|
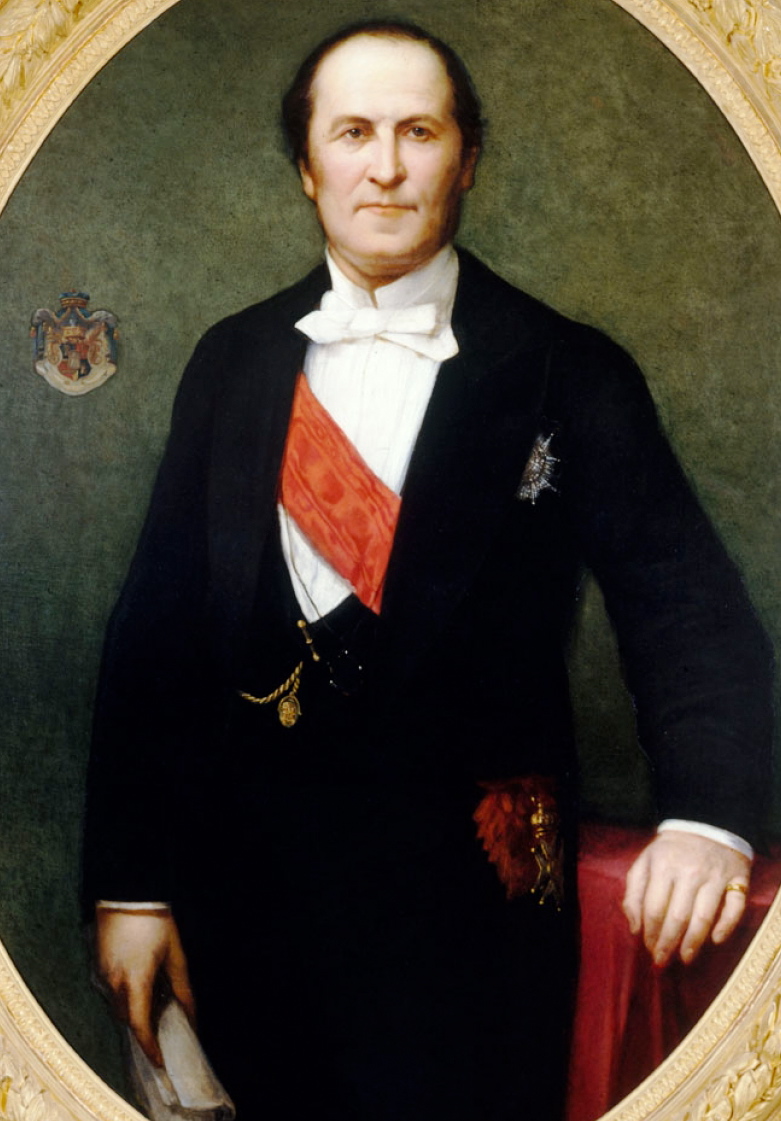
Henri Blondel
Jean Henry Blondel (20 January 1821 – 14 September 1897) was a prolific French architect. Among his works were the Passage du Bourg l'Abbé entrance on the Rue Palestro (1863), the La Belle Jardinière store on Rue du Pont-Neuf (1866-7), Hotel Continental at the corner of Rue de Castiglione and Rue de Rivoli (1876), the Bourse de commerce building (1885-9) and the Rue du Louvre building at 15 Rue du Louvre (1889). Biography Blondel was born in Rheims early in 1821, during the period of economic hardships that followed the Napoleonic Wars. He was a pupil at the School of Arts and Crafts (''École des arts et métiers'') as it was then known) in nearby Châlons-sur-Marne, before moving to Paris where he embarked on an apprenticeship under Auguste Caristie. He continued his training period, working for the architect François Rolland (1806-1888), and then went on to work for Henri Labrouste (1801-1875) before establishing his own architecture practice around 1855. Blon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reims
Reims ( , , ; also spelled Rheims in English) is the most populous city in the French department of Marne, and the 12th most populous city in France. The city lies northeast of Paris on the Vesle river, a tributary of the Aisne. Founded by the Gauls, Reims became a major city in the Roman Empire. Reims later played a prominent ceremonial role in French monarchical history as the traditional site of the coronation of the kings of France. The royal anointing was performed at the Cathedral of Reims, which housed the Holy Ampulla of chrism allegedly brought by a white dove at the baptism of Frankish king Clovis I in 496. For this reason, Reims is often referred to in French as ("the Coronation City"). Reims is recognized for the diversity of its heritage, ranging from Romanesque to Art-déco. Reims Cathedral, the adjacent Palace of Tau, and the Abbey of Saint-Remi were listed together as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1991 because of their outstanding Romanesque ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Châlons-en-Champagne
Châlons-en-Champagne () is a city in the Grand Est region of France. It is the capital of the department of Marne, despite being only a quarter the size of the city of Reims. Formerly called Châlons-sur-Marne, the city was officially renamed in 1998. It should not be confused with the Burgundian town of Chalon-sur-Saône. History Châlons is conjectured to be the site of several battles including the Battle of Châlons fought in 274 between Roman Emperor Aurelian and Emperor Tetricus I of the Gallic Empire. The Catalaunian Fields was the site of the battle of Châlons in 451 which turned back the westward advance of Attila. It is the setting of the last operetta of Johann Strauss II, '' Die Göttin der Vernunft (The Goddess of Reason)'', (1897) and is mentioned in, “It’s the Great Pumpkin, Charlie Brown,” as Snoopy’s crash site after doing battle with the Red Baron. Plan de la cathedrale Châlons-sur-Marne 1859 Archives nationales France.jpg, Châlons en Cham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crédit Foncier De France
Crédit Foncier de France (CFF) was a major French bank, active from 1852 to 2019 when its activities were entirely subsumed into Groupe BPCE, although the brand name appears to remain active. History The Crédit Foncier (English: landed credit) initially made loans to communes. The movement was initiated by Louis Wolowski and Count Xavier Branicki, and sanctioned by Emperor Napoléon III in 1852 in an attempt to modernize the medieval French banking system and expand French investment outside Europe. Its name became the “Banque Foncière of Paris.” Similar institutions at Nevers and Marseilles were amalgamated into one under the title of “Crédit Foncier de France.” The amount of the loan could not exceed half of the value of the property pledged or hypothecated, and that the repayment of the loan was by an annuity, which included the interest and part of the principal, terminable at a certain date. The Crédit Foncier had a monopoly on mortgages. In French banking te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Des Débats
The ''Journal des débats'' ( French for: Journal of Debates) was a French newspaper, published between 1789 and 1944 that changed title several times. Created shortly after the first meeting of the Estates-General of 1789, it was, after the outbreak of the French Revolution, the exact record of the debates of the National Assembly, under the title ''Journal des Débats et des Décrets'' ("Journal of Debates and Decrees"). Published weekly rather than daily, it was headed for nearly forty years by Bertin l'Aîné and was owned for a long time by the Bertin family. During the First Empire it was opposed to Napoleon and had a new title imposed on it, the ''Journal de l'Empire''. During the first Bourbon Restoration (1813–1814), the ''Journal'' took the title ''Journal des Débats Politiques et Littéraires'', and, under the second Restoration, it took a conservative rather than reactionary position. Under Charles X and his entourage, the ''Journal'' changed to a position s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
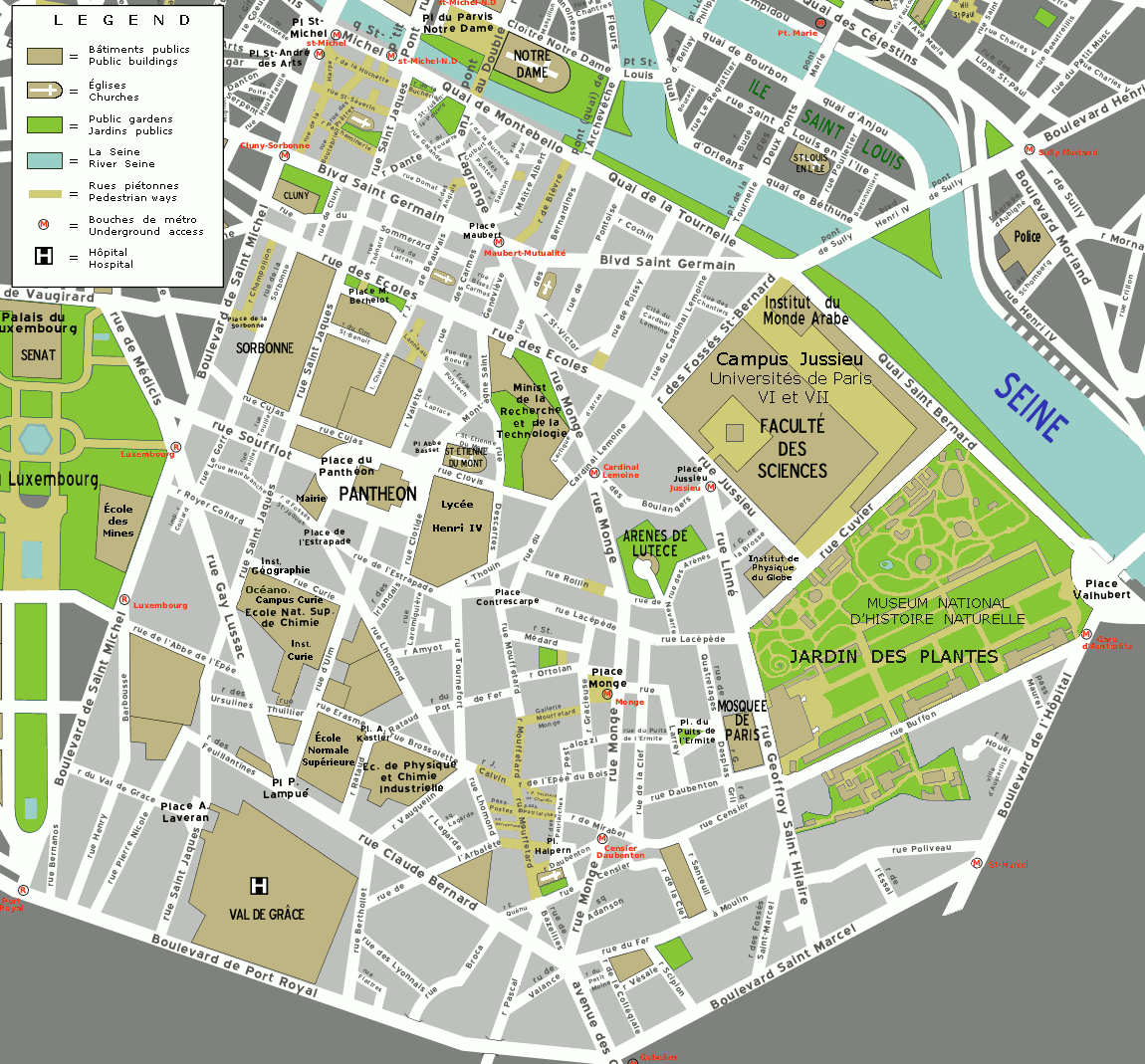
Boulevard Saint-Germain
Boulevard Saint-Germain () is a major street in Paris on the Rive Gauche of the Seine. It curves in a 3.5-kilometre (2.1 miles) arc from the Pont de Sully in the east (the bridge at the edge of Île Saint-Louis) to the Pont de la Concorde (the bridge to the Place de la Concorde) in the west and traverses the 5th, 6th and 7th arrondissements. At its midpoint, the boulevard is traversed by the north-south Boulevard Saint-Michel. The boulevard is most famous for crossing the Saint-Germain-des-Prés quarter from which it derives its name. History The Boulevard Saint-Germain was the most important part of Haussmann's renovation of Paris (1850s and '60s) on the Left Bank. The Boulevard replaced numerous small streets which approximated its path, including, from west to east (to the current boulevard Saint-Michel), the Rue Saint-Dominique, Rue Taranne, Rue Sainte-Marguerite, Rue des Boucheries and Rue des Cordeliers.''Saint-Germain-des-Prés et son faubourg'', Dominique Leborgne, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulevard Saint-Michel
Boulevard Saint-Michel () is one of the two major streets in the Latin Quarter of Paris, the other being Boulevard Saint-Germain. It is a tree-lined boulevard which runs south from the Pont Saint-Michel on the Seine and Place Saint-Michel, crosses Boulevard Saint-Germain and continues alongside the Sorbonne and the Jardin du Luxembourg, ending at the Place Camille Jullian just before the Port-Royal RER station and the Avenue de l'Observatoire. It was created by Baron Haussmann to run parallel to Rue Saint-Jacques which marks the historical north-south axis of Paris. It is known colloquially as ''Boul'Mich'' in French. The boulevard serves as a boundary between the 5th and 6th arrondissements of Paris; odd-numbered buildings on the eastern side are in the 5th arrondissement and even numbers on the western side are in the 6th. It has a length of 1,380 m (4,530 ft), an average width of 30 m (98 ft) and takes its name from the Pont Saint-Michel. As the centra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulevard De Sébastopol
The Boulevard de Sébastopol is an important roadway in Paris, France, which serves to delimit the 1st and 2nd arrondissements from the 3rd and 4th arrondissements of the city. The boulevard is 1.3 km in length, starting from the place du Châtelet and ends at the boulevard Saint-Denis, when it becomes the Boulevard de Strasbourg. The boulevard is a main thoroughfare, and consists of four vehicular lanes, one of which is reserved for buses. Although the road is line with some shops and restaurants, its importance is that of a thoroughfare running north–south in central Paris. It separates Le Marais from Les Halles. History The boulevard de Sébastopol is one of the most important roads opened up by the Baron Haussmann during his transformation of Paris in the 1850s. It was conceived as a major artery running a north–south axis across Paris, leading to the Gare de l'Est. The road was christened ''Boulevard du Centre'' when it was opened in 1854. Following N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second French Empire
The Second French Empire (; officially the French Empire, ), was the 18-year Imperial Bonapartist regime of Napoleon III from 14 January 1852 to 27 October 1870, between the Second and the Third Republic of France. Historians in the 1930s and 1940s often disparaged the Second Empire as a precursor of fascism. That interpretation is no longer widely held, and by the late 20th century they were giving it as an example of a modernising regime. Historians have generally given the Empire negative evaluations on its foreign policy, and somewhat more positive evaluations of domestic policies, especially after Napoleon III liberalised his rule after 1858. He promoted French business and exports. The greatest achievements included a grand railway network that facilitated commerce and tied the nation together with Paris as its hub. This stimulated economic growth and brought prosperity to most regions of the country. The Second Empire is given high credit for the rebuilding of Par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
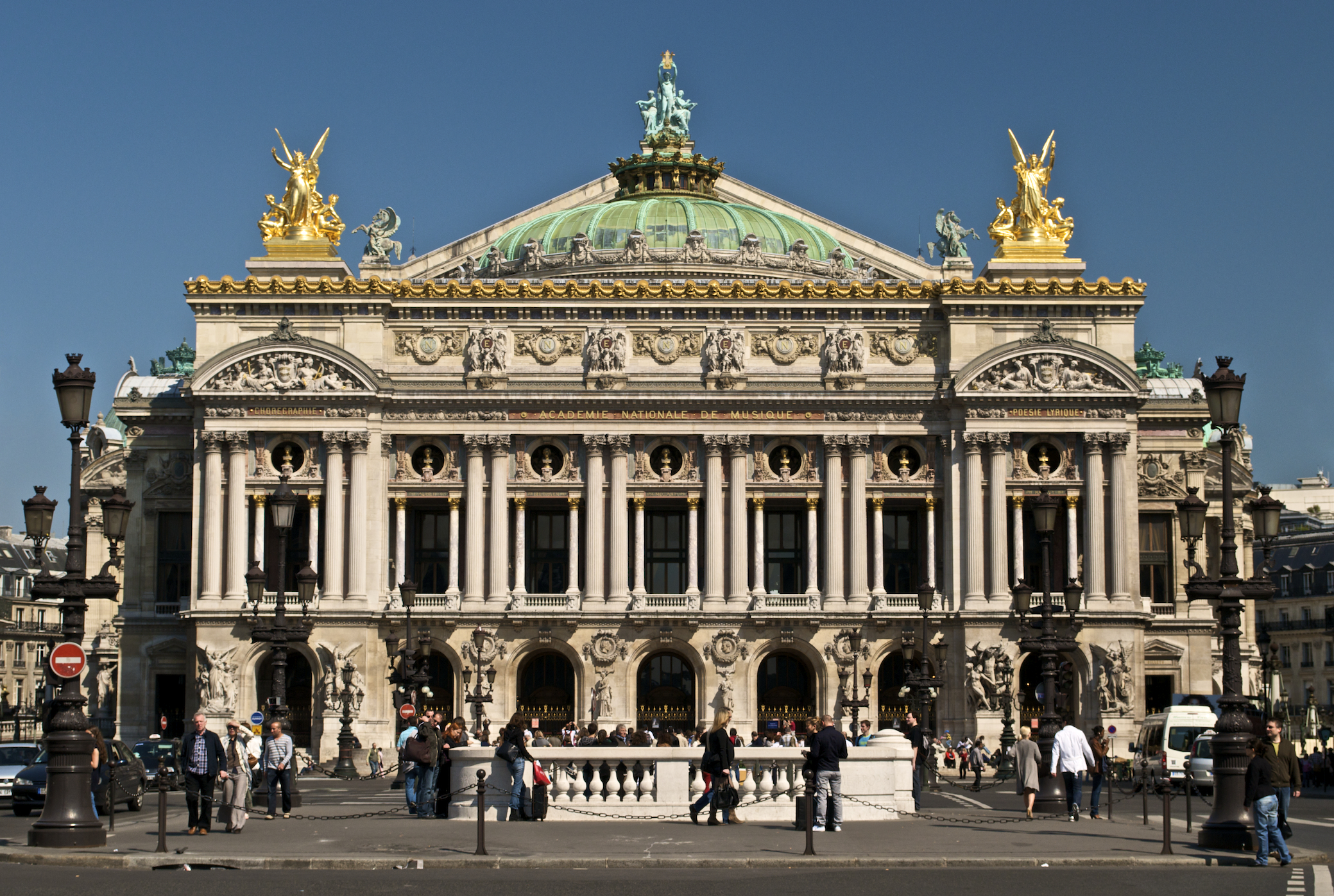
Second Empire Architecture
Second Empire style, also known as the Napoleon III style, is a highly eclectic style of architecture and decorative arts, which uses elements of many different historical styles, and also made innovative use of modern materials, such as iron frameworks and glass skylights. It flourished during the reign of Emperor Napoleon III in France (1852–1871) and had an important influence on architecture and decoration in the rest of Europe and North America. Major examples of the style include the Opéra Garnier (1862–1871) in Paris by Charles Garnier, the Bibliothèque nationale de France, the Church of Saint Augustine (1860–1871), and the Philadelphia City Hall (1871–1901). The architectural style was closely connected with Haussmann's renovation of Paris carried out during the Second Empire; the new buildings, such as the Opéra, were intended as the focal points of the new boulevards. Characteristics The Napoleon III or Second Empire style took its inspiration fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georges-Eugène Haussmann
Georges-Eugène Haussmann, commonly known as Baron Haussmann (; 27 March 180911 January 1891), was a French official who served as prefect of Seine (1853–1870), chosen by Emperor Napoleon III to carry out a massive urban renewal programme of new boulevards, parks and public works in Paris commonly referred to as Haussmann's renovation of Paris.http://www.culture.gouv.fr/documentation/joconde/fr/decouvrir/zoom/zoom-haussmann.htm - Joconde - visites guidées - zooms - baron Haussmann 2012-03-05 Critics forced his resignation for extravagance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon III
Napoleon III (Charles Louis Napoléon Bonaparte; 20 April 18089 January 1873) was the first President of France (as Louis-Napoléon Bonaparte) from 1848 to 1852 and the last monarch of France as Emperor of the French from 1852 to 1870. A nephew of Napoleon I, he was the last monarch to rule over France. Elected to the presidency of the Second Republic in 1848, he seized power by force in 1851, when he could not constitutionally be reelected; he later proclaimed himself Emperor of the French. He founded the Second Empire, reigning until the defeat of the French Army and his capture by Prussia and its allies at the Battle of Sedan in 1870. Napoleon III was a popular monarch who oversaw the modernization of the French economy and filled Paris with new boulevards and parks. He expanded the French overseas empire, made the French merchant navy the second largest in the world, and engaged in the Second Italian War of Independence as well as the disastrous Franco-Prussian War, dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |