|
Herbert William Gartrell
Herbert William Gartrell (14 August 1882 – 8 June 1945) was a South Australian academic and professor of mining and metallurgy at the University of Adelaide. Biography Gartrell was born in Maitland, South Australia to blacksmith William Pascoe Gartrell ( –1910) and Martha Gartrell, né Finch ( –1919) of Gawler. He was educated at Port Adelaide under headmaster Allen Martin and won a scholarship to study at St Peter's College, Adelaide, and proceeded to the University of Adelaide, graduating BA and BSc in 1902. In 1903 he won the Tate Memorial Medal for an original essay on Port Victor granite. In 1905 he was awarded an Angas engineering scholarship, which he used to travel to the US and Canada, where he gained valuable work experience and completed studies for an MA at the Columbia University in New York City. He was appointed foundation lecturer in Mining and Metallurgy at Adelaide University in 1910 and in November 1916 enrolled with the 1st AIF, and left for France in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories by area, and second smallest state by population. It has a total of 1.8 million people. Its population is the second most highly centralised in Australia, after Western Australia, with more than 77 percent of South Australians living in the capital Adelaide, or its environs. Other population centres in the state are relatively small; Mount Gambier, the second-largest centre, has a population of 33,233. South Australia shares borders with all of the other mainland states, as well as the Northern Territory; it is bordered to the west by Western Australia, to the north by the Northern Territory, to the north-east by Queensland, to the east by New South Wales, to the south-east by Victoria, and to the south by the Great Australian Bight.M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
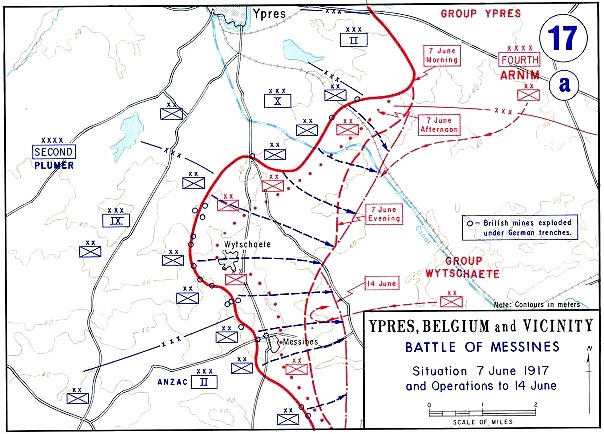
1st Australian Tunnelling Company
The 1st Australian Tunnelling Company was one of the Tunnelling companies of the Royal Engineers, tunnelling companies of the Royal Australian Engineers during World War I. The tunnelling units were occupied in offensive and defensive mining involving the placing and maintaining of Mining (military), mines under enemy lines, as well as other underground work such as the construction of Dugout (shelter)#World War I, deep dugouts for troop accommodation, the digging of subways, saps (narrow trenches dug to approach enemy trenches), cable trenches, and underground chambers for signals and medical services. Background By January 1915 it had become evident to the British Expeditionary Force (World War I), BEF at the Western Front (World War I), Western Front that the Germans were Mining (military), mining to a planned system. As the British had failed to develop suitable counter-tactics or underground listening devices before the war, field marshals John French, 1st Earl of Ypres, F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1945 Deaths
1945 marked the end of World War II and the fall of Nazi Germany and the Empire of Japan. It is also the only year in which Nuclear weapon, nuclear weapons Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, have been used in combat. Events Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix. January * January 1 – WWII: ** Nazi Germany, Germany begins Operation Bodenplatte, an attempt by the ''Luftwaffe'' to cripple Allies of World War II, Allied air forces in the Low Countries. ** Chenogne massacre: German prisoners are allegedly killed by American forces near the village of Chenogne, Belgium. * January 6 – WWII: A German offensive recaptures Esztergom, Kingdom of Hungary (1920–1946), Hungary from the Russians. * January 12 – WWII: The Soviet Union begins the Vistula–Oder Offensive in Eastern Europe, against the German Army (Wehrmacht), German Army. * January 13 – WWII: The Soviet Union begins the East Prussian Offensive, to eliminate German forces in East Pruss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1882 Births
Year 188 (CLXXXVIII) was a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known in the Roman Empire as the Year of the Consulship of Fuscianus and Silanus (or, less frequently, year 941 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 188 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Publius Helvius Pertinax becomes pro-consul of Africa from 188 to 189. Japan * Queen Himiko (or Shingi Waō) begins her reign in Japan (until 248). Births * April 4 – Caracalla (or Antoninus), Roman emperor (d. 217) * Lu Ji (or Gongji), Chinese official and politician (d. 219) * Sun Shao, Chinese general of the Eastern Wu state (d. 241) Deaths * March 17 – Julian, pope and patriarch of Alexandria * Fa Zhen (or Gaoqing), Chinese scholar (b. AD 100) * Lucius Antistius Burrus, Roman politician (executed) * Ma Xiang, Chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Australian Institute Of Technology
The University of South Australia (UniSA) is a public research university in the Australian state of South Australia. It is a founding member of the Australian Technology Network of universities, and is the largest university in South Australia with approximately 37,000 students. The university was founded in its current form in 1991 with the merger of the South Australian Institute of Technology (SAIT, established in 1889 as the South Australian School of Mines and Industries) and the South Australian College of Advanced Education (SACAE, established 1856). The legislation to establish and name the new University of South Australia was introduced by the Hon Mike Rann MP, Minister of Employment and Further Education. Under the University's Act, its original mission was "to preserve, extend and disseminate knowledge through teaching, research, scholarship and consultancy, and to provide educational programs that will enhance the diverse cultural life of the wider community". Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Missionary Society
The London Missionary Society was an interdenominational evangelical missionary society formed in England in 1795 at the instigation of Welsh Congregationalist minister Edward Williams. It was largely Reformed in outlook, with Congregational missions in Oceania, Africa, and the Americas, although there were also Presbyterians (notable for their work in China), Methodists, Baptists, and various other Protestants involved. It now forms part of the Council for World Mission. Origins In 1793, Edward Williams, then minister at Carr's Lane, Birmingham, wrote a letter to the churches of the Midlands, expressing the need for interdenominational world evangelization and foreign missions.Wadsworth KW, ''Yorkshire United Independent College -Two Hundred Years of Training for Christian Ministry by the Congregational Churches of Yorkshire'' Independent Press, London, 1954 It was effective and Williams began to play an active part in the plans for a missionary society. He left Birmingham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Payneham, South Australia
Payneham is an eastern suburb of Adelaide in the City of Norwood Payneham St Peters. It is part of a string of suburbs in Adelaide's east with a high proportion of Adelaide's Italian-Australian and French-Australian residents, many of whom can be traced back to the large-scale migration following the Second World War. Payneham's northern boundary is Payneham Road, and Portrush Road passes south–north through the middle of the suburb. History Payneham was named for himself by Samuel Payne (c. 1803–1847), who with his wife Ann, née Maslen, and two children arrived in April 1838 aboard ''Lord Goderich'' from London, and occupied section 285, Hundred of Adelaide in 1839. Payneham Post Office Payneham is an eastern suburb of Adelaide in the City of Norwood Payneham St Peters. It is part of a string of suburbs in Adelaide's east with a high proportion of Adelaide's Italian-Australian and French-Australian residents, many of whom can be ... opened on 18 July 1850 and was renam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council For Scientific And Industrial Research
The Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR) is South Africa's central and premier scientific research and development organisation. It was established by an act of parliament in 1945 and is situated on its own campus in the city of Pretoria. It is the largest research and development (R&D) organisation in Africa and accounts for about 10% of the entire African R&D budget. It has a staff of approximately 3,000 technical and scientific researchers, often working in multi-disciplinary teams. CSIR contract research and development Overview The CSIR contract R&D portfolio aims to enable clear understanding of national imperatives and the needs of industry to optimise the impact of the CSIR's R&D outputs. It leverages public, private and international partnerships in support of cutting-edge science, engineering and technology (SET).The organisation has clients in both the private sector (micro, small, medium and large enterprises; formal and informal), as well as in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of South Australia
The University of South Australia (UniSA) is a public research university in the Australian state of South Australia. It is a founding member of the Australian Technology Network of universities, and is the largest university in South Australia with approximately 37,000 students. The university was founded in its current form in 1991 with the merger of the South Australian Institute of Technology (SAIT, established in 1889 as the South Australian School of Mines and Industries) and the South Australian College of Advanced Education (SACAE, established 1856). The legislation to establish and name the new University of South Australia was introduced by the Hon Mike Rann MP, Minister of Employment and Further Education. Under the University's Act, its original mission was "to preserve, extend and disseminate knowledge through teaching, research, scholarship and consultancy, and to provide educational programs that will enhance the diverse cultural life of the wider community". Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
257th Tunnelling Company
The 257th Tunnelling Company was one of the tunnelling companies of the Royal Engineers created by the British Army during World War I. The tunnelling units were occupied in offensive and defensive mining involving the placing and maintaining of mines under enemy lines, as well as other underground work such as the construction of deep dugouts for troop accommodation, the digging of subways, saps (a narrow trench dug to approach enemy trenches), cable trenches and underground chambers for signals and medical services.The Tunnelling Companies RE , access date 25 April 2015 Background By January 1915 it had become evident to the BEF at the[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st AIF
The First Australian Imperial Force (1st AIF) was the main expeditionary force of the Australian Army during the First World War. It was formed as the Australian Imperial Force (AIF) following Britain's declaration of war on Germany on 15 August 1914, with an initial strength of one infantry division and one light horse brigade. The infantry division subsequently fought at Gallipoli between April and December 1915, with a newly raised second division, as well as three light horse brigades, reinforcing the committed units. After being evacuated to Egypt, the AIF was expanded to five infantry divisions, which were committed to the fighting in France and Belgium along the Western Front in March 1916. A sixth infantry division was partially raised in 1917 in the United Kingdom, but was broken up and used as reinforcements following heavy casualties on the Western Front. Meanwhile, two mounted divisions remained in the Middle East to fight against Turkish forces in the Sinai an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |