|
High-altitude Flatus Expulsion
High-altitude flatus expulsion (HAFE) is a gastrointestinal syndrome which involves the spontaneous passage of increased quantities of rectal gases at high altitudes. First described by Joseph Hamel in c. 1820 and occasionally described afterward.E.Y. Davis, FRCP(Ret), "Hafe In Nepal" West J Med. 1981 April; 134(4): 366, identifying "Flatulence Accompanying Rigorous Trekking," Kathmandu Medical Bulletin, 1972. A landmark study of this phenomenon was published in 1981 by Paul Auerbach and York Miller. The feeling of fullness or need to expel brought on by this differential in atmospheric pressure has been verified by studies involving military pilots subjected to pressure changes simulating flight. See also * High-altitude pulmonary edema * High-altitude cerebral edema * Flatulence Flatulence, in humans, is the expulsion of gas from the intestines via the anus, commonly referred to as farting. "Flatus" is the medical word for gas generated in the stomach or bowels. A proportio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrointestinal
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and is div ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rectal Gases
Flatulence, in humans, is the expulsion of gas from the intestines via the anus, commonly referred to as farting. "Flatus" is the medical word for gas generated in the stomach or bowels. A proportion of intestinal gas may be swallowed environmental air, and hence flatus is not entirely generated in the stomach or bowels. The scientific study of this area of medicine is termed flatology. Flatus is brought to the rectum and pressurized by muscles in the intestines. It is normal to pass flatus ("to fart"), though volume and frequency vary greatly among individuals. It is also normal for intestinal gas to have a feculent or unpleasant odor, which may be intense. The noise commonly associated with flatulence ("blowing a raspberry") is produced by the anus and buttocks, which act together in a manner similar to that of an embouchure. Both the sound and odor are sources of embarrassment, annoyance or amusement ( flatulence humor). There are several general symptoms related to intest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Auerbach
Paul Stuart Auerbach (January 4, 1951 – June 23, 2021) was an American physician and author in the academic discipline of wilderness medicine. He was the founder and past president of the Wilderness Medical Society. Auerbach was the editor for the ''Journal of Wilderness Medicine'' (currently ''Wilderness and Environmental Medicine'') published by the Wilderness Medical Society from 1990 to 1995.Dr. Auerbach's CV dated June 2009 Auerbach was also the author of a number of articles and books on topics such as emergency medicine, hazardous marine animals, and scuba diving, including two books of underwater photography. Background Auerbach was born in Plainfield, New Jersey. He graduated from North Plainfield High School in 1969. Auerbach then went to Duke University located in Durham, North Carolina, where he completed a Bachelor of Arts in religion, graduating magna cum laude in 1973. Auerbach received his Doctorate of Medicine from the Duke University School of Medi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
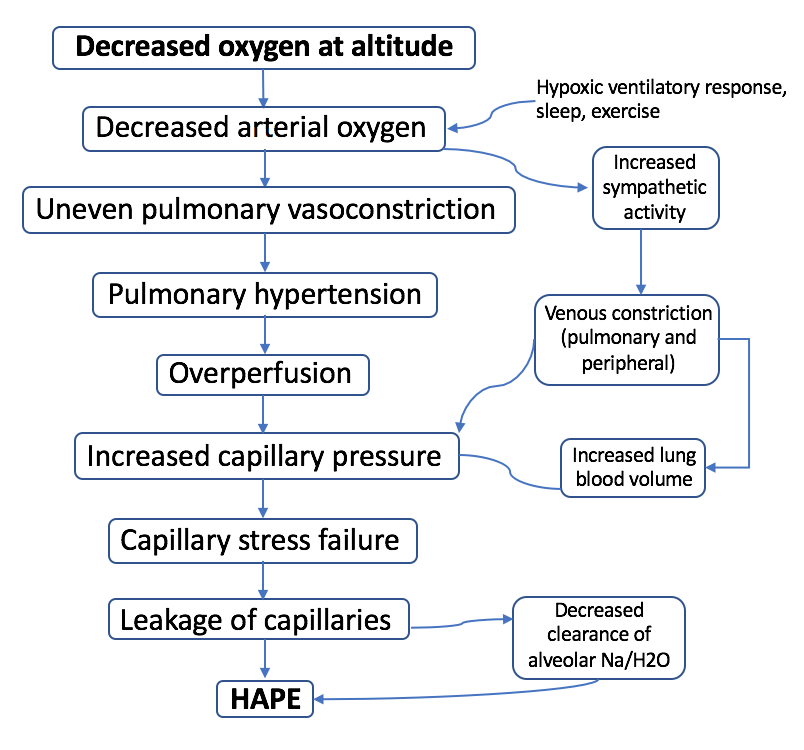
High-altitude Pulmonary Edema
High-altitude pulmonary edema (HAPE) is a life-threatening form of non-cardiogenic pulmonary edema that occurs in otherwise healthy people at altitudes typically above . However, cases have also been reported between in more vulnerable subjects. Classically, HAPE occurs in persons normally living at low altitude who travel to an altitude above 2,500 meters (8,200 feet). Re-entry HAPE is also an entity that has been described in persons who normally live at high altitude but who develop pulmonary edema after returning from a stay at low altitude. It is severe presentation of altitude sickness. There are many factors that can make a person more susceptible to developing HAPE, including genetic factors, but detailed understanding is lacking and currently under investigation. HAPE remains the major cause of death related to high-altitude exposure, with a high mortality rate in the absence of adequate emergency treatment. Signs and symptoms Physiological and symptomatic changes ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-altitude Cerebral Edema
High-altitude cerebral edema (HACE) is a medical condition in which the brain swells with fluid because of the physiological effects of traveling to a high altitude. It generally appears in patients who have acute mountain sickness and involves disorientation, lethargy, and nausea among other symptoms. It occurs when the body fails to acclimatize while ascending to a high altitude. It appears to be a vasogenic edema (fluid penetration of the blood–brain barrier), although cytotoxic edema (cellular retention of fluids) may play a role as well. Individuals with the condition must immediately descend to a lower altitude or coma and death can occur. Patients are usually given supplemental oxygen and dexamethasone as well. HACE can be prevented by ascending to heights slowly to allow the body more time to acclimatize. Acetazolamide also helps prevent the condition. Untreated patients usually die within 48 hours. Those who receive treatment may take weeks to fully recover. It is a rar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flatulence
Flatulence, in humans, is the expulsion of gas from the intestines via the anus, commonly referred to as farting. "Flatus" is the medical word for gas generated in the stomach or bowels. A proportion of intestinal gas may be swallowed environmental air, and hence flatus is not entirely generated in the stomach or bowels. The scientific study of this area of medicine is termed flatology. Flatus is brought to the rectum and pressurized by muscles in the intestines. It is normal to pass flatus ("to fart"), though volume and frequency vary greatly among individuals. It is also normal for intestinal gas to have a feculent or unpleasant odor, which may be intense. The noise commonly associated with flatulence ("blowing a raspberry") is produced by the anus and buttocks, which act together in a manner similar to that of an embouchure. Both the sound and odor are sources of embarrassment, annoyance or amusement (flatulence humor). There are several general symptoms related to intest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountaineering And Health
Mountaineering or alpinism, is a set of outdoor activities that involves ascending tall mountains. Mountaineering-related activities include traditional outdoor climbing, skiing, and traversing via ferratas. Indoor climbing, sport climbing, and bouldering are also considered variants of mountaineering by some. Unlike most sports, mountaineering lacks widely applied formal rules, regulations, and governance; mountaineers adhere to a large variety of techniques and philosophies when climbing mountains. Numerous local alpine clubs support mountaineers by hosting resources and social activities. A federation of alpine clubs, the International Climbing and Mountaineering Federation (UIAA), is the International Olympic Committee-recognized world organization for mountaineering and climbing. The consequences of mountaineering on the natural environment can be seen in terms of individual components of the environment (land relief, soil, vegetation, fauna, and landscape) and location/ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |