict, located northeast of Gaza along the southern coastal plain of Palestine. Situated where the Battle of La Forbie took place in 1244, it was depopulated during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War.Khalidi, 1992, p.101. History Settlement at the site of Hirbiya dates back to the Canaanite period. It was known as "Forbie" to the Crusaders. In 1226, the Syrian geographer Yaqut al-Hamawi called it "Firbiya" (or "Farbaya") and noted that it was within the administrative jurisdiction of Ascalon. The village was the site of a crucial battle, called the Battle of La Forbie, between the Crusaders and the Ayyubids, which ended in a decisive Ayyubid victory. Historians consider it second in strategic significance only to the Battle of Hattin in 1187. A circular well, made of masonry, and the foundations of a small tower was still found there in the late 19th century. Ottoman era Hirbiya was incorporated into t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of La Forbie
The Battle of La Forbie, also known as the Battle of Hiribya, was fought October 17, 1244 – October 18, 1244 between the allied armies (drawn from the Kingdom of Jerusalem, the crusading orders, the breakaway Ayyubids of Damascus, Homs, and Kerak) and the Egyptian army of the Ayyubid Sultan as-Salih Ayyub, reinforced with Khwarezmian mercenaries. The resulting Ayyubid victory led to the call for the Seventh Crusade and marked the collapse of Christian power in the Holy Land. Prelude The capture of Jerusalem by the Khwarezmians in August had caused great alarm among both the Christian and the Muslim states. Al-Mansur, the Emir of Homs and an-Nasir Dawud, ruling Kerak, joined the Templars, the Hospitallers, the Teutonic Knights, the Order of Saint Lazarus, and the remaining forces of the Kingdom of Jerusalem to take the field against the Egyptian Sultanate. The two armies met near La Forbie, a small village northeast of Gaza. On the allied side, Al-Mansur was pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaza Subdistrict, Mandatory Palestine
The Gaza Subdistrict ( ar, قضاء غزة, he, נפת עזה) was one of the subdistricts of Mandatory Palestine. It was situated in the southern Mediterranean coastline of the British Mandate of Palestine. After the 1948 Arab-Israeli War, the district disintegrated, with Israel controlling the northern and eastern portions while Egypt held control of the southern and central parts – which became the Gaza Strip, under Egyptian military between 1948 and 1967, Israeli military rule between 1967 and 2005, part of the Palestinian National Authority (with some aspects of retained Israeli rule until the 2005 withdrawal) after the Oslo Accords until 2007, and is currently ruled by the Hamas as a de facto separate entity from the Palestinian National Authority. The parts which Israel held since 1948 were merged into Israeli administrative districts, their connection with Gaza severed. Borders * Beersheba Subdistrict (Southeast) * Ramle Subdistrict (Northeast) * Hebron Subdistrict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zikim
Zikim ( he, זִיקִים) is a kibbutz in southern Israel. Located in the northern Negev desert, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hof Ashkelon Regional Council. In it had a population of . History The kibbutz was established in 1949 on land that had belonged to the depopulated Palestinian village of Hiribya, by a group of young Romanian Jews who belonged to Hashomer Hatzair before their arrival in Mandatory Palestine in 1947. At that time, Jewish settlement in the Negev was very sparse, and each new location was considered to be a "point of light" (''zik'') in the wilderness. Michael Har-Segor, later an Israeli historian, came up with the name while imprisoned in Romania for his activity in Hashomer Hatzair. He says he translated a quote from Pushkin into Hebrew: "From sparks shall come a flame." Zikim attracted members of Hashomer Hatzair from around the world, most recently from South America. British actor Bob Hoskins, although not Jewish, worked as a volunteer in Ziki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karmia
Karmia ( he, כַּרְמִיָּה) is a kibbutz in southern Israel. Located between Ashkelon and the Gaza Strip, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hof Ashkelon Regional Council. In it had a population of . History Kibbutz Karmia was established on 20 May 1950 by a Nahal gar'in of Hashomer Hatzair members from France and Tunisia who had been trained in Beit Zera. It was established on the land the Palestinian village of Hiribya, which was depopulated during the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. Its name is derived from the Hebrew for vineyard (, ''Kerem''), which were common in the area. In 1972 a blanket factory was established in the kibbutz. The kibbutz absorbed 54 families from Elei Sinai and Nisanit, which were evacuated as part of the disengagement plan. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yad Mordechai
Yad Mordechai ( he, יַד מָרְדְּכַי, ''lit.'' Memorial of Mordechai) is a kibbutz in Southern Israel. Located 10 km (6.2 mi) south of Ashkelon, it falls under the jurisdiction of Hof Ashkelon Regional Council. In it had a population of . History The community was founded in 1936 by Hashomer Hatzair members from Poland and initially organized themselves in a kibbutz called Mitzpe Yam close to Netanya, which was also founded in 1936. However, the 14 dunams allocated to the kibbutz were insufficient to develop the kibbutz. As part of settlement in the Negev, the community moved to its site near Ashkelon in December 1943. The kibbutz was renamed in memorial to Mordechai Anielewicz, who was the first commander of the Jewish Fighting Organization in the Warsaw Ghetto uprising. During the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, the kibbutz was attacked by Egypt in the Battle of Yad Mordechai. Among the many Holocaust memorials in Israel, the "From Holocaust to Revival Museum" especi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liwa Of Gaza
Gaza Sanjak ( ar, سنجق غزة) was a sanjak of the Damascus Eyalet, Ottoman Empire centered in Gaza. In the 16th century it was divided into ''nawahi'' (singular: ''nahiya''; third-level subdivisions): Gaza in the south and Ramla in the north. List of settlements In the 1596- daftar, the sanjak contained the following nahiyah and villages/town Gaza Nahiyah *Al-Sawafir al-Sharqiyya, Bayt Tima, Hamama,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 142 Al-Tina, Yibna, Isdud, Arab Suqrir,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 143 Deir al-Balah, Burayr, Jabalia, Beit Lahia, Al-Majdal, Askalan, Bayt 'Affa, Najd, Ni'ilya,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 144 Bayt Jirja, Hiribya, Qatra, Iraq Suwaydan, Kawkaba, Beit Jimal Monastery, Al-Batani al-Sharqi,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 145 Al-Qubayba, Al-Faluja, Bayt Daras, Al-Maghar,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1977, p. 146 Hatta, Jusayr, Zikrin, Zayta, Barqa, Beit Hanoun, Dayr Sunayd, Simsim,Hütteroth and Abdulfattah, 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandatory Palestine
Mandatory Palestine ( ar, فلسطين الانتدابية '; he, פָּלֶשְׂתִּינָה (א״י) ', where "E.Y." indicates ''’Eretz Yiśrā’ēl'', the Land of Israel) was a geopolitical entity established between 1920 and 1948 in the region of Palestine under the terms of the League of Nations Mandate for Palestine. During the First World War (1914–1918), an Arab uprising against Ottoman rule and the British Empire's Egyptian Expeditionary Force under General Edmund Allenby drove the Ottoman Turks out of the Levant during the Sinai and Palestine Campaign. The United Kingdom had agreed in the McMahon–Hussein Correspondence that it would honour Arab independence if the Arabs revolted against the Ottoman Turks, but the two sides had different interpretations of this agreement, and in the end, the United Kingdom and France divided the area under the Sykes–Picot Agreementan act of betrayal in the eyes of the Arabs. Further complicating the issue was t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Well
A well is an excavation or structure created in the ground by digging, driving, or drilling to access liquid resources, usually water. The oldest and most common kind of well is a water well, to access groundwater in underground aquifers. The well water is drawn up by a pump, or using containers, such as buckets or large water bags that are raised mechanically or by hand. Water can also be injected back into the aquifer through the well. Wells were first constructed at least eight thousand years ago and historically vary in construction from a simple scoop in the sediment of a dry watercourse to the qanats of Iran, and the stepwells and sakiehs of India. Placing a lining in the well shaft helps create stability, and linings of wood or wickerwork date back at least as far as the Iron Age. Wells have traditionally been sunk by hand digging, as is still the case in rural areas of the developing world. These wells are inexpensive and low-tech as they use mostly manual labour, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) // CITED: p. 36 (PDF p. 38/338) also known as the Turkish Empire, was an empire that controlled much of Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and Northern Africa between the 14th and early 20th centuries. It was founded at the end of the 13th century in northwestern Anatolia in the town of Söğüt (modern-day Bilecik Province) by the Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. After 1354, the Ottomans crossed into Europe and, with the conquest of the Balkans, the Ottoman beylik was transformed into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed the Conqueror. Under the reign of Suleiman the Magnificent, the Ottoman Empire marked the peak of its power and prosperity, as well a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Defter
A ''defter'' (plural: ''defterler'') was a type of tax register and land cadastre in the Ottoman Empire. Description The information collected could vary, but ''tahrir defterleri'' typically included details of villages, dwellings, household heads (adult males and widows), ethnicity/religion (because these could affect tax liabilities/exemptions), and land use. The defter-i hakâni was a land registry, also used for tax purposes. Each town had a defter and typically an officiator or someone in an administrative role to determine whether the information should be recorded. The officiator was usually some kind of learned man who had knowledge of state regulations. The defter was used to record family interactions such as marriage and inheritance. These records are useful for historians because such information allows for a more in-depth understanding of land ownership among Ottomans. This is particularly helpful when attempting to study the daily affairs of Ottoman citizens. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahiya
A nāḥiyah ( ar, , plural ''nawāḥī'' ), also nahiya or nahia, is a regional or local type of administrative division that usually consists of a number of villages or sometimes smaller towns. In Tajikistan, it is a second-level division while in Syria, Iraq, Lebanon, Jordan, Xinjiang, and the former Ottoman Empire, where it was also called a '' bucak'', it is a third-level or lower division. It can constitute a division of a ''qadaa'', ''mintaqah'' or other such district-type of division and is sometimes translated as " subdistrict". Ottoman Empire The nahiye ( ota, ناحیه) was an administrative territorial entity of the Ottoman Empire, smaller than a . The head was a (governor) who was appointed by the Pasha. The was a subdivision of a Selçuk Akşin Somel. "Kazâ". ''The A to Z of the Ottoman Empire''. Volume 152 of A to Z Guides. Rowman & Littlefield, 2010. p. 151. and corresponded roughly to a city with its surrounding villages. s, in turn, were divided into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |