|
Henri Dikongué
Henri Dikongué (born 6 December 1967) is a Cameroonian singer and guitarist. Dikongué was born in Douala to a family of musicians. He attended a music school in Paris, where he attempted unsuccessfully to release a first album. He started a music and acting troupe and worked with actor Martin Yog and musicians Alfred M'Bongo and Manuel Wandji, as well as Maranatha, a South African chorus. After finally choosing to settle in Paris in 1989, he perfected his skills with classical guitar and collaborated with African musicians such as Manu Dibango and Papa Wemba. In 1995 he released his first album, ''Wa''. His music mixes elements from makossa, bikutsi, reggae and rumba. He sings in his native tongue, Duala. His second album, ''C'est la Vie'', was released in 1997 (in the US under the Tinder Records label) and sold about 10,000 copies. Between 1997 and 1998, he toured Germany and the United States. His third album, ''N'oublie jamais'', was released in 2000. This album in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douala
Douala is the largest city in Cameroon and its economic capital. It is also the capital of Cameroon's Littoral Region (Cameroon), Littoral Region. Home to Central Africa's largest port and its major international airport, Douala International Airport (DLA), it is the commercial and economic capital of Cameroon and the entire Economic Community of Central African States, CEMAC region comprising Gabon, Congo, Chad, Equatorial Guinea, Central African Republic and Cameroon. Consequently, it handles most of the country's major exports, such as Petroleum, oil, Cocoa bean, cocoa and coffee, timber, metals and fruits. , the city and its surrounding area had an estimated population of 5,768,400. The city sits on the estuary of Wouri River and its climate is tropical. History The first Europeans to visit the area were the Portuguese people, Portuguese in about 1472. At the time, the estuary of Wouri River was known as the Rio dos Camarões (Shrimp River). By 1650, it had become the site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maranatha
__NOTOC__ ''Maranatha'' (Aramaic: ') is an Aramaic phrase which occurs once in the New Testament (). It also appears in Didache 10:14. It is transliterated into Greek letters rather than translated and, given the nature of early manuscripts, the lexical difficulty rests in determining just which two Aramaic words constitute the single Greek expression. Translations and use The NRSV of 1 Corinthians 16:22 translates the expression as: "Our Lord, come!" but notes that it could also be translated as: "Our Lord has come"; the NIV translates: "Come, O Lord"; the ''Message'' version paraphrases it as: "Make room for the Master!" In the ''Catechism of the Catholic Church'', "Maranatha" was translated as "Come, Lord!". In the Latin Church, the word "Maranatha" has been used as a solemn formula of excommunication (alongside "anathema"). Analysis The NAB notes: Use in contemplative prayer Based on the teachings of John Cassian, John Main recommended the recitation of ''Maranatha' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papa Wemba
Jules Shungu Wembadio Pene Kikumba (14 June 1949 – 24 April 2016), known professionally as Papa Wemba (), was a Congolese singer and musician who played Congolese rumba, soukous, and ndombolo. Dubbed the "King of Rumba Rock", he was one of the most popular musicians of his time in Africa and played an important role in world music. He was also a fashion icon who popularized the Sape look and style through his musical group Viva la Musica, with whom he performed on stages throughout the world.Margalit Fox (25 April 2016). Musical history Papa Wemba's road to fame and prominence began when he joined the music group Zaiko Langa Langa in the late 1960s. This was followed by his success as a founding member both of Isifi Lokole and then Yoka Lokole,"Both groups used the lokole, a hollow tree trunk played with two sticks, as a rhythmic foundation" along with a short stint as a member of Afrisa International for a few months. During these early stages of his career, he was estab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AllMusic
AllMusic (previously known as All Music Guide and AMG) is an American online music database. It catalogs more than three million album entries and 30 million tracks, as well as information on musicians and bands. Initiated in 1991, the database was first made available on the Internet in 1994. AllMusic is owned by RhythmOne. History AllMusic was launched as ''All Music Guide'' by Michael Erlewine, a "compulsive archivist, noted astrologer, Buddhist scholar and musician". He became interested in using computers for his astrological work in the mid-1970s and founded a software company, Matrix, in 1977. In the early 1990s, as CDs replaced LPs as the dominant format for recorded music, Erlewine purchased what he thought was a CD of early recordings by Little Richard. After buying it he discovered it was a "flaccid latter-day rehash". Frustrated with the labeling, he researched using metadata to create a music guide. In 1990, in Big Rapids, Michigan, he founded ''All Music Guide' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makossa
Makossa is a Cameroonian style of urban music. Like much other late 20th century music of Sub-Saharan Africa, it uses strong electric bass rhythms and prominent brass. In the 1980s makossa had a wave of mainstream success across Africa and to a lesser extent abroad. Makossa, which means "(I) dance" in the Douala language, Section "Cultural-based terms" (last line) originated from a Douala dance called the '' kossa''. Emmanuel Nelle Eyoum started using the refrain ''kossa kossa'' in his songs with his group "Los Calvinos". The style began to take shape in the 1950s though the first recordings were not seen until a decade later. There were artists such as Eboa Lotin, Misse Ngoh and especially Manu Dibango, who popularised makossa throughout the world with his song "Soul Makossa" in 1972. The chant from the song, ''mamako, mamasa, maka makossa'', was later used by Michael Jackson in "Wanna Be Startin' Somethin'" in 1983. Many other performers followed suit. The 2010 World cup al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bikutsi
Bikutsi is a musical genre from Cameroon. It developed from the traditional styles of the Beti, or Ewondo, people, who live around the city of Yaoundé. It was popular in the middle of the 20th century in West Africa. It is primarily dance music. Etymology The word 'bikutsi' literally means 'beat the earth' or 'let's beat the earth' (''bi''- indicates a plural, -''kut''- means 'to beat' and -''chi'' means 'earth'.) The name indicates a dance that is accompanied by stomping the feet on the ground. Description Bikutsi is characterised by an intense rhythm (3+3, with a strong "two" feel), though it is occasionally and its tempo is usually quarternote. it is played at all sorts of Beti gatherings, including parties, funerals and weddings. Beti gatherings fall into two major categories: * Ekang phase: the time when imaginary, mythological and spiritual issues are discussed * Bikutsi phase: when real-life issues are discussed A double sided harp with calabash amplification call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reggae
Reggae () is a music genre that originated in Jamaica in the late 1960s. The term also denotes the modern popular music of Jamaica and its diaspora. A 1968 single by Toots and the Maytals, " Do the Reggay" was the first popular song to use the word "reggae", effectively naming the genre and introducing it to a global audience. While sometimes used in a broad sense to refer to most types of popular Jamaican dance music, the term ''reggae'' more properly denotes a particular music style that was strongly influenced by traditional mento as well as American jazz and rhythm and blues, and evolved out of the earlier genres ska and rocksteady. Reggae usually relates news, social gossip, and political commentary. It is instantly recognizable from the counterpoint between the bass and drum downbeat and the offbeat rhythm section. The immediate origins of reggae were in ska and rocksteady; from the latter, reggae took over the use of the bass as a percussion instrument. Reggae is d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
African Rumba
Congolese rumba is a popular genre of dance music that originated in the Congo basin during the 1940s, deriving from Cuban son. The style gained popularity throughout Africa during the 1960s and 1970s. It is known as Lingala in Kenya, Uganda, and Tanzania after the Lingala language of the lyrics in the majority of the songs. In Zambia and Zimbabwe, where Congolese music is also influential, it is still usually referred to as rumba. It is also an individual dance. In December 2021, Congolese rumba was added to the UNESCO list of intangible cultural heritage. History In the 1930s and 1940s, Afro-Cuban son groups, such as Septeto Habanero, Trio Matamoros, and Los Guaracheros de Oriente, were played over Radio Congo Belge in Léopoldville (Kinshasa), gaining widespread popularity in the country during the following decades. Once local bands tried to emulate the sound of Cuban son (incorrectly referred to as "rumba" in Africa, despite being unrelated to Cuban rumba), their music b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duala Language
Duala (''ɓwambo ba duālā in douala)'' (also spelt Douala, Diwala, Dwela, Dualla and Dwala) is a dialect cluster spoken by the Duala and Mungo peoples of Cameroon. Douala belongs to the Bantu language family, in a subgroup called Sawabantu. It is a tonal language with subject–verb–object word order. Maho (2009) treats Douala as a cluster of five languages: Douala proper, Bodiman, Oli (Ewodi, Wuri), Pongo and Mongo. He also notes a Douala-based pidgin named ''Jo''. History The origins of Duala come from the migrations of the Duala people during the sixteenth century from the Congo River Basin to the coastal areas of southern Cameroon. While it is a Bantu language, Guthrie estimates that it only retained as little as 14% of the roots of Proto-Bantu. Alfred Saker, a British missionary and linguist, completed in the first translation of the Bible into Duala in 1870. After the German colonization of Cameroon in 1885, the Basel Mission promoted Duala as a lingua franca in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C'est La Vie (Henri Dikongué Album)
''C'est la Vie'' is an album by the Cameroonian musician Henri Dikongué. It was released in 1997. The album was dedicated to Fela Kuti and Robert Mitchum. It was a success on European world music charts, and sold more than 9,000 copies in its first month of release. Dikongué promoted it by touring North America. Production The album was produced by Gilles Fruchaux. The title track was sung in French; Dikongué wrote all of the album's songs, and also played classical guitar. Dikongué was influenced by the sound of bossa nova. Critical reception '' JazzTimes'' noted that "Dikongue's musical turf isn’t the dance-driven world of intensely rhythmic West African styles, but a softer melange, grounded in elements of Brazilian influences and a general emphasis on acoustic instruments." Robert Christgau wrote that Dikongué is "what happens when Afropop becomes world music—when it targets broad-minded European connoisseurs rather than rhythm-schooled African sophisticates." '' T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
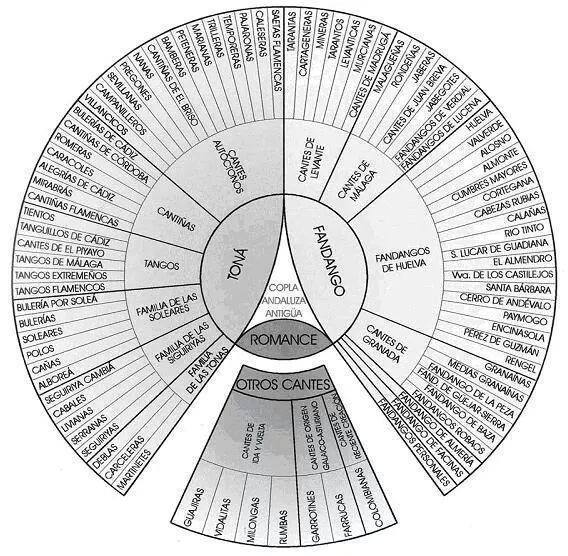
Flamenco
Flamenco (), in its strictest sense, is an art form based on the various folkloric music traditions of southern Spain, developed within the gitano subculture of the region of Andalusia, and also having historical presence in Extremadura and Murcia. In a wider sense, it is a portmanteau term used to refer to a variety of both contemporary and traditional musical styles typical of southern Spain. Flamenco is closely associated to the gitanos of the Romani ethnicity who have contributed significantly to its origination and professionalization. However, its style is uniquely Andalusian and flamenco artists have historically included Spaniards of both gitano and non-gitano heritage. The oldest record of flamenco music dates to 1774 in the book ''Las Cartas Marruecas'' by José Cadalso. The development of flamenco over the past two centuries is well documented: "the theatre movement of sainetes (one-act plays) and tonadillas, popular song books and song sheets, customs, studies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)