|
Hib
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, non-motile, coccobacillary, facultatively anaerobic, capnophilic pathogenic bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. The bacteria are mesophilic and grow best at temperatures between 35 and 37℃. ''H. influenzae'' was first described in 1892 by Richard Pfeiffer during an influenza pandemic when he incorrectly described ''Haemophilus influenzae'' as the causative microbe, which is why the bacteria retain the name "influenza". ''H. influenzae'' is responsible for a wide range of localized and invasive infections, typically in infants and children, including pneumonia, meningitis, or bloodstream infections. Treatment consists of antibiotics, however ''H. influenzae'' is often resistant to the penicillin family but augmentin can be used in mild cases. The recommended form of prevention is a series of the Hib vaccine and boosters, which are most often given under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hib Vaccine
The ''Haemophilus influenzae'' type B vaccine, also known as Hib vaccine, is a vaccine used to prevent ''Haemophilus influenzae'' type b (Hib) infection. In countries that include it as a routine vaccine, rates of severe Hib infections have decreased more than 90%. It has therefore resulted in a decrease in the rate of meningitis, pneumonia, and epiglottitis. It is recommended by both the World Health Organization (WHO) and the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Two or three doses should be given before six months of age. In the United States a fourth dose is recommended between 12 and 15 months of age. The first dose is recommended around six weeks of age with at least four weeks between doses. If only two doses are used, another dose later in life is recommended. It is given by injection into a muscle. Severe side effects are extremely rare. About 20 to 25% of people develop pain at the site of injection while about 2% develop a fever. There is no cle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DTaP-IPV/Hib Vaccine
DTaP-IPV/Hib vaccine is a 5-in-1 combination vaccine that protects against diphtheria, tetanus, whooping cough, polio, and ''Haemophilus influenzae type B''. Its generic name is 'diphtheria and tetanus toxoids and acellular pertussis adsorbed, inactivated poliovirus and haemophilus B conjugate vaccine', and it is also known as DTaP- IPV- Hib. Uses DTaP-IPV/Hib vaccine is administered to young children to immunise against diphtheria, tetanus, pertussis, poliomyelitis, and diseases caused by ''Haemophilus influenzae type B''. Formulations A branded formulation marketed in the United States is Pentacel, manufactured by Sanofi Pasteur. Pentacel is known in the UK and Canada as Pediacel. An equivalent vaccine marketed in the UK and Canada by GlaxoSmithKline is Infanrix IPV + Hib. This is a two-part vaccine. The DTaP-IPV component is supplied as a sterile liquid, which is used to reconstitute lyophilized (freeze-dried) Hib vaccine. Pentaxim is a liquid formulation marketed b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
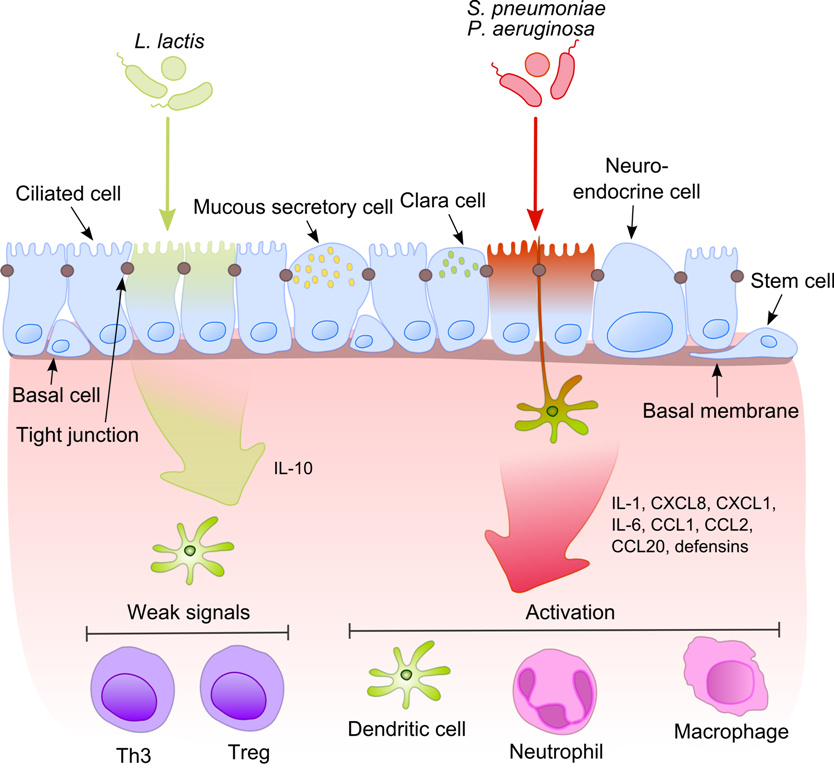
Upper Respiratory Tract Infection
An upper respiratory tract infection (URTI) is an illness caused by an acute infection, which involves the upper respiratory tract, including the nose, sinuses, pharynx, larynx or trachea. This commonly includes nasal obstruction, sore throat, tonsillitis, pharyngitis, laryngitis, sinusitis, otitis media, and the common cold. Most infections are viral in nature, and in other instances, the cause is bacterial. URTIs can also be fungal or helminthic in origin, but these are less common. In 2015, 17.2 billion cases of URTIs are estimated to have occurred. As of 2014, they caused about 3,000 deaths, down from 4,000 in 1990. Signs and symptoms In uncomplicated colds, coughing and nasal discharge may persist for 14 days or more even after other symptoms have resolved. Acute URTIs include rhinitis, pharyngitis/tonsillitis, and laryngitis often referred to as a common cold, and their complications: sinusitis, ear infection, and sometimes bronchitis (though bronchi are generally cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) is a coenzyme central to metabolism. Found in all living cells, NAD is called a dinucleotide because it consists of two nucleotides joined through their phosphate groups. One nucleotide contains an adenine nucleobase and the other nicotinamide. NAD exists in two forms: an oxidized and reduced form, abbreviated as NAD and NADH (H for hydrogen), respectively. In metabolism, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another. The cofactor is, therefore, found in two forms in cells: NAD is an oxidizing agent – it accepts electrons from other molecules and becomes reduced. This reaction, also with H+, forms NADH, which can then be used as a reducing agent to donate electrons. These electron transfer reactions are the main function of NAD. However, it is also used in other cellular processes, most notably as a substrate of enzymes in adding or removing chemical groups to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pathogenic Bacterium
Pathogenic bacteria are bacteria that can cause disease. This article focuses on the bacteria that are pathogenic to humans. Most species of bacteria are harmless and are often beneficial but others can cause infectious diseases. The number of these pathogenic species in humans is estimated to be fewer than a hundred. By contrast, several thousand species are part of the gut flora present in the digestive tract. The body is continually exposed to many species of bacteria, including beneficial commensals, which grow on the skin and mucous membranes, and saprophytes, which grow mainly in the soil and in decaying matter. The blood and tissue fluids contain nutrients sufficient to sustain the growth of many bacteria. The body has defence mechanisms that enable it to resist microbial invasion of its tissues and give it a natural immunity or innate resistance against many microorganisms. Pathogenic bacteria are specially adapted and endowed with mechanisms for overcoming the norm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chocolate Agar
Chocolate agar (CHOC) or chocolate blood agar (CBA), is a nonselective, enriched growth medium used for isolation of pathogenic bacteria. It is a variant of the blood agar plate, containing red blood cells that have been lysed by slowly heating to 80°C. Chocolate agar is used for growing fastidious respiratory bacteria, such as ''Haemophilus influenzae'' and ''Neisseria meningitidis''. In addition, some of these bacteria, most notably ''H. influenzae'', need growth factors such as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (factor V or NAD) and hemin (factor X), which are inside red blood cells; thus, a prerequisite to growth for these bacteria is the presence of red blood cell lysates. The heat also inactivates enzymes which could otherwise degrade NAD. The agar is named for its color and contains no chocolate products. Variants Chocolate agar with the addition of bacitracin becomes selective for the genus ''Haemophilus''. Another variant of chocolate agar called Thayer–Martin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalosporin
The cephalosporins (sg. ) are a class of β-lactam antibiotics originally derived from the fungus ''Acremonium'', which was previously known as ''Cephalosporium''. Together with cephamycins, they constitute a subgroup of β-lactam antibiotics called cephems. Cephalosporins were discovered in 1945, and first sold in 1964. Discovery The aerobic mold which yielded cephalosporin C was found in the sea near a sewage outfall in Su Siccu, by Cagliari harbour in Sardinia, by the Italian pharmacologist Giuseppe Brotzu in July 1945. Structure Cephalosporin contains a 6-membered dihydrothiazine ring. Substitutions at position 3 generally affect pharmacology; substitutions at position 7 affect antibacterial activity, but these cases are not always true. Medical uses Cephalosporins can be indicated for the prophylaxis and treatment of infections caused by bacteria susceptible to this particular form of antibiotic. First-generation cephalosporins are active predominantly against Gram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemophilus Influenzae Sputum 1000x Edited
''Haemophilus'' is a genus of Gram-negative, pleomorphic, coccobacilli bacteria belonging to the family Pasteurellaceae. While ''Haemophilus'' bacteria are typically small coccobacilli, they are categorized as pleomorphic bacteria because of the wide range of shapes they occasionally assume. These organisms inhabit the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract, mouth, vagina, and intestinal tract. The genus includes commensal organisms along with some significant pathogenic species such as ''H. influenzae''—a cause of sepsis and bacterial meningitis in young children—and '' H. ducreyi'', the causative agent of chancroid. All members are either aerobic or facultatively anaerobic. This genus has been found to be part of the salivary microbiome. Metabolism Members of the genus ''Haemophilus'' will not grow on blood agar plates, as all species require at least one of these blood factors for growth: hemin (X-factor) and/or nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (V-fact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest Radiograph In Influensa And H Influenzae, Posteroanterior, Annotated
The thorax or chest is a part of the anatomy of humans, mammals, and other tetrapod animals located between the neck and the abdomen. In insects, crustaceans, and the extinct trilobites, the thorax is one of the three main divisions of the creature's body, each of which is in turn composed of multiple segments. The human thorax includes the thoracic cavity and the thoracic wall. It contains organs including the heart, lungs, and thymus gland, as well as muscles and various other internal structures. Many diseases may affect the chest, and one of the most common symptoms is chest pain. Etymology The word thorax comes from the Greek θώραξ ''thorax'' "breastplate, cuirass, corslet" via la, thorax. Plural: ''thoraces'' or ''thoraxes''. Human thorax Structure In humans and other hominids, the thorax is the chest region of the body between the neck and the abdomen, along with its internal organs and other contents. It is mostly protected and supported by the rib cage, spine, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest Radiograph
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine. Like all methods of radiography, chest radiography employs ionizing radiation in the form of X-rays to generate images of the chest. The mean radiation dose to an adult from a chest radiograph is around 0.02 mSv (2 mrem) for a front view (PA, or posteroanterior) and 0.08 mSv (8 mrem) for a side view (LL, or latero-lateral). Together, this corresponds to a background radiation equivalent time of about 10 days. Medical uses Conditions commonly identified by chest radiography * Pneumonia * Pneumothorax * Interstitial lung disease * Heart failure * Bone fracture * Hiatal hernia Chest radiographs are used to diagnose many conditions involving the chest wall, including its bones, and also structures contained within the thoracic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
X-ray Of COPD Exacerbation - Anteroposterior View
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30 petahertz to 30 exahertz ( to ) and energies in the range 145 eV to 124 keV. X-ray wavelengths are shorter than those of UV rays and typically longer than those of gamma rays. In many languages, X-radiation is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it on November 8, 1895. He named it ''X-radiation'' to signify an unknown type of radiation.Novelline, Robert (1997). ''Squire's Fundamentals of Radiology''. Harvard University Press. 5th edition. . Spellings of ''X-ray(s)'' in English include the variants ''x-ray(s)'', ''xray(s)'', and ''X ray(s)''. The most familiar use of X-rays is checking for fractures (broken bones), but X-rays are also used in other ways. For ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coccobacillus
A coccobacillus (plural coccobacilli), or bacilluscocco, is a type of bacterium with a shape intermediate between cocci (spherical bacteria) and bacilli (rod-shaped bacteria). Coccobacilli, then, are very short rods which may be mistaken for cocci. ''Haemophilus influenzae'', ''Gardnerella vaginalis'', and ''Chlamydia trachomatis'' are coccobacilli. ''Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans'' is a Gram-negative coccobacillus prevalent in subgingival plaques. ''Acinetobacter'' strains may grow on solid media as coccobacilli. ''Bordetella pertussis'' is a Gram-negative coccobacillus responsible for causing whooping cough. ''Yersinia pestis'', the bacterium that causes plague, is also coccobacillus. ''Coxiella burnetii'' is also a coccobacillus. Bacteria from the genus ''Brucella'' are medically important coccobacilli that cause brucellosis. ''Haemophilus ducreyi ''Haemophilus ducreyi'' is a fastidious gram-negative coccobacillus bacteria. It causes the sexually transmitted dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |