|
Henry Walton Bibb
Henry Walton Bibb (May 10, 1815 in Shelby County, Kentucky – August 1,1854 in Windsor) was an American author and abolitionist who was born a slave. Bibb told his life story in his narrative ''The Life and Adventures of Henry Bibb: An American Slave'', which included many failed escape attempts followed finally by success when he escaped to Detroit. After leaving Detroit to move to Canada with his family, due to issues with the legality of his assistance in the Underground Railroad, he founded the abolitionist newspaper, ''Voice of the Fugitive''. He lived in Canada until his death. Biography Bibb was born on May 10, 1815 to an enslaved woman, Mildred Jackson, on a Shelby County, Kentucky plantation. His father was Senator James Bibb, a relative of George M. Bibb, a Kentucky state senator. Williard Greenwood, a slaveholder, sold his six siblings away to different buyers. Bibb was hired out by his father for his wages. After wishing to learn to read the Bible he received som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Bibb
Henry Walton Bibb (May 10, 1815 in Shelby County, Kentucky – August 1,1854 in Windsor) was an American author and abolitionist who was born a slave. Bibb told his life story in his narrative ''The Life and Adventures of Henry Bibb: An American Slave'', which included many failed escape attempts followed finally by success when he escaped to Detroit. After leaving Detroit to move to Canada with his family, due to issues with the legality of his assistance in the Underground Railroad, he founded the abolitionist newspaper, ''Voice of the Fugitive''. He lived in Canada until his death. Biography Bibb was born on May 10, 1815 to an enslaved woman, Mildred Jackson, on a Shelby County, Kentucky plantation. His father was Senator James Bibb, a relative of George M. Bibb, a Kentucky state senator. Williard Greenwood, a slaveholder, sold his six siblings away to different buyers. Bibb was hired out by his father for his wages. After wishing to learn to read the Bible he received some ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick Douglass
Frederick Douglass (born Frederick Augustus Washington Bailey, February 1817 or 1818 – February 20, 1895) was an American social reformer, abolitionist, orator, writer, and statesman. After escaping from slavery in Maryland, he became a national leader of the abolitionist movement in Massachusetts and New York, becoming famous for his oratory and incisive antislavery writings. Accordingly, he was described by abolitionists in his time as a living counterexample to slaveholders' arguments that slaves lacked the intellectual capacity to function as independent American citizens. Northerners at the time found it hard to believe that such a great orator had once been a slave. It was in response to this disbelief that Douglass wrote his first autobiography. Douglass wrote three autobiographies, describing his experiences as a slave in his ''Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass, an American Slave'' (1845), which became a bestseller and was influential in promoting t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enslaved People
Slavery is a social-economic system under which people are enslaved: deprived of personal freedom and forced to perform labor or services without compensation. These people are referred to as slaves, or as enslaved people. The following is a list of historical people who were enslaved at some point during their lives, in alphabetical order by first name. Several names have been added under the letter representing the person's last name. A * Abdul Rahman Ibrahima Sori (1762–1829), a prince from West Africa and enslaved in the United States for 40 years until President John Quincy Adams freed him. * Abraham, an enslaved black man who carried messages between the frontier and Charles Town during wars with the Cherokee, for which he was freed. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
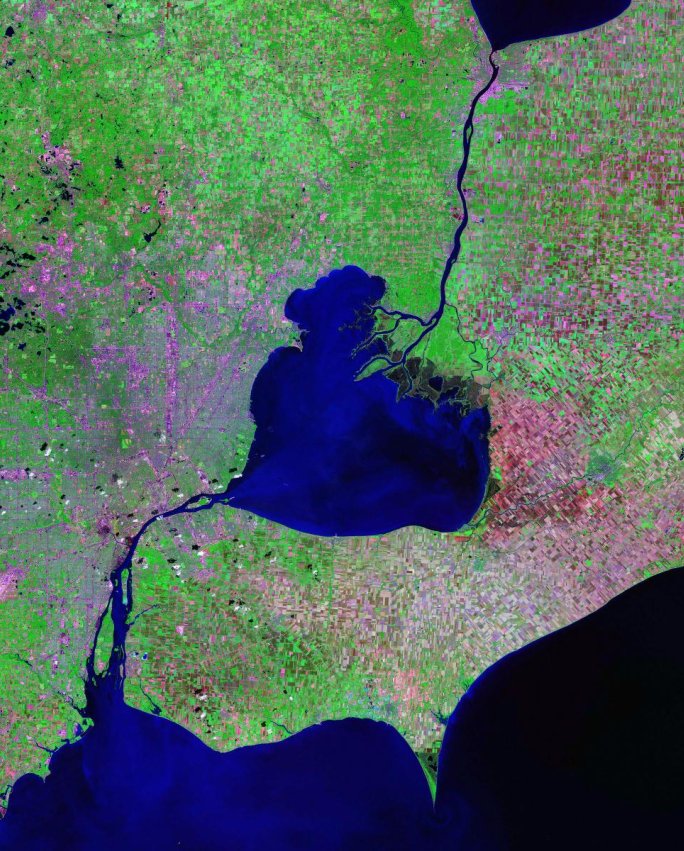
Detroit River
The Detroit River flows west and south for from Lake St. Clair to Lake Erie as a strait in the Great Lakes system. The river divides the metropolitan areas of Detroit, Michigan, and Windsor, Ontario, Windsor, Ontario—an area collectively referred to as Detroit–Windsor—and forms part of the Canada–United States border, border between Canada and the United States. The Ambassador Bridge, the Detroit–Windsor Tunnel, and the Michigan Central Railway Tunnel connect the cities. The river's English name comes from the French language, French (translated as "River of the Strait"). The Detroit River has served an important role in the history of Detroit and Windsor, and is one of the world's busiest waterways. It is an important transportation route connecting Lake Michigan, Lake Huron, and Lake Superior to Lake Erie and eventually to Lake Ontario, the Saint Lawrence Seaway, St. Lawrence Seaway and the Erie Canal. When Detroit underwent rapid industrialization at the turn of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Josiah Henson
Josiah Henson (June 15, 1789 – May 5, 1883) was an author, abolitionist, and minister. Born into slavery, in Port Tobacco, Charles County, Maryland, he escaped to Upper Canada (now Ontario) in 1830, and founded a settlement and laborer's school for other fugitive slaves at Dawn, near Dresden, in Kent County, Upper Canada, of Ontario. Henson's autobiography, ''The Life of Josiah Henson, Formerly a Slave, Now an Inhabitant of Canada, as Narrated by Himself'' (1849), is believed to have inspired the title character of Harriet Beecher Stowe's 1852 novel ''Uncle Tom's Cabin'' (1852). Following the success of Stowe's novel, Henson issued an expanded version of his memoir in 1858, ''Truth Stranger Than Fiction. Father Henson's Story of His Own Life'' (published Boston: John P. Jewett & Company, 1858). Interest in his life continued, and nearly two decades later, his life story was updated and published as ''Uncle Tom's Story of His Life: An Autobiography of the Rev. Josiah Henson'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refugee Home Society
The Refugee Home Society was an organization founded in Michigan and Ontario in 1851 that was designed to help former enslaved people become established in a community and remain free. It was located 20 miles from Windsor, Ontario, the border with the United States. The settlement provided purchase of land an easy terms, education, and a community with three churches by 1861. Background The War of 1812 and Levi Coffin's visit to Upper Canada in 1844, led fugitive slaves come in great numbers to Amherstburg, Ontario, where American officers were station near Fort Malden, and to Windsor and Sandwich, Ontario by 1822. The African American refugees came to the area to farm the land and create successful lives. As a result, a number of settlements were created: Anderdon, Brion, Dawn, Dresden, Edgar, Elgin, Elmstead, Gambia, Gosfield, Gesto, Gilgal, Haiti Village, Harrow, Ontario, Little River, Marble Village, the Matthew settlement, Mt. Pleasant, New Canaan, Ontario, Puce, Ontario, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Voice Of The Fugitive
''Voice of the Fugitive'' was Canada's first Black newspaper that was directed towards freedom seekers and Black refugees from the United States. Founded and edited by Henry Bibb and his wife Mary Bibb, it was first published on January 1st, 1851 in Sandwich, Ontario and moved to Windsor shortly after. The paper was published on a bi-weekly schedule on Wednesdays, where it was priced at $1 per year. The paper was available across Ontario and made its way to America's Northern States such as Michigan, New York, Pennsylvania and Ohio. In 1852, James Theodore Holly joined the newspaper as co-owner and co-editor, and was officially named as "corresponding editor and travelling agent". This helped Bibb to actively engage with other political and charitable commitments, speaking duties and other writing engagements. Despite Mary Bibb not being listed as a co-editor, she actively contributed to the paper. Mary Bibb had written several articles, connected with a network of abolitionists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windsor, Ontario
Windsor is a city in southwestern Ontario, Canada, on the south bank of the Detroit River directly across from Detroit, Michigan, United States. Geographically located within but administratively independent of Essex County, it is the southernmost city in Canada and marks the southwestern end of the Quebec City–Windsor Corridor. The city's population was 229,660 at the 2021 census, making it the third-most populated city in Southwestern Ontario, after London and Kitchener. The Detroit–Windsor urban area is North America's most populous trans-border conurbation, and the Ambassador Bridge border crossing is the busiest commercial crossing on the Canada–United States border. Windsor is a major contributor to Canada's automotive industry and is culturally diverse. Known as the "Automotive Capital of Canada", Windsor's industrial and manufacturing heritage is responsible for how the city has developed through the years. History Early settlement At the time when the fir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada (french: link=no, province du Haut-Canada) was a part of British Canada established in 1791 by the Kingdom of Great Britain, to govern the central third of the lands in British North America, formerly part of the Province of Quebec since 1763. Upper Canada included all of modern-day Southern Ontario and all those areas of Northern Ontario in the which had formed part of New France, essentially the watersheds of the Ottawa River or Lakes Huron and Superior, excluding any lands within the watershed of Hudson Bay. The "upper" prefix in the name reflects its geographic position along the Great Lakes, mostly above the headwaters of the Saint Lawrence River, contrasted with Lower Canada (present-day Quebec) to the northeast. Upper Canada was the primary destination of Loyalist refugees and settlers from the United States after the American Revolution, who often were granted land to settle in Upper Canada. Already populated by Indigenous peoples, land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sandwich, Ontario
Old Sandwich Town (Olde Sandwich Towne) is located along the Canada–United States border, Canada–US border of the Detroit River, and was established in 1797.Windsor Architectural Conservation Advisory Committee (WACAC). ''Historic Sandwich Town: Walk through Ontario’s oldest, continuous European settlement: a field study''. (Windsor, Ontario: University of Windsor, Faculty of Education, 1987) It is considered one of the oldest, most historically significant settlements in OntarioMorgan, Carl. ''Birth of a City''. (Tecumseh, Ontario: TraveLife, 1991) and has been the site of several historically significant events in Ontario's history. Many historic buildings remain in Old Sandwich Town and the area hosts an annual festival to celebrate its heritage. The area is now a neighbourhood of the city of Windsor, Ontario, Windsor. History This area south of what was named the Detroit River was initially inhabited by various First Nations in Canada, First Nations, including the Ojib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary E
Mary may refer to: People * Mary (name), a feminine given name (includes a list of people with the name) Religious contexts * New Testament people named Mary, overview article linking to many of those below * Mary, mother of Jesus, also called the Blessed Virgin Mary * Mary Magdalene, devoted follower of Jesus * Mary of Bethany, follower of Jesus, considered by Western medieval tradition to be the same person as Mary Magdalene * Mary, mother of James * Mary of Clopas, follower of Jesus * Mary, mother of John Mark * Mary of Egypt, patron saint of penitents * Mary of Rome, a New Testament woman * Mary, mother of Zechariah and sister of Moses and Aaron; mostly known by the Hebrew name: Miriam * Mary the Jewess one of the reputed founders of alchemy, referred to by Zosimus. * Mary 2.0, Roman Catholic women's movement * Maryam (surah) "Mary", 19th surah (chapter) of the Qur'an Royalty * Mary, Countess of Blois (1200–1241), daughter of Walter of Avesnes and Margaret of Blois ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fugitive Slave Act Of 1850
The Fugitive Slave Act or Fugitive Slave Law was passed by the United States Congress on September 18, 1850, as part of the Compromise of 1850 between Southern interests in slavery and Northern Free-Soilers. The Act was one of the most controversial elements of the 1850 compromise and heightened Northern fears of a slave power conspiracy. It required that all escaped slaves, upon capture, be returned to the slaver and that officials and citizens of free states had to cooperate. Abolitionists nicknamed it the "Bloodhound Bill", after the dogs that were used to track down people fleeing from slavery. The Act contributed to the growing polarization of the country over the issue of slavery, and was one of the factors that led to the Civil War. Background By 1843, several hundred enslaved people a year escaped to the North successfully, making slavery an unstable institution in the border states. The earlier Fugitive Slave Act of 1793 was a Federal law that was written w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |