|
Hesperian
The Hesperian is a system (stratigraphy), geologic system and geologic timescale, time period on the planet Mars characterized by widespread Volcanology of Mars, volcanic activity and catastrophic flooding that carved immense outflow channels across the surface. The Hesperian is an intermediate and transitional period of Martian history. During the Hesperian, Mars changed from the wetter and perhaps warmer world of the Noachian (Mars), Noachian to the dry, cold, and dusty planet seen today. The absolute age of the Hesperian Period is uncertain. The beginning of the period followed the end of the Late Heavy Bombardment and probably corresponds to the start of the lunar Late Imbrian period, around 3700 million years ago (Myr, Mya). The end of the Hesperian Period is much more uncertain and could range anywhere from 3200 to 2000 Mya, with 3000 Mya being frequently cited. The Hesperian Period is roughly coincident with the Earth's early Archean Eon. With the decline of heavy impacts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noachian (Mars)
The Noachian is a system (stratigraphy), geologic system and early geologic timescale, time period on the planet Mars characterized by high rates of meteorite and asteroid Impact event, impacts and the possible presence of abundant surface water. The absolute age of the Noachian period is uncertain but probably corresponds to the lunar Pre-Nectarian to Early Imbrian periods of 4100 to 3700 million years ago, during the interval known as the Late Heavy Bombardment. Many of the large impact basins on the Moon and Mars formed at this time. The Noachian Period is roughly equivalent to the Earth's Hadean and early Archean eons when the first life forms likely arose. Noachian-aged terrains on Mars are prime Lander (spacecraft), spacecraft landing sites to search for fossil evidence of extraterrestrial life, life. During the Noachian, the atmosphere of Mars was denser than it is today, and the climate possibly warm enough to allow rainfall. Large lakes and rivers were present in the sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hesperia Planum
Hesperia Planum is a broad lava plain in the southern highlands of the planet Mars. The plain is notable for its moderate number of impact craters and abundant wrinkle ridges. It is also the location of the ancient volcano Tyrrhena Mons ( Tyrrhena Patera). The Hesperian time period on Mars is named after Hesperia Planum.Scott, D.H.; Carr, M.H. (1978). Geologic Map of Mars. U.S. Geological Survey Miscellaneous Investigations Series Map I-1083. Name origin Most place names on Mars are derived from sources in the Bible or classical antiquity. '' Hesperia'' is a Greco-Latin poetic term for "lands to the west," which to the ancient Greeks and Romans meant Italy, while Spain was referred as ''Hesperia Ultima'' . ''Planum'' (pl. ''plana'') is Latin for plateau or high plain. It is a descriptor term used in planetary geology for a relatively smooth, elevated terrain on another planet or moon.USGS Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. http://planetarynames.wr.usgs.gov/DescriptorTerms. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
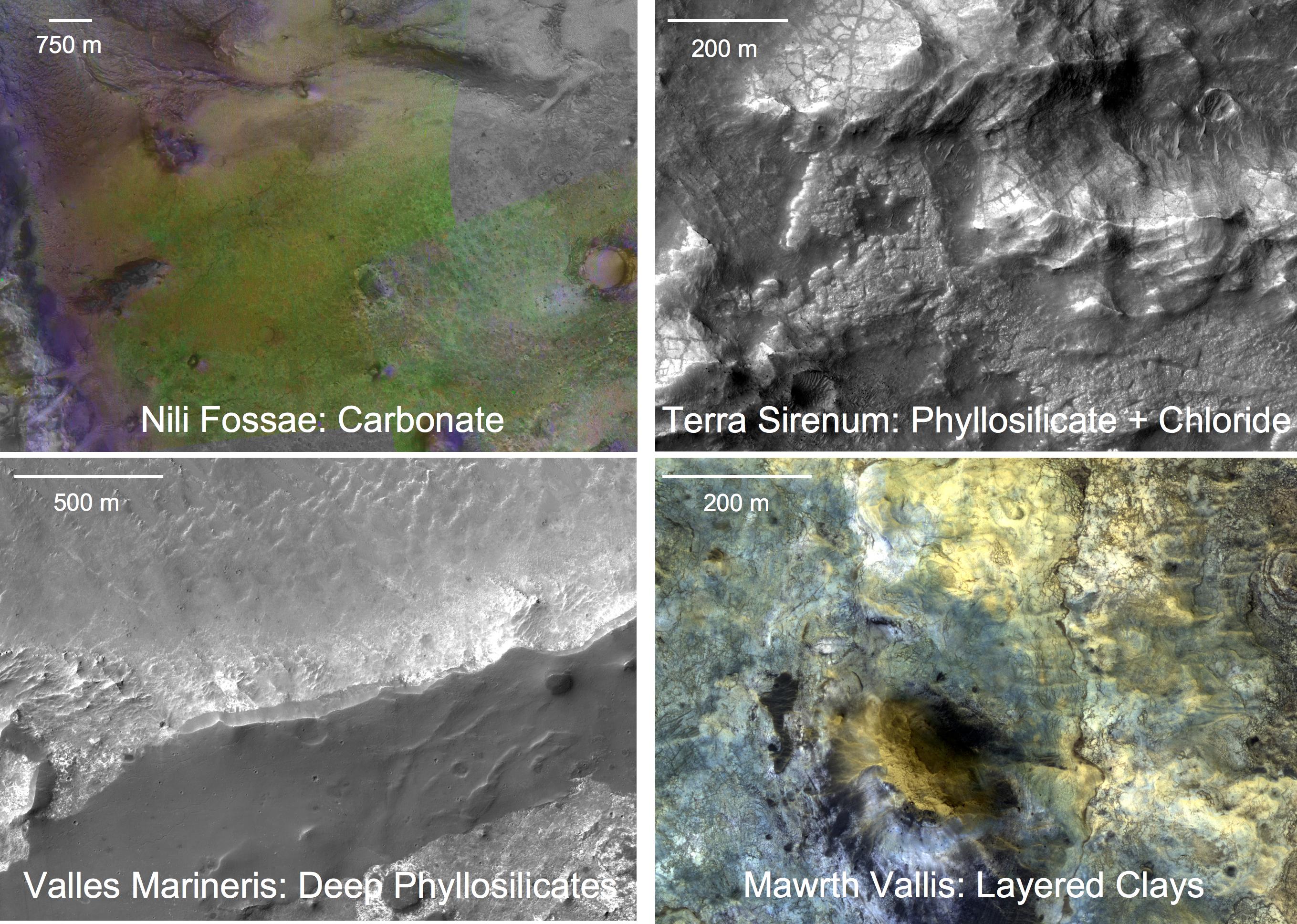
Volcanology Of Mars
Volcanic activity, or volcanism, has played a significant role in the geologic evolution of Mars. Scientists have known since the Mariner 9 mission in 1972 that volcanic features cover large portions of the Martian surface. These features include extensive lava flows, vast lava plains, and the largest known volcanoes in the Solar System. Martian volcanic features range in age from Noachian (>3.7 billion years) to late Amazonian (< 500 million years), indicating that the planet has been volcanically active throughout its history, and some speculate it probably still is so today. Both and Mars are large, differentiated |
Volcanism On Mars
Volcanic activity, or volcanism, has played a significant role in the geologic evolution of Mars. Scientists have known since the Mariner 9 mission in 1972 that volcanic features cover large portions of the Martian surface. These features include extensive lava flows, vast lava plains, and the largest known volcanoes in the Solar System. Martian volcanic features range in age from Noachian (>3.7 billion years) to late Amazonian (< 500 million years), indicating that the planet has been volcanically active throughout its history, and some speculate it probably still is so today. Both and Mars are large, differentiated |
Olympus Mons
Olympus Mons (; Latin for Mount Olympus) is a large shield volcano on Mars. The volcano has a height of over 21.9 km (13.6 mi or 72,000 ft) as measured by the Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA). Olympus Mons is about two and a half times Mount Everest's height above sea level. It is one of the largest volcanoes, the tallest planetary mountain, and approximately tied with Rheasilvia as the tallest mountain currently discovered in the Solar System. It is associated with the Tharsis Montes, a large volcanic region on Mars. Olympus Mons is the youngest of the large volcanoes on Mars, having formed during Mars's Hesperian Period with eruptions continuing well into the Amazonian. It had been known to astronomers since the late 19th century as the albedo feature Nix Olympica (Latin for "Olympic Snow"). Its mountainous nature was suspected well before space probes confirmed its identity as a mountain. The volcano is located in Mars's western hemisphere, with the cent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury (planet), Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Mars (mythology), Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin atmosphere (less than 1% that of Earth's), and has a crust primarily composed of elements similar to Earth's crust, as well as a core made of iron and nickel. Mars has surface features such as impact craters, valleys, dunes and polar ice caps. It has two small and irregularly shaped moons, Phobos (moon), Phobos and Deimos (moon), Deimos. Some of the most notable surface features on Mars include Olympus Mons, the largest volcano and List of tallest mountains in the Solar System, highest known mountain in the Solar System and Valles Marineris, one of the largest canyons in the Solar System. The North Polar Basin (Mars), Borealis basin in the Northern Hemisphere covers approximately 40% of the planet and may be a la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outflow Channel
Outflow channels are extremely long, wide swathes of scoured ground on Mars. They extend many hundreds of kilometers in length and are typically greater than one kilometer in width. They are thought to have been carved by huge outburst floods. Crater counts indicate that most of the channels were cut since the early Hesperian, though the age of the features is variable between different regions of Mars. Some outflow channels in the Amazonis and Elysium Planitiae regions have yielded ages of only tens of million years, extremely young by the standards of Martian topographic features. The largest, Kasei Vallis, is around long, greater than wide and exceeds in depth cut into the surrounding plains. The outflow channels contrast with the Martian channel features known as " valley networks", which much more closely resemble the dendritic planform more typical of terrestrial river drainage basins. Outflow channels tend to be named after the names for Mars in various ancient world ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geologic Timescale
The geologic time scale, or geological time scale, (GTS) is a representation of time based on the rock record of Earth. It is a system of chronological dating that uses chronostratigraphy (the process of relating strata to time) and geochronology (scientific branch of geology that aims to determine the age of rocks). It is used primarily by Earth scientists (including geologists, paleontologists, geophysicists, geochemists, and paleoclimatologists) to describe the timing and relationships of events in geologic history. The time scale has been developed through the study of rock layers and the observation of their relationships and identifying features such as lithologies, paleomagnetic properties, and fossils. The definition of standardized international units of geologic time is the responsibility of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS), a constituent body of the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), whose primary objective is to precisely define gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outflow Channels
Outflow channels are extremely long, wide swathes of scoured ground on Mars. They extend many hundreds of kilometers in length and are typically greater than one kilometer in width. They are thought to have been carved by huge outburst floods. Crater counts indicate that most of the channels were cut since the early Hesperian, though the age of the features is variable between different regions of Mars. Some outflow channels in the Amazonis and Elysium Planitiae regions have yielded ages of only tens of million years, extremely young by the standards of Martian topographic features. The largest, Kasei Vallis, is around long, greater than wide and exceeds in depth cut into the surrounding plains. The outflow channels contrast with the Martian channel features known as " valley networks", which much more closely resemble the dendritic planform more typical of terrestrial river drainage basins. Outflow channels tend to be named after the names for Mars in various ancient world ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mars Orbital Laser Altimeter
260px, MOLA topographic images of the two hemispheres of Mars. This image appeared on the cover of ''Science'' magazine in May 1999. The Mars Orbiter Laser Altimeter (MOLA) was one of five instruments on the ''Mars Global Surveyor'' (MGS) spacecraft, which operated in Mars orbit from September 1997 to November 2006. However, the MOLA instrument transmitted altimetry data only until June 2001. The MOLA instrument transmitted infrared laser pulses towards Mars at a rate of 10 times per second, and measured the time of flight to determine the range (distance) of the MGS spacecraft to the Martian surface. The range measurements resulted in precise topographic maps of Mars. The precision maps are applicable to studies in geophysics, geology and atmospheric circulation. MOLA also functioned as a passive radiometer, and measured the radiance of the surface of Mars at 1064 nanometers. Planetary laser altimetry A laser altimeter is an instrument that measures the distance from an orbiti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the processes of mineral origin and formation, classification of minerals, their geographical distribution, as well as their utilization. History Early writing on mineralogy, especially on gemstones, comes from ancient Babylonia, the ancient Greco-Roman world, ancient and medieval China, and Sanskrit texts from ancient India and the ancient Islamic world. Books on the subject included the ''Naturalis Historia'' of Pliny the Elder, which not only described many different minerals but also explained many of their properties, and Kitab al Jawahir (Book of Precious Stones) by Persian scientist Al-Biruni. The German Renaissance specialist Georgius Agricola wrote works such as '' De re metallica'' (''On Metals'', 1556) and ''De Natura Fossilium'' ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfate
The sulfate or sulphate ion is a polyatomic anion with the empirical formula . Salts, acid derivatives, and peroxides of sulfate are widely used in industry. Sulfates occur widely in everyday life. Sulfates are salts of sulfuric acid and many are prepared from that acid. Spelling "Sulfate" is the spelling recommended by IUPAC, but "sulphate" was traditionally used in British English. Structure The sulfate anion consists of a central sulfur atom surrounded by four equivalent oxygen atoms in a tetrahedral arrangement. The symmetry is the same as that of methane. The sulfur atom is in the +6 oxidation state while the four oxygen atoms are each in the −2 state. The sulfate ion carries an overall charge of −2 and it is the conjugate base of the bisulfate (or hydrogensulfate) ion, , which is in turn the conjugate base of , sulfuric acid. Organic sulfate esters, such as dimethyl sulfate, are covalent compounds and esters of sulfuric acid. The tetrahedral molecular geometry of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |