|
Hippopotamus Antiquus
''Hippopotamus antiquus'', sometimes called the European hippopotamus, is an extinct species of ''Hippopotamus'' that ranged across Europe during the Early and Middle Pleistocene. Chronology In Italy, the first appearance of the taxon is during the late Early Pleistocene, around 1.2 Ma, remains from Coste San Giacomo, suggested to date to around 2 Ma, have an uncertain stratigraphic context. ''H. antiquus'' first became widespread north of the Alps around 1.1 to 1 million years ago. The youngest confirmed remains of the taxon date to MIS 15, (621–563,000 years ago), but there are possibly later records dating to MIS 11 (424,000 to 374,000 years ago). Later records of ''Hippopotamus'' in continental Europe beginning in MIS 13 (~524,000-474,000 years ago), are believed to belong to the modern hippopotamus (''Hippopotamus amphibius''). Biology ''H. antiquus'' ranged from the Iberian Peninsula to the British Isles to the Rhine River to Greece."150 Years of Neanderthal Discover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Pleistocene
The Early Pleistocene is an unofficial sub-epoch in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, being the earliest division of the Pleistocene Epoch within the ongoing Quaternary Period. It is currently estimated to span the time between 2.580 ± 0.005 Ma (million years ago) and 0.773 ± 0.005 Ma. The term Early Pleistocene applies to both the Gelasian Age (to 1.800 ± 0.005 Ma) and the Calabrian Age. While the Gelasian and the Calabrian have officially been defined by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS) to effectively constitute the Early Pleistocene, the succeeding Chibanian and Tarantian ages have yet to be ratified. These proposed ages are unofficially termed the Middle Pleistocene and Late Pleistocene The Late Pleistocene is an unofficial Age (geology), age in the international geologic timescale in chronostratigraphy, also known as Upper Pleistocene from a Stratigraphy, stratigraphic perspective. It is intended to be the fourth div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interglacial
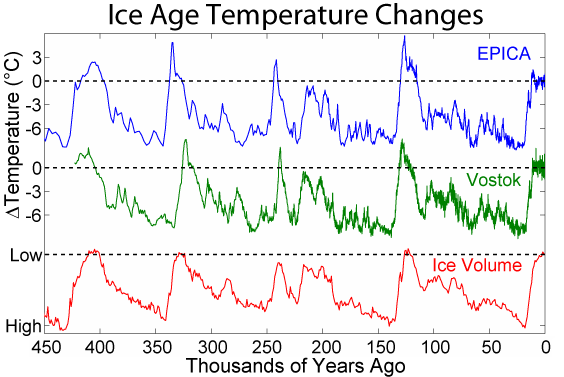
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Even-toed Ungulates
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the two r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinct Hippopotamuses
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and recover may have been lost before this point. Because a species' potential range may be very large, determining this moment is difficult, and is usually done retrospectively. This difficulty leads to phenomena such as Lazarus taxa, where a species presumed extinct abruptly "reappears" (typically in the fossil record) after a period of apparent absence. More than 99% of all species that ever lived on Earth, amounting to over five billion species, are estimated to have died out. It is estimated that there are currently around 8.7 million species of eukaryote globally, and possibly many times more if microorganisms, like bacteria, are included. Notable extinct animal species include non-avian dinosaurs, saber-toothed cats, dodos, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, and Corsica. Crete rests about south of the Greek mainland, and about southwest of Anatolia. Crete has an area of and a coastline of 1,046 km (650 mi). It bounds the southern border of the Aegean Sea, with the Sea of Crete (or North Cretan Sea) to the north and the Libyan Sea (or South Cretan Sea) to the south. Crete and a number of islands and islets that surround it constitute the Region of Crete ( el, Περιφέρεια Κρήτης, links=no), which is the southernmost of the 13 top-level administrative units of Greece, and the fifth most populous of Greece's regions. Its capital and largest city is Heraklion, on the north shore of the island. , the region had a population of 636,504. The Dodecanese are located to the no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insular Dwarfism
Insular dwarfism, a form of phyletic dwarfism, is the process and condition of large animals evolving or having a reduced body size when their population's range is limited to a small environment, primarily islands. This natural process is distinct from the intentional creation of dwarf breeds, called dwarfing. This process has occurred many times throughout evolutionary history, with examples including dinosaurs, like '' Europasaurus'' and ''Magyarosaurus dacus'', and modern animals such as elephants and their relatives. This process, and other "island genetics" artifacts, can occur not only on islands, but also in other situations where an ecosystem is isolated from external resources and breeding. This can include caves, desert oases, isolated valleys and isolated mountains ("sky islands"). Insular dwarfism is one aspect of the more general "island effect" or "Foster's rule", which posits that when mainland animals colonize islands, small species tend to evolve larger bodies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cretan Dwarf Hippopotamus
''Hippopotamus creutzburgi'', the Cretan dwarf hippopotamus, is an extinct species of hippopotamus from the island of Crete. ''Hippopopotamus'' colonized Crete probably 800,000 years ago and lived there during the Middle Pleistocene. Bones of ''H. creutzburgi'' were found by Dorothea Bate on the Katharo plateau, in eastern Crete, in the 1900s.Bate, D.M.A., (1905): I. Four and a half months in Crete in search of Pleistocene mammalian remains. Geol. Mag. 2: 13-204. A similar species, the Cyprus dwarf hippopotamus (''Phanourios minor'') lived on the island of Cyprus until the Holocene. It was at least 20% smaller than either subspecies of Cretan hippo. See also * Cyprus dwarf hippopotamus *Hippopotamus melitensis *Hippopotamus pentlandi ''Hippopotamus pentlandi'' is an extinct hippopotamus from Sicily. It arrived during the Pleistocene. It is the largest of the insular dwarf hippos known from the Pleistocene of the Mediterranean The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotopic Signature
An isotopic signature (also isotopic fingerprint) is a ratio of non-radiogenic ' stable isotopes', stable radiogenic isotopes, or unstable radioactive isotopes of particular elements in an investigated material. The ratios of isotopes in a sample material are measured by isotope-ratio mass spectrometry against an isotopic reference material. This process is called isotope analysis. Stable isotopes The atomic mass of different isotopes affect their chemical kinetic behavior, leading to natural isotope separation processes. Carbon isotopes For example, different sources and sinks of methane have different affinity for the 12C and 13C isotopes, which allows distinguishing between different sources by the 13C/12C ratio in methane in the air. In geochemistry, paleoclimatology and paleoceanography this ratio is called δ13C. The ratio is calculated with respect to Pee Dee Belemnite (PDB) standard: :\delta \ce_\mathrm = \left(\frac - 1\right) \cdot 1000 ‰ Similarly, carbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metapodial
Metapodials are long bones of the hand (metacarpals) and feet (metatarsal The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the med ...s) which connect the digits to the lower leg bones. In humans, five are present in each hand and foot. In quadrupeds, these form the lower limb, rather than being part of the extremity, thus what looks to be the elbow of a sheep is actually the wrist. Bones of the upper limb Bones of the lower limb Bones of the hand {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippopotamus Gorgops
''Hippopotamus gorgops'' is an extinct species of hippopotamus. It first appeared in Africa during the late Pliocene, and eventually migrated into Europe (where its fossils were first discovered) during the early Pleistocene. It became extinct during the Middle Pleistocene. Fossil records found at Ubeidiya, Israel suggested that they migrated out of Africa around 1.6 million years ago. Some have speculated that ''H. gorgops'' and '' H. behemoth'' are actually the same species given their similar sizes and where they have been found. Taxonomy With an estimated length of , a shoulder height of , and a weight of 3,900-4,500 kg (8,600-9,900 lb), ''H. gorgops'' was larger than its living relative, ''H. amphibius''. Another feature setting it apart from ''H. amphibius'' was the placement of its eyes. Modern hippos have eyes placed high on the skull The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippopotamus Amphibius
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extant species in the family Hippopotamidae, the other being the pygmy hippopotamus (''Choeropsis liberiensis'' or ''Hexaprotodon liberiensis''). Its name comes from the ancient Greek for "river horse" (). Aside from elephants and rhinos, the hippopotamus is the largest land mammal. It is also the largest extant land artiodactyl. Despite their physical resemblance to pigs and other terrestrial even-toed ungulates, the closest living relatives of the hippopotamids are cetaceans (whales, dolphins, porpoises, etc.), from which they diverged about 55 million years ago. Hippos are recognisable for their barrel-shaped torsos, wide-opening mouths with large canine tusks, nearly hairless bodies, pillar-like legs, and large size: adults average for bull ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippopotamus Antiquus
''Hippopotamus antiquus'', sometimes called the European hippopotamus, is an extinct species of ''Hippopotamus'' that ranged across Europe during the Early and Middle Pleistocene. Chronology In Italy, the first appearance of the taxon is during the late Early Pleistocene, around 1.2 Ma, remains from Coste San Giacomo, suggested to date to around 2 Ma, have an uncertain stratigraphic context. ''H. antiquus'' first became widespread north of the Alps around 1.1 to 1 million years ago. The youngest confirmed remains of the taxon date to MIS 15, (621–563,000 years ago), but there are possibly later records dating to MIS 11 (424,000 to 374,000 years ago). Later records of ''Hippopotamus'' in continental Europe beginning in MIS 13 (~524,000-474,000 years ago), are believed to belong to the modern hippopotamus (''Hippopotamus amphibius''). Biology ''H. antiquus'' ranged from the Iberian Peninsula to the British Isles to the Rhine River to Greece."150 Years of Neanderthal Discover ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)

