|
Hertzian Contact Stress
{{disambiguation ...
Hertzian may refer to: * Hertzian antenna * Hertzian cone, the cone produced when an object passes through a solid, such as a bullet through glass * Hertzian contact stress, localized stresses that develop as two curved surfaces come in contact and deform slightly under imposed loads * Hertzian dipole, defined as a finite oscillating current over an infinitesimal length at a specified position * Hertzian wave, the original name of radio waves * Hertzian wave telegraphy Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimental technologies for tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertzian Antenna
Heinrich Rudolf Hertz ( ; ; 22 February 1857 – 1 January 1894) was a German physicist who first conclusively proved the existence of the electromagnetic waves predicted by James Clerk Maxwell's equations of electromagnetism. The unit of frequency, cycle per second, was named the " hertz" in his honor.IEC History . Iec.ch. Biography Heinrich Rudolf Hertz was born in 1857 in Hamburg, then a sovereign state of the German Confederation, into a prosperous and cultured Hanseatic family. His father was[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertzian Cone
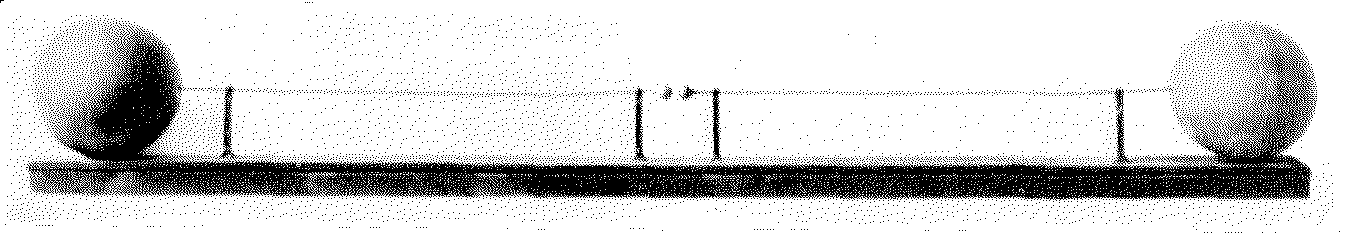
A Hertzian cone is the cone produced when an object passes through a solid, such as a bullet through glass. More technically, it is a cone of force that propagates through a brittle, amorphous, or cryptocrystalline solid material from a point of impact. This force eventually removes a full or partial cone in the material. This is the physical principle that explains the form and characteristics of the flakes removed from a core of tool stone during the process of lithic reduction. This phenomenon is named after the German physicist Heinrich Rudolf Hertz, who first described this type of wave-front propagation through various media. Although it might not be agreed by all, natural phenomena which have been grouped with the Hertzian cone phenomena include the crescentic " chatter marks" made on smoothed bedrock by glacial ice dragging along boulders at its base, the numerous crescentic impact marks sometimes seen on pebbles and cobbles, and the shatter cones found at bolide impa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertzian Contact Stress
{{disambiguation ...
Hertzian may refer to: * Hertzian antenna * Hertzian cone, the cone produced when an object passes through a solid, such as a bullet through glass * Hertzian contact stress, localized stresses that develop as two curved surfaces come in contact and deform slightly under imposed loads * Hertzian dipole, defined as a finite oscillating current over an infinitesimal length at a specified position * Hertzian wave, the original name of radio waves * Hertzian wave telegraphy Wireless telegraphy or radiotelegraphy is transmission of text messages by radio waves, analogous to electrical telegraphy using cables. Before about 1910, the term ''wireless telegraphy'' was also used for other experimental technologies for tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
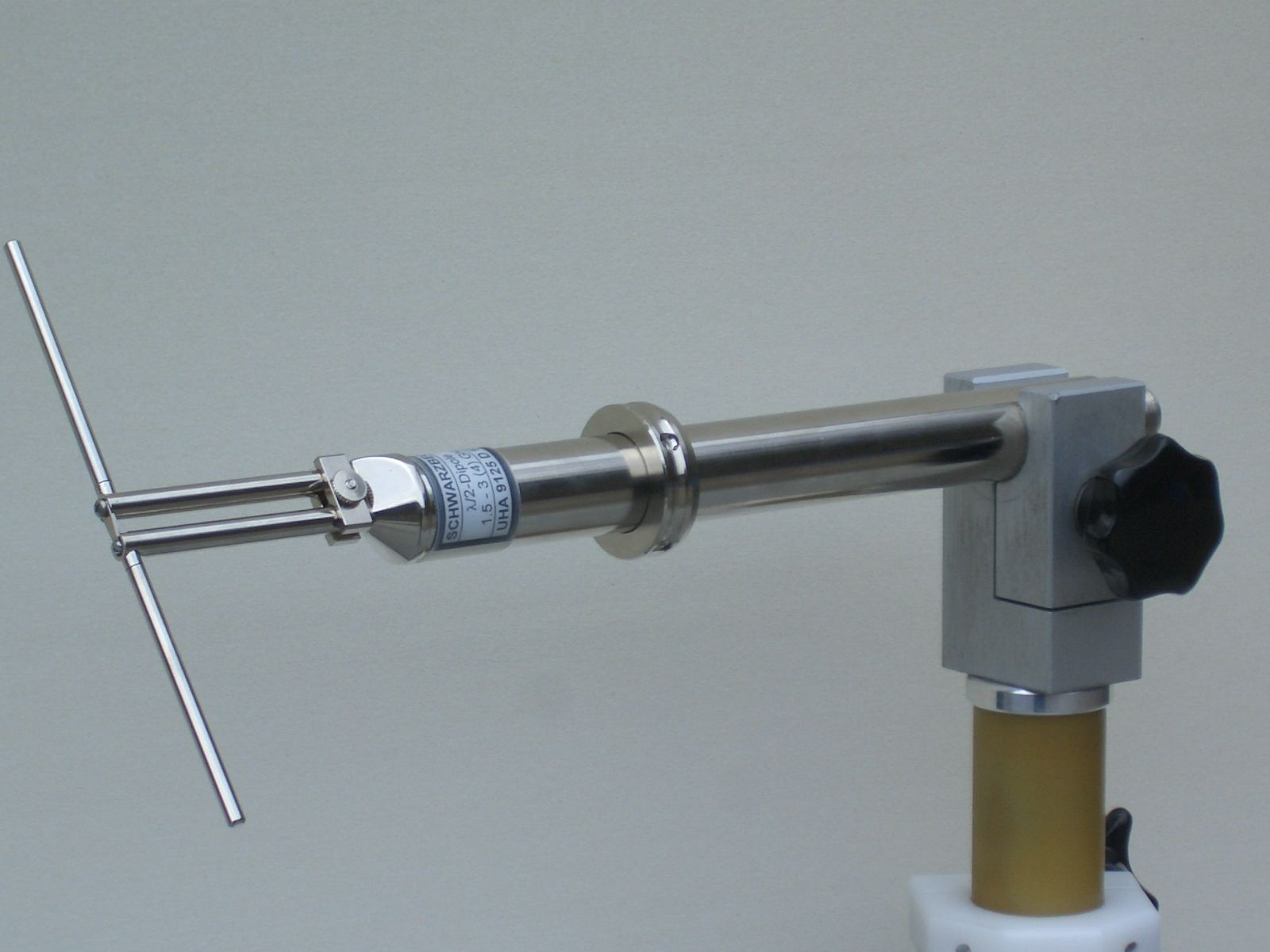
Hertzian Dipole
In radio and telecommunications a dipole antenna or doublet is the simplest and most widely used class of antenna. The dipole is any one of a class of antennas producing a radiation pattern approximating that of an elementary electric dipole with a radiating structure supporting a line current so energized that the current has only one node at each end. A dipole antenna commonly consists of two identical conductive elements such as metal wires or rods. The driving current from the transmitter is applied, or for receiving antennas the output signal to the receiver is taken, between the two halves of the antenna. Each side of the feedline to the transmitter or receiver is connected to one of the conductors. This contrasts with a monopole antenna, which consists of a single rod or conductor with one side of the feedline connected to it, and the other side connected to some type of ground. A common example of a dipole is the "rabbit ears" television antenna found on broadcast te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hertzian Wave
Radio waves are a type of electromagnetic radiation with the longest wavelengths in the electromagnetic spectrum, typically with frequencies of 300 gigahertz (GHz) and below. At 300 GHz, the corresponding wavelength is 1 mm (shorter than a grain of rice); at 30 Hz the corresponding wavelength is (longer than the radius of the Earth). Like all electromagnetic waves, radio waves in a vacuum travel at the speed of light, and in the Earth's atmosphere at a close, but slightly lower speed. Radio waves are generated by charged particles undergoing acceleration, such as time-varying electric currents. Naturally occurring radio waves are emitted by lightning and astronomical objects, and are part of the blackbody radiation emitted by all warm objects. Radio waves are generated artificially by an electronic device called a transmitter, which is connected to an antenna which radiates the waves. They are received by another antenna connected to a radio receiver, which p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |