|
Henry D'Andeli
Henry d'Andeli was a 13th-century Norman poet notable for his work ''La Bataille des Vins'' (English Battle of the Wines), and for the satirical poem ''Battle of the Seven Arts''. He also wrote ''Dit du Chancelier Philippe'' on the subject of his contemporary Philip the Chancellor. The fabliau '' Lai d'Aristote'', which was formerly ascribed to him, is now thought to be by Henry of Valenciennes. Battle of the arts In his mock-epic battle (c1230-50), d'Andeli laments the defeat of rhetoric (represented by Grammar/Orléans) at the hands of Logic/Paris Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. S .... Grammar is forced to flee to Egypt; and Poetry in the person of 'Sir Versifier' to the Loire countryside - d'Andeli predicting that "It will be thirty years before he dares show his fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Francia, West Franks and Gallo-Roman culture, Gallo-Romans. The term is also used to denote emigrants from the duchy who conquered other territories such as England and Sicily. The Norse settlements in West Francia followed a series of raids on the French northern coast mainly from Denmark, although some also sailed from Norway and Sweden. These settlements were finally legitimized when Rollo, a Scandinavian Viking leader, agreed to swear fealty to Charles the Simple, King Charles III of West Francia following the Siege of Chartres (911), siege of Chartres in 911. The intermingling in Normandy produced an Ethnic group, ethnic and cultural "Norman" identity in the first half of the 10th century, an identity which continued to evolve over the ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Wines
The Battle of the Wines (''fr. La Bataille des Vins''), sometimes called "The Battle of the Blends" was a notable poem written by Henry d'Andeli in 1224 and tells the story of a famous wine tasting organized by the French king Philip Augustus. Over 70 samples from France and across Europe, including Cyprus, Spain and the Mosel region, were tasted and judged by an English priest. The priest classified the wines he tasted as either ''Celebrated'' for those which pleased him or ''Excommunicated'' for those that did not meet his standards. In the end a sweet wine from Cyprus (widely believed to be Commandaria''BBC.co.uk'' (May 21, 2002)Wine - the Last 1,000 Years/ref>) won the overall tasting and was awarded the supreme title of " Apostle". Wines from France Celebrated wines * Laon * Clermont * Crouy * Soissons * Montmorency * Hautvillers * Épernay * Argenteuil * Deuil * Pierrefitte * Marly * Trilbardou * Sézanne * Saint-Yon * Samois * Orléans * Jargeau * Tonn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philip The Chancellor
Philippe le Chancelier, also known as "Philippus Cancellarius Parisiensis" (Philip, Chancellor of Paris) (''c'' 1160–December 26, 1236) was a French theologian, Latin lyric poet, and possibly a composer as well. He was the illegitimate son of Philippe, Archdeacon of Paris (born 1125), and was part of a family of powerful clerics. He was born and studied theology in Paris. He was chancellor of Notre Dame de Paris starting in 1217 until his death, and was also Archdeacon of Noyon. Philip is portrayed as an enemy to the Mendicant orders becoming prevalent at the time, but this has been greatly exaggerated. He may have even joined the Franciscan order soon before his death.Thomas B. Payne. "Philip the Chancellor", ''Grove Music Online'', ed. L. Macy (accessed April 1, 2006)grovemusic.com(subscription access) Philip was one of the most prolific Medieval lyric poets. He was the subject of Henri d'Andeli's ''Dit du Chancelier Philippe''. Philip's most influential work was his ''Summa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fabliau
A ''fabliau'' (; plural ''fabliaux'') is a comic, often anonymous tale written by jongleurs in northeast France between c. 1150 and 1400. They are generally characterized by sexual and scatological obscenity, and by a set of contrary attitudes—contrary to the church and to the nobility. Several of them were reworked by Giovanni Boccaccio for the '' Decameron'' and by Geoffrey Chaucer for his '' Canterbury Tales''. Some 150 French ''fabliaux'' are extant, the number depending on how narrowly ''fabliau'' is defined. According to R. Howard Bloch, ''fabliaux'' are the first expression of literary realism in Europe. Some nineteenth-century scholars, most notably Gaston Paris, argue that ''fabliaux'' originally came from the Orient and were brought to the West by returning crusaders. History and definition of the genre The ''fabliau'' is defined as a short narrative in (usually octosyllabic) verse, between 300 and 400 lines long,Cuddon 301. its content often comic or satiric.A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
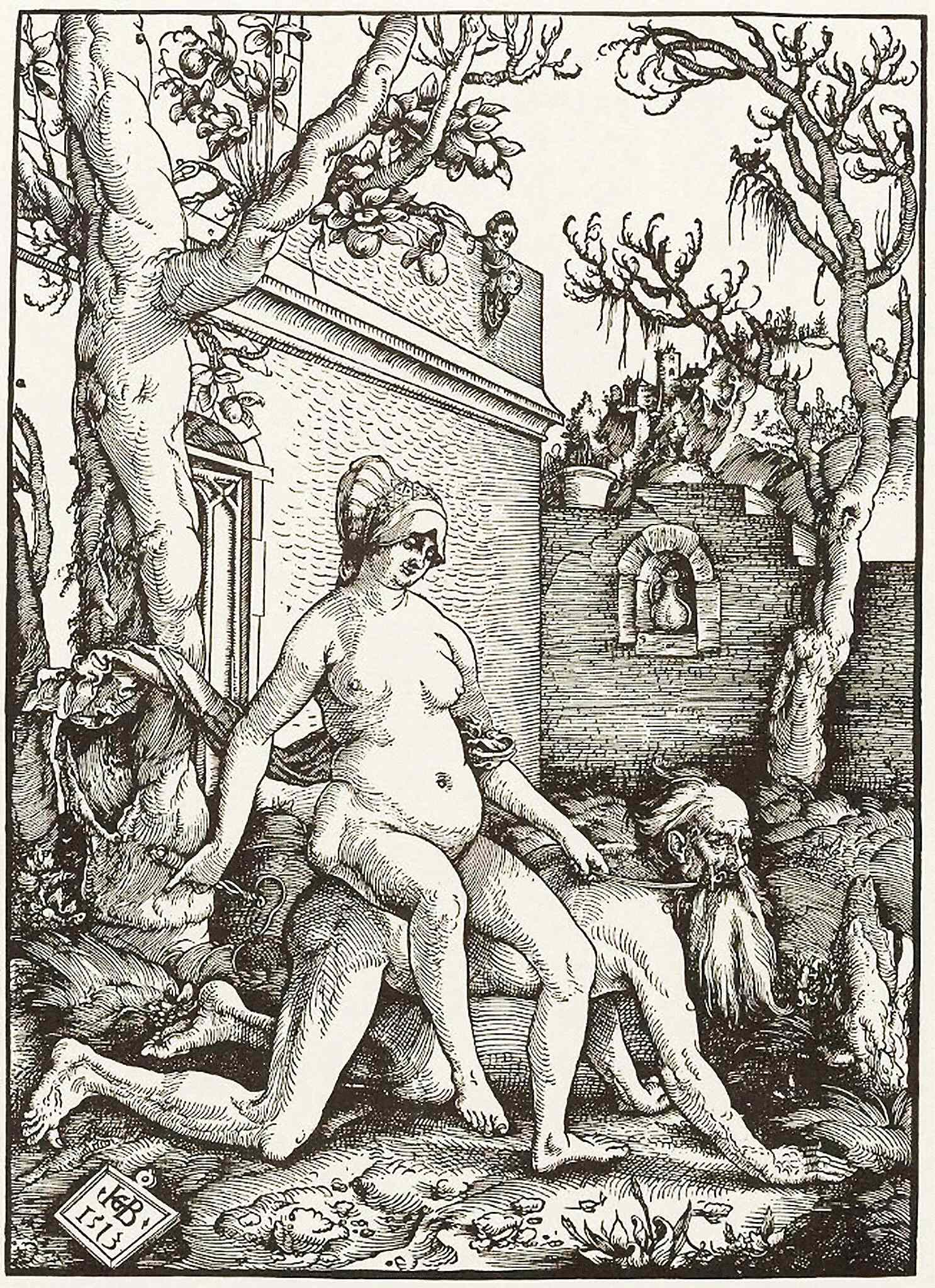
The Tale Of Phyllis And Aristotle
The tale of Phyllis and Aristotle is a medieval cautionary tale about the triumph of a seductive woman, Phyllis, over the greatest male intellect, the ancient Greek philosopher Aristotle. It is one of several Power of Women stories from that time. Among early versions is the French ''Lai d'Aristote'' from 1220. The story of the dominatrix and the famous intellectual was taken up by artists from the 12th century onwards, in media from stone sculpture in churches to panels of wood or ivory, textiles such as carpets and tapestries, engravings, oil paintings, brass jugs (aquamanile), and stained glass. Artists attracted to the theme include Hans Baldung, Albrecht Dürer, Lucas Cranach the Elder, and Alessandro Turchi. Story The tale varies in the telling, but the core of it is as follows: Aristotle advises his pupil Alexander to avoid Phyllis, the seductive mistress of his father, the king, but is himself captivated by her. She agrees to ride him, on condition that she play the rol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Of Valenciennes
Henry of Valenciennes was an early 13th-century French writer, historian and chronicler of the Latin Empire. Biography Henry of Valenciennes was a chronicler under Henry of Flanders who left for the Fourth Crusade with the army of his patron. In 1204, following the capture of Constantinople by the Franco-Venetian forces, he became a canon in the Hagia Sophia. In 1206, the year of his patron's accession to the throne of the Latin Empire, he was tasked with compiling a chronicle mostly focused on his deeds, roughly picking up where Geoffrey of Villehardouin's chronicle concludes. As a result, Henry's chronicle is usually included with Geoffrey's in the surviving manuscripts. It abruptly ends in 1209 or 1210, but it is notable for its account of the battle of Philippopolis. Henry is also credited with the '' Lai d'Aristote'', previously attributed to the Norman Henry d'Andeli. See also *Geoffrey of Villehardouin Geoffrey of Villehardouin (c. 1150 – c. 1213) was a French knigh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orléans
Orléans (;"Orleans" (US) and , ) is a city in north-central France, about 120 kilometres (74 miles) southwest of Paris. It is the prefecture of the Departments of France, department of Loiret and of the Regions of France, region of Centre-Val de Loire. Orléans is located on the river Loire nestled in the heart of the Loire Valley, classified as a Loire Valley, World Heritage Site, where the river curves south towards the Massif Central. In 2019, the city had 116,269 inhabitants within its municipal boundaries. Orléans is the center of Orléans Métropole that has a population of 288,229. The larger Functional area (France), metropolitan area has a population of 451,373, the 20th largest in France. The city owes its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economist Intelli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernardus Silvestris
Bernardus Silvestris, also known as Bernard Silvestris and Bernard Silvester, was a medieval Platonist philosopher and poet of the 12th century. Biography Little is known about Bernardus's life. In the nineteenth century, it was assumed that Bernardus was the same person as Bernard of Chartres, but the scholarly consensus is now that the two were different people. There is little evidence connecting Bernardus to Chartres, yet his work is consistent with the scholarship associated with Chartres in the twelfth century and is in that sense "Chartrian". Bernardus dedicated his '' Cosmographia'' to Thierry of Chartres, who became chancellor of Chartres in 1141; he most likely wrote the letter in order to win the favour of a powerful figure, known for his interest in science. André Vernet, who edited Bernardus' ''Cosmographia'', believed that he lived from 1085 to 1178. The most secure date in his life is 1147–48, when the ''Cosmographia'' was supposedly read to Pope Eugene III, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goliard
The goliards were a group of generally young clergy in Europe who wrote satirical Latin poetry in the 12th and 13th centuries of the Middle Ages. They were chiefly clerics who served at or had studied at the universities of France, Germany, Spain, Italy, and England, who protested against the growing contradictions within the church through song, poetry and performance. Disaffected and not called to the religious life, they often presented such protests within a structured setting associated with carnival, such as the Feast of Fools, or church liturgy. Etymology The derivation of the word is uncertain. It may come from the Latin ''gula,'' gluttony. It may also originate from a mythical "Bishop Golias," a medieval Latin form of the name Goliath, the giant who fought King David in the Bible—thus suggestive of the monstrous nature of the goliard. Another source may be ''gailliard,'' a "gay fellow". Many scholars believe the term ''goliard'' is derived from a letter between Ber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Of Garland
Johannes de Garlandia or John of Garland was a medieval grammarian and university teacher. His dates of birth and death are unknown, but he probably lived from about 1190 to about 1270. He was born in England, and studied at Oxford and then at the medieval University of Paris, where he was teaching by 1220. He lived and taught on the Left Bank at the ''Clos de Garlande'', after which Rue Galande is named. This is the origin of the name by which he is usually known. The main facts of his life are stated in his long poem ''De triumphis ecclesiae'' ("On the triumphs of the Church"). In 1229, he was one of the first Masters of the new University of Toulouse. His poem ''Epithalamium Beatae Mariae Virginis'' was presented in 1230 to the Papal legate Romanus de Sancto Angelo, one of the founders of the university. He was in Toulouse during the turbulent events of 1229–1231 (see Albigensian Crusade), which he describes in ''De Triumphis''. After the death of bishop Foulques of Toul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Poets
List of poets who have written in the French language: A * Louise-Victorine Ackermann (1813–1890) * Adam de la Halle (v.1250 – v.1285) * Pierre Albert-Birot (1876–1967) * Anne-Marie Albiach (1937–2012) * Pierre Alféri (1963) * Marc Alyn (1937) * Catherine d'Amboise (1475–1550) * Jean Amrouche (1906–1962) * Guillaume Apollinaire (1880–1918) * Louis Aragon (1897–1982) * Jacques Arnold (1912–1995) * Hans Arp (1887–1966) * Antonin Artaud (1896–1948) * Théodore Agrippa d'Aubigné (1552–1630) * Jacques Audiberti (1899–1965) * Pierre Autin-Grenier (1947) B * Jean-Antoine de Baïf (1532–1589) * Théodore de Banville (1823–1891) * Jules Barbey d'Aurevilly (1807–1889) * Henri Auguste Barbier (1805–1882) * Natalie Clifford Barney (1876–1972) * Linda Maria Baros (1981) * Guillaume de Salluste Du Bartas (1544–1590) * Henry Bataille (1872–1922) * Henry Bauchau (1913–2012) * Charles Baudelaire (1821–1867) * Marcel Béalu (1908–1993) * Phili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

