|
Hippocampus Bargibanti
''Hippocampus bargibanti'', also known as Bargibant's seahorse or the pygmy seahorse, is a seahorse of the family Syngnathidae found in the central Indo-Pacific area. It is tiny, usually less than in size and lives exclusively on fan corals.Epoch Times Staff. (8/11/2011.) "Science in Pictures: Pygmy Seahorses." ''The Epoch Times, Northern California Edition''. There are two known color variations: grey with red tubercles, and yellow with orange tubercles. It is unknown whether these color varieties are linked to specific host gorgonians (corals).Reijnen, B.T., van der Meij, S.E.T., van Ofwegen, L.P. (2011) "Fish, fans and hydroids: host species of pygmy seahorses." ''ZooKeys'' 103: 1-26. Description The pygmy seahorse is well camouflaged and extremely difficult to spot amongst the gorgonian coral it inhabits. So effective is this camouflage that the species wasn't actually discovered until its host gorgonian was being examined in a laboratory.ARKive species fact-file In 1969 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
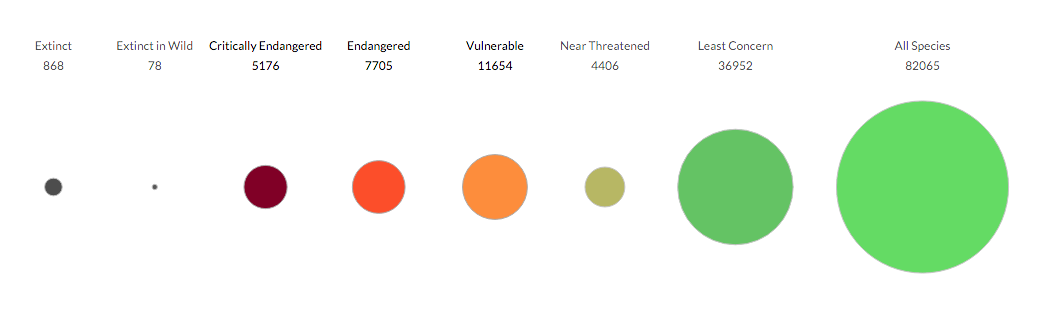
The IUCN Red List Of Threatened Species
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit. The aim of the IUCN Red List is to convey the urgency of conservation issues to the public and policy makers, as well as help the international community to reduce species extinction. According to IUCN the formally stated goals of the Red List are to provide sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea. Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the 14th-largest country by area, at . With over 275 million people, Indonesia is the world's fourth-most populous country and the most populous Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population. Indonesia is a presidential republic with an elected legislature. It has 38 provinces, of which nine have special status. The country's capital, Jakarta, is the world's second-most populous urban area. Indonesia shares land borders with Papua New Guinea, East Timor, and the eastern part of Malaysia, as well as maritime borders with Singapore, Vietnam, Thailand, the Philippines, Australia, Palau, and India ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus (genus)
A seahorse (also written ''sea-horse'' and ''sea horse'') is any of 46 species of small marine fish in the genus ''Hippocampus''. "Hippocampus" comes from the Ancient Greek (), itself from () meaning "horse" and () meaning "sea monster" or "sea animal". Having a head and neck suggestive of a horse, seahorses also feature segmented bony armour, an upright posture and a curled prehensile tail. Along with the pipefishes and seadragons (''Phycodurus'' and ''Phyllopteryx'') they form the family Syngnathidae. Habitat Seahorses are mainly found in shallow tropical and temperate salt water throughout the world, from about 45°S to 45°N. They live in sheltered areas such as seagrass beds, estuaries, coral reefs, and mangroves. Four species are found in Pacific waters from North America to South America. In the Atlantic, ''Hippocampus erectus'' ranges from Nova Scotia to Uruguay. '' H. zosterae'', known as the dwarf seahorse, is found in the Bahamas. Colonies have been found in Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pygmy
In anthropology, pygmy peoples are ethnic groups whose average height is unusually short. The term pygmyism is used to describe the phenotype of endemic short stature (as opposed to disproportionate dwarfism occurring in isolated cases in a population) for populations in which adult men are on average less than tall. The term is primarily associated with the African Pygmies, the hunter-gatherers of the Congo Basin (comprising the Bambenga, Bambuti and Batwa). The terms "Asiatic Pygmies" and "Oceanian pygmies" have been used to describe the Negrito populations of Southeast Asia and Australo-Melanesian peoples of short stature. The Taron people of Myanmar are an exceptional case of a "pygmy" population of East Asian phenotype. Etymology The term ''pygmy'', as used to refer to diminutive people, derives from Greek πυγμαῖος ''pygmaios'' via Latin ''Pygmaei'' (sing. ''Pygmaeus''), derived from πυγμή – meaning a short forearm cubit, or a measure of length corres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocampus Bargibanti2
The hippocampus (via Latin from Greek , 'seahorse') is a major component of the brain of humans and other vertebrates. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in each side of the brain. The hippocampus is part of the limbic system, and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory, and in spatial memory that enables navigation. The hippocampus is located in the allocortex, with neural projections into the neocortex in humans, as well as primates. The hippocampus, as the medial pallium, is a structure found in all vertebrates. In humans, it contains two main interlocking parts: the hippocampus proper (also called ''Ammon's horn''), and the dentate gyrus. In Alzheimer's disease (and other forms of dementia), the hippocampus is one of the first regions of the brain to suffer damage; short-term memory loss and disorientation are included among the early symptoms. Damage to the hippocampus can also result from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institut De Recherche Pour Le Développement
The Institut de Recherche pour le Développement or IRD () is a French science and technology establishment under the joint supervision of the French Ministries of Higher Education and Research and Foreign Affairs. It operates internationally from its headquarters in Marseille, and two metropolitan centres of Montpellier and Bondy. It was created as the Office de la recherche scientifique et technique outre-mer or ORSTOM, ‘Overseas Scientific and Technical Research Office’) in 1943. Missions The IRD institute has three main missions: research on world development, overseas consultancy and training. It conducts scientific programs contributing to the sustainable development of the countries of the South, with an emphasis on the relationship between man and the environment. Organisation The IRD's scientific activities are organised through five departments: *Earth and Environment *Living Resources *Societies and Health *Expertise and consulting *Support and training ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Name (zoology)
In zoological nomenclature, the specific name (also specific epithet or species epithet) is the second part (the second name) within the scientific name of a species (a binomen). The first part of the name of a species is the name of the genus or the generic name. The rules and regulations governing the giving of a new species name are explained in the article species description. For example, the scientific name for humans is ''Homo sapiens'', which is the species name, consisting of two names: ''Homo'' is the " generic name" (the name of the genus) and ''sapiens'' is the "specific name". Historically, ''specific name'' referred to the combination of what are now called the generic and specific names. Carl Linnaeus, who formalized binomial nomenclature, made explicit distinctions between specific, generic, and trivial names. The generic name was that of the genus, the first in the binomial, the trivial name was the second name in the binomial, and the specific the proper term for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convention On The International Trade In Endangered Species Of Wild Flora And Fauna
CITES (shorter name for the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, also known as the Washington Convention) is a multilateral treaty to protect endangered plants and animals from the threats of international trade. It was drafted as a result of a resolution adopted in 1963 at a meeting of members of the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN). The convention was opened for signature in 1973 and CITES entered into force on 1 July 1975. Its aim is to ensure that international trade (import/export) in specimens of animals and plants included under CITES, does not threaten the survival of the species in the wild. This is achieved via a system of permits and certificates. CITES affords varying degrees of protection to more than 38,000 species. , Secretary-General of CITES is Ivonne Higuero. Background CITES is one of the largest and oldest conservation and sustainable use agreements in existence. There are three working lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquarium
An aquarium (plural: ''aquariums'' or ''aquaria'') is a vivarium of any size having at least one transparent side in which aquatic plants or animals are kept and displayed. Fishkeepers use aquaria to keep fish, invertebrates, amphibians, aquatic reptiles, such as turtles, and aquatic plants. The term ''aquarium'', coined by English naturalist Philip Henry Gosse, combines the Latin root , meaning 'water', with the suffix , meaning 'a place for relating to'. The aquarium principle was fully developed in 1850 by the chemist Robert Warington, who explained that plants added to water in a container would give off enough oxygen to support animals, so long as the numbers of animals did not grow too large. The aquarium craze was launched in early Victorian England by Gosse, who created and stocked the first public aquarium at the London Zoo in 1853, and published the first manual, ''The Aquarium: An Unveiling of the Wonders of the Deep Sea'' in 1854.Katherine C. Grier (2008) "Pet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IUCN Red List
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit. The aim of the IUCN Red List is to convey the urgency of conservation issues to the public and policy makers, as well as help the international community to reduce species extinction. According to IUCN the formally stated goals of the Red List are to provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Union For Conservation Of Nature
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natural resources. It is involved in data gathering and analysis, research, field projects, advocacy, and education. IUCN's mission is to "influence, encourage and assist societies throughout the world to conserve nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable". Over the past decades, IUCN has widened its focus beyond conservation ecology and now incorporates issues related to sustainable development in its projects. IUCN does not itself aim to mobilize the public in support of nature conservation. It tries to influence the actions of governments, business and other stakeholders by providing information and advice and through building partnerships. The organization is best known to the wider pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fry (biology)
Fish go through various life stages between fertilization and adulthood. The life of a fish start as spawned eggs which hatch into immotile larvae. These larval hatchlings are not yet capable of feeding themselves and carry a yolk sac which provides stored nutrition. Before the yolk sac completely disappears, the young fish must mature enough to be able to forage independently. When they have developed to the point where they are capable of feeding by themselves, the fish are called fry. When, in addition, they have developed scales and working fins, the transition to a juvenile fish is complete and it is called a fingerling, so called as they are typically about the size of human fingers. The juvenile stage lasts until the fish is fully grown, sexually mature and interacting with other adult fish. Growth stages Ichthyoplankton ''(planktonic or drifting fish)'' are the eggs and larvae of fish. They are usually found in the sunlit zone of the water column, less than 200 met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)