|
Henry 'Hotspur' Percy
Sir Henry Percy (20 May 1364 – 21 July 1403), nicknamed Hotspur, was an English knight who fought in several campaigns against the Scots in the northern border and against the French during the Hundred Years' War. The nickname "Hotspur" was given to him by the Scots as a tribute to his speed in advance and readiness to attack. The heir to a leading noble family in northern England, Hotspur was one of the earliest and prime movers behind the deposition of King Richard II in favour of Henry Bolingbroke in 1399. He later fell out with the new regime and rebelled, and was slain at the Battle of Shrewsbury in 1403 at the height of his fame. Career Henry Percy was born 20 May 1364 at either Alnwick Castle or Warkworth Castle in Northumberland, the eldest son of Henry Percy, 1st Earl of Northumberland, and Margaret Neville, daughter of Ralph de Neville, 2nd Lord Neville of Raby, and Alice de Audley.; . He was knighted by King Edward III in April 1377, together with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pennon
A pennon, also known as a pennant or pendant, is a long narrow flag which is larger at the hoist than at the fly. It can have several shapes, such as triangular, tapering (square tail) or triangular swallowtail (forked tail), etc. In maritime use, pennants are to be hung from the main truck. Pennon-style flags were one of the principal three varieties of flags carried during the Middle Ages (the other two were the banner and the standard). The pennon is a flag resembling the guidon in shape, but only half the size. It does not contain any coat of arms, but only crests, mottos and heraldic and ornamental devices. Pennoncell, streamer and wimpel are minor varieties of this style of flag (see variant types). Etymology Pennon comes from the Latin ''penna'', meaning "a wing" or "a feather". Initially it was a term for a "small pennant". Pennant have been used as a general (and imprecise) term for flags which are not strictly rectangular. Pendant is an obsolete spel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of England and France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French throne between the English House of Plantagenet and the French royal House of Valois. Over time, the war grew into a broader power struggle involving factions from across Western Europe, fuelled by emerging nationalism on both sides. The Hundred Years' War was one of the most significant conflicts of the Middle Ages. For 116 years, interrupted by several truces, five generations of kings from two rival dynasties fought for the throne of the dominant kingdom in Western Europe. The war's effect on European history was lasting. Both sides produced innovations in military technology and tactics, including professional standing armies and artillery, that permanently changed warfare in Europe; chivalry, which had reached its height during the conflict, subsequently declined. Stronge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Picardy
Picardy (; Picard and french: Picardie, , ) is a historical territory and a former administrative region of France. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region of Hauts-de-France. It is located in the northern part of France. History The historical province of Picardy stretched from north of Noyon to Calais via the whole of the Somme department and the north of the Aisne department. The province of Artois (Arras area) separated Picardy from French Flanders. Middle Ages From the 5th century, the area formed part of the Frankish Empire and, in the feudal period, it encompassed the six countships of Boulogne, Montreuil, Ponthieu, Amiénois, Vermandois and Laonnois.Dunbabin.France in the Making. Ch.4. The Principalities 888–987 In accordance with the provisions of the 843 Treaty of Verdun, the region became part of West Francia, the later Kingdom of France. The name "Picardy" derives from the Old French ''pic,'' meaning " pike", the characteristic weapon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calais
Calais ( , , traditionally , ) is a port city in the Pas-de-Calais department, of which it is a subprefecture. Although Calais is by far the largest city in Pas-de-Calais, the department's prefecture is its third-largest city of Arras. The population of the city proper is 72,929; that of the urban area is 149,673 (2018).Comparateur de territoire: Aire d'attraction des villes 2020 de Calais (073), Commune de Calais (62193) INSEE Calais overlooks the , the narrowest point in the English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Warden Of The Marches
The Lord Warden of the Marches was an office in the governments of Scotland and England. The holders were responsible for the security of the border between the two nations, and often took part in military action. They were also responsible, along with 'Conservators of the truce', for administering the special type of border law known as March law. The Marches on both sides of the border were traditionally split into West, Middle and East, each with their own warden answerable to the Lord Warden-general. The English Western March was based on Carlisle and the Eastern March on Berwick-upon-Tweed. The offices became unnecessary after the union of the crowns of England and Scotland under King James in 1603. For England Warden of the Marches * Robert de Clifford (1297–) (died 1314) *John de Warenne, 7th Earl of Surrey (1327–) *Henry de Percy, 2nd Baron Percy (1328–) *Ralph Neville, 2nd Baron Neville de Raby and Henry de Percy, 2nd Baron Percy (1334–) (jointly) * Gilbert W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of The Teutonic Order
The State of the Teutonic Order (german: Staat des Deutschen Ordens, ; la, Civitas Ordinis Theutonici; lt, Vokiečių ordino valstybė; pl, Państwo zakonu krzyżackiego), also called () or (), was a medieval Crusader state, located in Central Europe along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea. It was formed by the knights of the Teutonic Order during the 13th century Northern Crusades in the region of Prussia. The Livonian Brothers of the Sword merged in 1237 with the Teutonic Order of Prussia and became known as its branch, the Livonian Order, while their state ('' Terra Mariana'') became a part of the Teutonic Order State. At its greatest territorial extent, in the early 15th century, it encompassed Chełmno Land, Courland, Gotland, Livonia, Neumark, Pomerelia (Gdańsk Pomerania), Prussia and Samogitia, i.e. territories nowadays located in Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Germany, Poland, Russia, and Sweden. Following the battles of Battle of Grunwald, Grunwald in 1410 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edmund Mortimer, 3rd Earl Of March
Edmund de Mortimer, 3rd Earl of March and ''jure uxoris'' Earl of Ulster (1 February 135227 December 1381) was the son of Roger Mortimer, 2nd Earl of March, by his wife Philippa, daughter of William Montagu, 1st Earl of Salisbury and Catherine Grandison. Early life An infant at the death of his father, Edmund, as a ward of the crown, was placed by Edward III of England under the care of William of Wykeham and Richard FitzAlan, 10th Earl of Arundel. The position of the young earl, powerful on account of his possessions and hereditary influence in the Welsh marches, was rendered still more important by his marriage on 24 August 1369 at the age of 17 to the 14-year-old Philippa, the only child of the late Lionel of Antwerp, Duke of Clarence, the second son of Edward III. Lionel's late wife, Elizabeth, had been daughter and heiress of William Donn de Burgh, 3rd Earl of Ulster, and Lionel had himself been created Earl of Ulster before his marriage. Edmund inherited the title Ear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward III Of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring royal authority after the disastrous and unorthodox reign of his father, Edward II. EdwardIII transformed the Kingdom of England into one of the most formidable military powers in Europe. His fifty-year reign was one of the longest in English history, and saw vital developments in legislation and government, in particular the evolution of the English Parliament, as well as the ravages of the Black Death. He outlived his eldest son, Edward the Black Prince, and the throne passed to his grandson, Richard II. Edward was crowned at age fourteen after his father was deposed by his mother, Isabella of France, and her lover Roger Mortimer. At age seventeen he led a successful coup d'état against Mortimer, the ''de facto'' ruler of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knight Bachelor
The title of Knight Bachelor is the basic rank granted to a man who has been knighted by the monarch but not inducted as a member of one of the organised orders of chivalry; it is a part of the British honours system. Knights Bachelor are the most ancient sort of British knight (the rank existed during the 13th-century reign of King Henry III), but Knights Bachelor rank below knights of chivalric orders. A man who is knighted is formally addressed as " Sir irst Name urname or "Sir irst Name and his wife as "Lady urname. Criteria Knighthood is usually conferred for public service; amongst its recipients are all male judges of His Majesty's High Court of Justice in England. It is possible to be a Knight Bachelor and a junior member of an order of chivalry without being a knight of that order; this situation has become rather common, especially among those recognized for achievements in entertainment. For instance, Sir Michael Gambon, Sir Derek Jacobi, Sir Anthony Hopkins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Neville, 2nd Baron Neville De Raby
Ralph Neville, 2nd Baron Neville of Raby (c. 1291 – 5 August 1367) was an English aristocrat, the son of Ralph Neville, 1st Baron Neville de Raby by Eupheme de Clavering. Neville led the English forces to victory against King David II of Scotland at the Battle of Neville's Cross on 17 October 1346. Marriage and children He married Alice de Audley (d. 1358), daughter of Hugh de Audley, 1st Baron Audley of Stratton Audley and Isolde le Rous (and widow of Ralph de Greystoke, 1st Baron Greystoke (died 1323)), on 14 Jan 1326 with whom he had thirteen children: # Euphemia Neville (c. 1327 – 1394), married firstly in 1344 Robert Clifford, 4th Baron Clifford, secondly Reynold eginalducy, son of Thomas Baron Lucy and thirdly Walter Heselarton, knight. # John Neville, 3rd Baron Neville de Raby (1322/8–17 October 1388), married firstly Maud Percy and secondly Elizabeth Latimer and had issue with both # Margaret Neville (12 February 1329 – 12 May 1372), married firstly W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
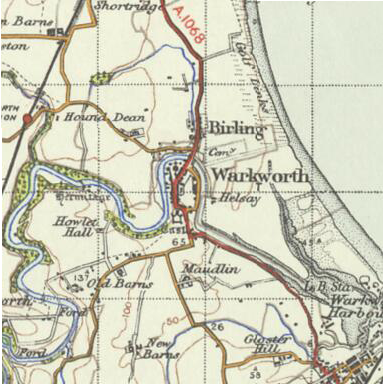
Warkworth Castle
Warkworth Castle is a ruined medieval castle in Warkworth in the English county of Northumberland. The village and castle occupy a loop of the River Coquet, less than a mile from England's north-east coast. When the castle was founded is uncertain: traditionally its construction has been ascribed to Prince Henry of Scotland, Earl of Northumbria, in the mid-12th century, but it may have been built by King Henry II of England when he took control of England's northern counties. Warkworth Castle was first documented in a charter of 1157–1164 when Henry II granted it to Roger fitz Richard. The timber castle was considered "feeble", and was left undefended when the Scots invaded in 1173. Roger's son Robert inherited and improved the castle. Robert was a favourite of King John, and hosted him at Warkworth Castle in 1213. The castle remained in the family line, with periods of guardianship when heirs were too young to control their estates. King Edward I s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alnwick Castle
Alnwick Castle () is a castle and country house in Alnwick in the English county of Northumberland. It is the seat of the 12th Duke of Northumberland, built following the Norman conquest and renovated and remodelled a number of times. It is a Grade I listed building now the home of Ralph Percy, 12th Duke of Northumberland and his family. In 2016, the castle received over 600,000 visitors per year when combined with adjacent attraction the Alnwick Garden. History Alnwick Castle guards a road crossing the River Aln. Ivo de Vesci, Baron of Alnwick, erected the first parts of the castle in about 1096. Beatrix de Vesci, the daughter of Yves de Vescy, married the Constable of Chestershire and Knaresborough, Eustace fitz John. By his marriage to Beatrix de Vesci he gained the baronies of Malton and Alnwick. The castle was first mentioned in 1136 when it was captured by King David I of Scotland. At this point it was described as "very strong". It was besieged in 1172 and aga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |