|
Hermann Fischer-Sigwart
Hermann Fischer-Sigwart (23 March 1842 – 23 July 1925) was a Swiss naturalist and conservationist who was a pharmacist by profession. He wrote several books on natural history and founded a museum in his hometown Zofingen. Fischer-Sigwart was educated at Zofingen and then worked in his father's pharmacy as an apprentice. He then worked at the Karlsruhe pharmacy and studies at the University of Jena The University of Jena, officially the Friedrich Schiller University Jena (german: Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, abbreviated FSU, shortened form ''Uni Jena''), is a public research university located in Jena, Thuringia, Germany. The un ... where he was influenced by the botanist Matthias Jacob Schleiden. He then worked in Neuchâtel, Neuchatel, followed by the Golden Pharmacy in Basel and then returned to manage his father's business in Zofingen. In 1903 he sold off his business and went to live in Rebberg where he was in close contact with nature. He began to make collec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Fischer-Sigwart
Hermann Fischer-Sigwart (23 March 1842 – 23 July 1925) was a Swiss naturalist and conservationist who was a pharmacist by profession. He wrote several books on natural history and founded a museum in his hometown Zofingen. Fischer-Sigwart was educated at Zofingen and then worked in his father's pharmacy as an apprentice. He then worked at the Karlsruhe pharmacy and studies at the University of Jena The University of Jena, officially the Friedrich Schiller University Jena (german: Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, abbreviated FSU, shortened form ''Uni Jena''), is a public research university located in Jena, Thuringia, Germany. The un ... where he was influenced by the botanist Matthias Jacob Schleiden. He then worked in Neuchâtel, Neuchatel, followed by the Golden Pharmacy in Basel and then returned to manage his father's business in Zofingen. In 1903 he sold off his business and went to live in Rebberg where he was in close contact with nature. He began to make collec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zofingen
Zofingen (french: Zofingue) is a city in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. It is the capital of the district of Zofingen. Zofingen is a walled city and home of an ancient monastic settlement. History In ancient times Zofingen was a settlement of the Celtic Helvetii. In later times the Romans built a manor. The Alemanni settled in the 6th century and formed one of the oldest parishes in Aargau. In the 11th century the House of Frohburg founded a canons monastery. The town was founded in 1201 by the counts of Frohburg. 1231 was the first written mention of Zofingen, which in 1299 came in the possession of the Habsburgs. In 1415 the Bernese conquered the city and in 1528 they introduced the Reformation. Since 1803 Zofingen has belonged to the canton of Aargau and has become a regional center. The neighboring Mühlethal was incorporated in 2002. Geography Zofingen has an area, , of . Of this area, or 18.8% is used for agricultural purposes, while or 47.3% is forested. Of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Jena
The University of Jena, officially the Friedrich Schiller University Jena (german: Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, abbreviated FSU, shortened form ''Uni Jena''), is a public research university located in Jena, Thuringia, Germany. The university was established in 1558 and is counted among the ten oldest universities in Germany. It is affiliated with six Nobel Prize winners, most recently in 2000 when Jena graduate Herbert Kroemer won the Nobel Prize for physics. In the 2023 Times Higher Education World University Rankings, the university was awarded 189th place in the world. It was renamed after the poet Friedrich Schiller who was teaching as professor of philosophy when Jena attracted some of the most influential minds at the turn of the 19th century. With Karl Leonhard Reinhold, Johann Gottlieb Fichte, G. W. F. Hegel, F. W. J. Schelling and Friedrich Schlegel on its teaching staff, the university was at the centre of the emergence of German idealism and early Romanti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthias Jacob Schleiden
Matthias Jakob Schleiden (; 5 April 1804 – 23 June 1881) was a German botanist and co-founder of cell theory, along with Theodor Schwann and Rudolf Virchow. Career Matthias Jakob Schleiden was born in Hamburg. on 5 April 1804. His father was the municipal physician of Hamburg. Schleiden pursued legal studies graduating in 1827. He then established a legal practice but after a period of emotional depression and attempted suicide, he changed professions. He studied natural science at the University of Göttingen in Göttingen, Germany, but transferred to the University of Berlin in 1835 to study plants. Johann Horkel, Schleiden's uncle, encouraged him to study plant embryology. He soon developed his love for botany and cats into a full-time pursuit. Schleiden preferred to study plant structure under the microscope. As a professor of botany at the University of Jena, he wrote ''Contributions to our Knowledge of Phytogenesis'' (1838), in which he stated that all plants are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
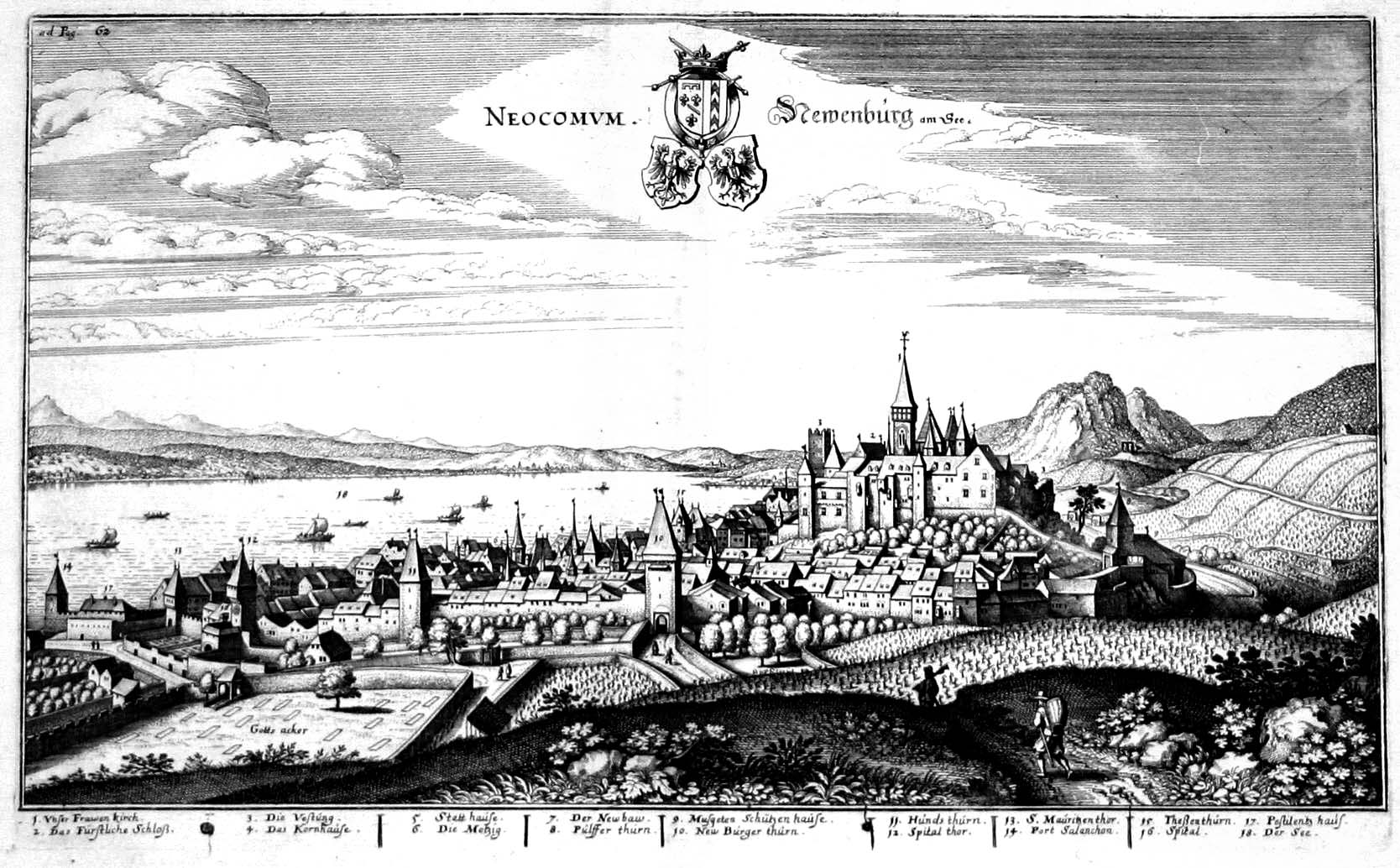
Neuchâtel
, neighboring_municipalities= Auvernier, Boudry, Chabrey (VD), Colombier, Cressier, Cudrefin (VD), Delley-Portalban (FR), Enges, Fenin-Vilars-Saules, Hauterive, Saint-Blaise, Savagnier , twintowns = Aarau (Switzerland), Besançon (France), Sansepolcro (Italy) Neuchâtel (, , ; german: Neuenburg) is the capital of the Swiss canton of Neuchâtel, situated on the shoreline of Lake Neuchâtel. Since the fusion in 2021 of the municipalities of Neuchâtel, Corcelles-Cormondrèche, Peseux, and Valangin, the city has approximately 45,000 inhabitants (80,000 in the metropolitan area). The city is sometimes referred to historically by the German name ; both the French and German names mean "New Castle". It was originally part of the Kingdom of Burgundy, then part of the Holy Roman Empire and later under Prussian control from 1707 until 1848, with an interruption during the Napoleonic Wars from 1802 to 1814. In 1848, Neuchâtel became a republic and a canton of Switzerland. Neuch� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basel
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese , neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS), Saint-Louis (FR-68), Weil am Rhein (DE-BW) , twintowns = Shanghai, Miami Beach , website = www.bs.ch Basel ( , ), also known as Basle ( ),french: Bâle ; it, Basilea ; rm, label= Sutsilvan, Basileia; other rm, Basilea . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine. Basel is Switzerland's third-most-populous city (after Zürich and Geneva) with about 175,000 inhabitants. The official language of Basel is (the Swiss variety of Standard) German, but the main spoken language is the local Basel German dialect. Basel is commonly considered to be the cultural capital of Switzerland and the city is famous for its many museums, including the Kunstmuseum, which is the first collection of art accessibl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Sarasin
Paul Sarasin, full name Paul Benedict Sarasin (11 December 1856 – 7 April 1929) was a Swiss people, Swiss naturalist and ethnologist. He is known as founder of National parks in Switzerland.Bibliography of Paul Sarasin ETH-Bibliothek Zürich, accessed 9 August 2010. Life and work Paul Sarasin studied medicine and natural science at the University of Basel with Leopold Ruetimeyer, where he also met Fritz Sarasin, and at the University of Würzburg. His dissertation had the title "Die Entwicklungsgeschichte der Bithynia (gastropod), Bithynia tentaculata" and was about the developmental history of a small aquatic snail. Paul Sarasin was a second cousin of Fritz Sarasin.Coan E. V., Kabat A. R. & Petit R. E. (15 February 2 ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albert Heim
Albert Heim (12 April 184931 August 1937) was a Swiss geologist, noted for his three-volume ''Geologie der Schweiz''. Born in Zürich, he was educated at Zürich and Berlin universities. Very early in life he became interested in the physical features of the Alps, and at the age of sixteen he made a model of the Tödi group. This came to the notice of Arnold Escher von der Linth, to whom Heim was indebted for much encouragement and geological instruction in the field. In 1873 he became professor of geology in the polytechnic school at Zürich, and in 1875 professor of geology in the university. In the same year he married Marie Heim-Vögtlin, Switzerland's first woman physician. In 1882 he was appointed director of the Geological Survey of Switzerland, and in 1884 the honorary degree of PhD was conferred upon him at the University of Berne. He was especially distinguished for his researches on the structure of the Alps and for the light thereby thrown on the structure of mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Schardt
Hans Schardt (18 June 1858 – 3 February 1931) was a Swiss geologist and a professor at the University of Neuchâtel and at the ETH and the University of Zurich. He contributed to studies on the folding and movement of layers of the earth based on stratigraphy. His studies where based on the Glarus thrust which he explained as a nappe. Life and work Schardt was born in Basel and moved to Yverdon to train as a pharmacist. He then trained to become a high-school teacher. He went to study geology at the University of Geneva and received a doctorate in 1884 after which he taught at the Collège in Montreux. Completing his habilitation in Lausanne in 1891, he went to Heidelberg and then became a professor at the Neuchâtel Academy where he began a geology institute. In 1911 he moved to the University of Zurich to succeed Albert Heim. He retired in 1928. Schardt noted the prealps and some Jurassic The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Naturalists
Swiss may refer to: * the adjectival form of Switzerland *Swiss people Places *Swiss, Missouri * Swiss, North Carolina *Swiss, West Virginia *Swiss, Wisconsin Other uses *Swiss-system tournament, in various games and sports *Swiss International Air Lines **Swiss Global Air Lines, a subsidiary *Swissair, former national air line of Switzerland *.swiss alternative TLD for Switzerland See also *Swiss made, label for Swiss products *Swiss cheese (other) *Switzerland (other) *Languages of Switzerland, none of which are called "Swiss" *International Typographic Style, also known as Swiss Style, in graphic design *Schweizer (other), meaning Swiss in German *Schweitzer, a family name meaning Swiss in German *Swisse Swisse is a vitamin, supplement, and skincare brand. Founded in Australia in 1969 and globally headquartered in Melbourne, and was sold to Health & Happiness, a Chinese company based in Hong Kong previously known as Biostime International, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1842 Births
__NOTOC__ Year 184 ( CLXXXIV) was a leap year starting on Wednesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Eggius and Aelianus (or, less frequently, year 937 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 184 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place China * The Yellow Turban Rebellion and Liang Province Rebellion break out in China. * The Disasters of the Partisan Prohibitions ends. * Zhang Jue leads the peasant revolt against Emperor Ling of Han of the Eastern Han Dynasty. Heading for the capital of Luoyang, his massive and undisciplined army (360,000 men), burns and destroys government offices and outposts. * June – Ling of Han places his brother-in-law, He Jin, in command of the imperial army and sends them to attack the Yellow Turban rebels. * Winter – Zha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |