|
Henry Middleton (captain)
Sir Henry Middleton (died 1613) was a sea captain and adventurer. He negotiated with the sultan of Ternate and the sultan of Tidore, competed against Dutch and Portuguese interests in the East Indies but still managed to buy cloves.Margaret Makepeace, 'Middleton, Sir Henry (d. 1613)', Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, 2004; online edn, Jan 2008 He had two brothers, John Middleton (d. 1602 or 1603), the eldest who was captain of EIC galleon Hector and director of EIC. David Middleton was also a mariner working for EIC. Henry was taken on at the Woolwich ship yards working first on the East India Company's '' Red Dragon''. The company was organising its first expedition to "East India". The prominent Elizabethan trader and privateer, James Lancaster was to command the four ships. Second in command was Middleton's brother John, a company captain who secured Henry as a mercantile agent with a berth on the voyage. They set off in April 1601 arriving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Trading In The East
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep Sea lane, waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, Naval warfare, warfare, Human migration, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, Columbian Exchange, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a Full-rigged ship, ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is Square rig, square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priaman
Pariaman ( Jawi: ), is a coastal city in West Sumatra, Indonesia. Pariaman covers an area of , with a coastline. It had a population of 79,043 at the 2010 Census and 94,224 at the 2020 census. "Pariaman" means "safe area". History According to the limited early sources available, by the sixteenth century Pariaman was an important port city serving the Minangkabau settlements in the interior highlands of central west Sumatra. Traders from western India and later from Europe visited the port, trading in pepper, gold, and other products of the interior. In the early seventeenth century the port came under control of the Sultanate of Aceh, to the north; an Acehnese governor was stationed in the town. The port formally came under Dutch control in 1663 by treaty with Aceh. In 1671 the Dutch built a lodge here and later, around 1684, a fort. Continuing clashes with local rulers and competition with other European trading companies resulted in the port being abandoned by the Dutch in 1770 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa. A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is the southern tip of Africa, based on the misbelief that the Cape was the dividing point between the Atlantic and Indian oceans, and have nothing to do with north or south. In fact, by looking at a map, the southernmost point of Africa is Cape Agulhas about to the east-southeast. The currents of the two oceans meet at the point where the warm-water Agulhas current meets the cold-water Benguela current and turns back on itself. That oceanic meeting point fluctuates between Cape Agulhas and Cape Point (about east of the Cape of Good Hope). When following the western side of the African coastline from the equator, however, the Cape of Good Hope marks the point where a ship begins to travel more eastward than southward. Thus, the first mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also be used for any other celestial body that is roughly spherical. In spatial (3D) geometry, as applied in astronomy, the equator of a rotating spheroid (such as a planet) is the parallel (circle of latitude) at which latitude is defined to be 0°. It is an imaginary line on the spheroid, equidistant from its poles, dividing it into northern and southern hemispheres. In other words, it is the intersection of the spheroid with the plane perpendicular to its axis of rotation and midway between its geographical poles. On and near the equator (on Earth), noontime sunlight appears almost directly overhead (no more than about 23° from the zenith) every day, year-round. Consequently, the equator has a rather stable daytime temperature throug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maio, Cape Verde
Maio is the easternmost of the Sotavento islands of Cape Verde. Maio is located south of the island of Boa Vista and east of Santiago. Administratively, the island forms one ''concelho'' (municipality): Maio. History The island was discovered in 1460. It was first settled at the end of the 16th century, when the land was used to raise livestock, especially goats. Salt was first exploited in the 17th century which caused the population to grow. The English exported salt to Europe from Porto Inglês, hence the name of that city.História Municipio do Maio The inconclusive was fought between British and French |
Cabo Da Roca
Cabo da Roca () or Cape Roca is a cape which forms the westernmost point of the Sintra Mountain Range, of mainland Portugal, of continental Europe, and of the Eurasian landmass. It is situated in the municipality of Sintra, near Azóia, in the southwest of the district of Lisbon. Notably the point includes a lighthouse that started operation in 1772. History Cabo da Roca was known to the Romans as ''Promontorium Magnum'' and during the Age of Sail as the Rock of Lisbon. Lighthouse Geography The cape is within the Sintra-Cascais Natural Park, 42 kilometres west of the city of Lisbon and in the southwest of Sintra. A location () is inscribed on a stone plaque, located on a monument at the site. The western coast is a mixture of sandy beaches and rocky cliff promontories: around Cabo da Roca, cliffs are more than 100 metres in height, and cut into crystalline rocks, composed of strongly folded and faulted sedimentary units. These forms are disturbed by dikes and sma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plymouth
Plymouth () is a port city and unitary authority in South West England. It is located on the south coast of Devon, approximately south-west of Exeter and south-west of London. It is bordered by Cornwall to the west and south-west. Plymouth's early history extends to the Bronze Age when a first settlement emerged at Mount Batten. This settlement continued as a trading post for the Roman Empire, until it was surpassed by the more prosperous village of Sutton founded in the ninth century, now called Plymouth. In 1588, an English fleet based in Plymouth intercepted and defeated the Spanish Armada. In 1620, the Pilgrim Fathers departed Plymouth for the New World and established Plymouth Colony, the second English settlement in what is now the United States of America. During the English Civil War, the town was held by the Roundhead, Parliamentarians and was besieged between 1642 and 1646. Throughout the Industrial Revolution, Plymouth grew as a commercial shipping port, handling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Downs (ship Anchorage)
The Downs is a roadstead (area of sheltered, favourable sea) in the southern North Sea near the English Channel off the east Kent coast, between the North and the South Foreland in southern England. In 1639 the Battle of the Downs took place here, when the Dutch navy destroyed a Spanish fleet which had sought refuge in neutral English waters. From the Elizabethan era onwards, the presence of the Downs helped to make Deal one of the premier ports in England, and in the 19th century, it was equipped with its own telegraph and timeball tower to enable ships to set their marine chronometers. The anchorage has depths down to 12 fathoms (22 m). Even during southerly gales some shelter was afforded, though under this condition wrecks were not infrequent. Storms from any direction could also drive ships onto the shore or onto the sands, which—in spite of providing the sheltered water—were constantly shifting, and not always adequately marked. The Downs served in the age of sail as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravesend, Kent
Gravesend is a town in northwest Kent, England, situated 21 miles (35 km) east-southeast of Charing Cross (central London) on the south bank of the River Thames and opposite Tilbury in Essex. Located in the diocese of Rochester, it is the administrative centre of the Borough of Gravesham. Its geographical situation has given Gravesend strategic importance throughout the maritime and communications history of South East England. A Thames Gateway commuter town, it retains strong links with the River Thames, not least through the Port of London Authority Pilot Station and has witnessed rejuvenation since the advent of High Speed 1 rail services via Gravesend railway station. The station was recently refurbished and now has a new bridge. Toponymy Recorded as Gravesham in the Domesday Book of 1086 when it belonged to Odo, Earl of Kent and Bishop of Bayeux, the half-brother of William the Conqueror, its name probably derives from ''graaf-ham'': the home of the reeve or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch East India Company
The United East India Company ( nl, Verenigde Oostindische Compagnie, the VOC) was a chartered company established on the 20th March 1602 by the States General of the Netherlands amalgamating existing companies into the first joint-stock company in the world, granting it a 21-year monopoly to carry out trade activities in Asia. Shares in the company could be bought by any resident of the United Provinces and then subsequently bought and sold in open-air secondary markets (one of which became the Amsterdam Stock Exchange). It is sometimes considered to have been the first multinational corporation. It was a powerful company, possessing quasi-governmental powers, including the ability to wage war, imprison and execute convicts, negotiate treaties, strike its own coins, and establish colonies. They are also known for their international slave trade. Statistically, the VOC eclipsed all of its rivals in the Asia trade. Between 1602 and 1796 the VOC sent almost a million Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
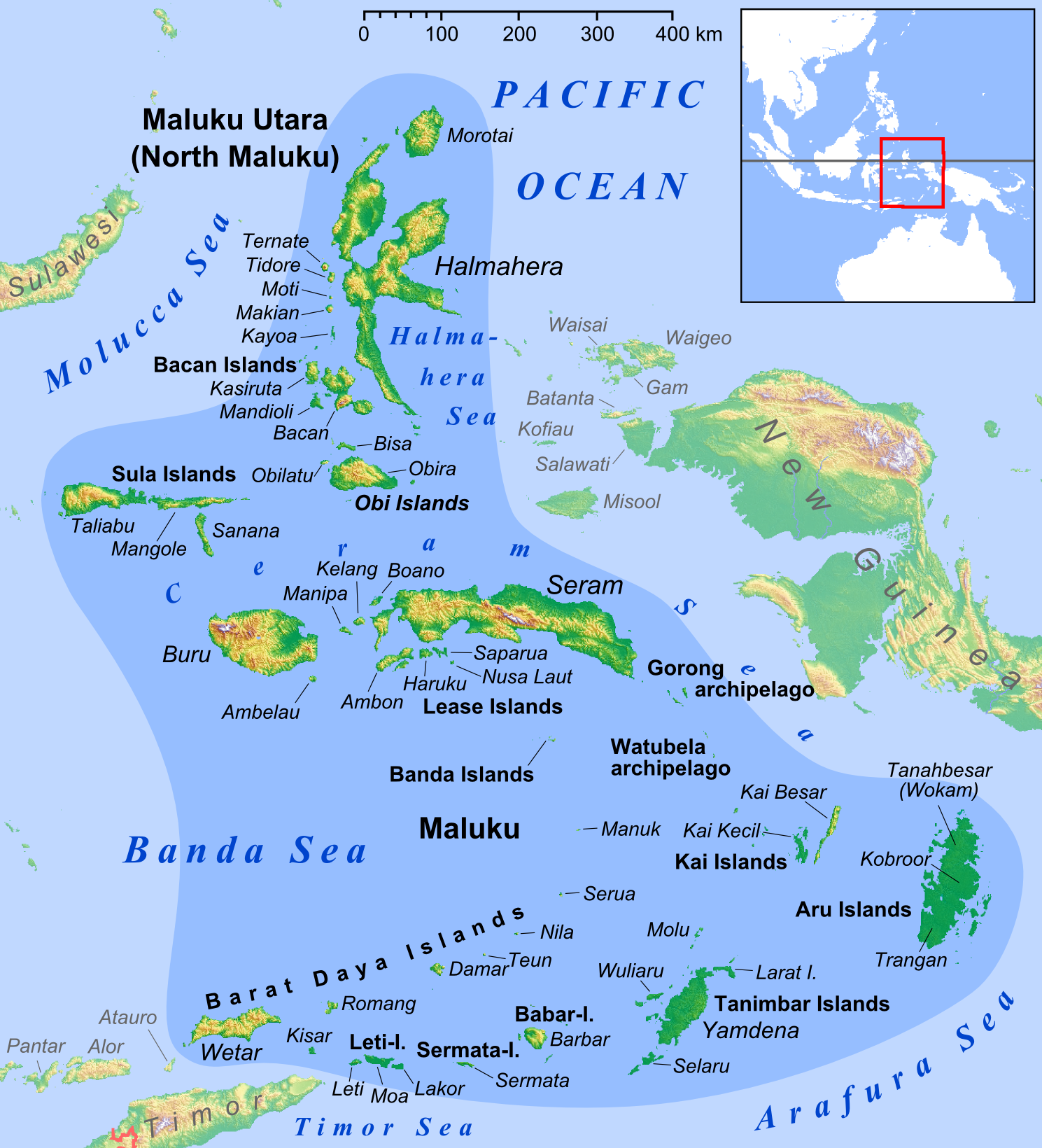
Banda Islands
The Banda Islands ( id, Kepulauan Banda) are a volcanic group of ten small volcanic islands in the Banda Sea, about south of Seram Island and about east of Java, and constitute an administrative district (''kecamatan'') within the Central Maluku Regency in the Indonesian province of Maluku. The islands rise out of deep ocean and have a total land area of approximately . They had a population of 18,544 at the 2010 Census and 20,924 at the 2020 Census. Until the mid-19th century the Banda Islands were the world's only source of the spices nutmeg and mace, produced from the nutmeg tree. The islands are also popular destinations for scuba diving and snorkeling. The main town and administrative centre is Bandanaira, located on the island of the same name. History Pre-European history The first documented human presence in the Banda Islands comes from a rock shelter site on Pulau Ay that was in use at least 8,000 years ago. The earliest mention of the Banda Islands are fou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ambon Island
Ambon Island is part of the Maluku Islands of Indonesia. The island has an area of and is mountainous, well watered, and fertile. Ambon Island consists of two territories: the city of Ambon, Maluku, Ambon to the south and various districts (''kecamatan'') of the Central Maluku Regency to the north. The main city and seaport is Ambon, Maluku, Ambon (with a 2020 Census population of 347,288), which is also the capital of Maluku (province), Maluku Provinces of Indonesia, province, while those districts of Maluku Tengah Regency situated on Ambon Island had a 2020 Census population of 128,069. Ambon has an Pattimura Airport, airport and is home to the Pattimura University and Open University (Universitas Terbuka), state universities, and a few private universities, which include Darussalam University (Universitas Darussalam, UNDAR) and Universitas Kristen Indonesia Maluku (UKIM). Geography Ambon Island lies off the southwest coast of the much larger Seram island. It is on the north ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







%2C_Hoorn.jpg)
_toont_Zuidoost-Molukse_kleding_en_gebruiken_TMnr_20017958.jpg)