|
Henipavirus Structure
''Henipavirus'' is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses in the family ''Paramyxoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales'' containing six established species, and numerous others still under study. Henipaviruses are naturally harboured by several species of small mammals, notably pteropid fruit bats (flying foxes), microbats of several species, and shrews. Henipaviruses are characterised by long genomes and a wide host range. Their recent emergence as zoonotic pathogens capable of causing illness and death in domestic animals and humans is a cause of concern. In 2009, RNA sequences of three novel viruses in phylogenetic relationship to known henipaviruses were detected in African straw-colored fruit bats (''Eidolon helvum'') in Ghana. The finding of these novel henipaviruses outside Australia and Asia indicates that the region of potential endemicity of henipaviruses may be worldwide. These African henipaviruses are slowly being characterised. ''Nipah'' and '' Hendra henipaviruses' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission Electron Micrograph
Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) is a microscopy technique in which a beam of electrons is transmitted through a specimen to form an image. The specimen is most often an ultrathin section less than 100 nm thick or a suspension on a grid. An image is formed from the interaction of the electrons with the sample as the beam is transmitted through the specimen. The image is then magnified and focused onto an imaging device, such as a fluorescent screen, a layer of photographic film, or a sensor such as a scintillator attached to a charge-coupled device. Transmission electron microscopes are capable of imaging at a significantly higher resolution than light microscopes, owing to the smaller de Broglie wavelength of electrons. This enables the instrument to capture fine detail—even as small as a single column of atoms, which is thousands of times smaller than a resolvable object seen in a light microscope. Transmission electron microscopy is a major analytical method i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoonosis
A zoonosis (; plural zoonoses) or zoonotic disease is an infectious disease of humans caused by a pathogen (an infectious agent, such as a bacterium, virus, parasite or prion) that has jumped from a non-human (usually a vertebrate) to a human. Typically, the first infected human transmits the infectious agent to at least one other human, who, in turn, infects others. Major modern diseases such as Ebola virus disease and salmonellosis are zoonoses. HIV was a zoonotic disease transmitted to humans in the early part of the 20th century, though it has now evolved into a separate human-only disease. Most strains of influenza that infect humans are human diseases, although many strains of bird flu and swine flu are zoonoses; these viruses occasionally recombine with human strains of the flu and can cause pandemics such as the 1918 Spanish flu or the 2009 swine flu. ''Taenia solium'' infection is one of the neglected tropical diseases with public health and veterinary concern in en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Polymerase
In molecular biology, RNA polymerase (abbreviated RNAP or RNApol), or more specifically DNA-directed/dependent RNA polymerase (DdRP), is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. Using the enzyme helicase, RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as a template for the synthesis of RNA, a process called transcription. A transcription factor and its associated transcription mediator complex must be attached to a DNA binding site called a promoter region before RNAP can initiate the DNA unwinding at that position. RNAP not only initiates RNA transcription, it also guides the nucleotides into position, facilitates attachment and elongation, has intrinsic proofreading and replacement capabilities, and termination recognition capability. In eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides. RNAP produces RNA that, functionally, is either for protein coding, i.e. messenger RNA (mRNA); or n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleocapsid
A capsid is the protein shell of a virus, enclosing its genetic material. It consists of several oligomeric (repeating) structural subunits made of protein called protomers. The observable 3-dimensional morphological subunits, which may or may not correspond to individual proteins, are called capsomeres. The proteins making up the capsid are called capsid proteins or viral coat proteins (VCP). The capsid and inner genome is called the nucleocapsid. Capsids are broadly classified according to their structure. The majority of the viruses have capsids with either helical or icosahedral structure. Some viruses, such as bacteriophages, have developed more complicated structures due to constraints of elasticity and electrostatics. The icosahedral shape, which has 20 equilateral triangular faces, approximates a sphere, while the helical shape resembles the shape of a spring, taking the space of a cylinder but not being a cylinder itself. The capsid faces may consist of one or more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matrix Protein
Viral matrix proteins are structural proteins linking the viral envelope with the virus core. They play a crucial role in virus assembly, and interact with the RNP complex as well as with the viral membrane. They are found in many enveloped viruses including paramyxoviruses, orthomyxoviruses, herpesviruses, retroviruses, filoviruses and other groups. An example is the M1 protein of the influenza virus, showing affinity to the glycoproteins inserted in the host cell membrane on one side and affinity for the RNP complex molecules on the other side, which allows formation at the membrane of a complex made of the viral ribonucleoprotein at the inner side indirectly connected to the viral glycoproteins protruding from the membrane. This assembly complex will now bud out of the cell as new mature viruses. Viral matrix proteins, like many other viral proteins, can exert different functions during the course of the infection. For example, in rhabdoviruses, binding of M proteins to nucle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipid
Lipids are a broad group of naturally-occurring molecules which includes fats, waxes, sterols, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglycerides, diglycerides, phospholipids, and others. The functions of lipids include storing energy, signaling, and acting as structural components of cell membranes. Lipids have applications in the cosmetic and food industries, and in nanotechnology. Lipids may be broadly defined as hydrophobic or amphiphilic small molecules; the amphiphilic nature of some lipids allows them to form structures such as vesicles, multilamellar/unilamellar liposomes, or membranes in an aqueous environment. Biological lipids originate entirely or in part from two distinct types of biochemical subunits or "building-blocks": ketoacyl and isoprene groups. Using this approach, lipids may be divided into eight categories: fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, sphingolipids, saccharolipids, and polyketides (derived from condensati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleomorphism (microbiology)
In microbiology, pleomorphism (from Ancient Greek , ''pléō'', "more", and , ''morphḗ'', form), also pleiomorphism, is the ability of some microorganisms to alter their morphology, biological functions or reproductive modes in response to environmental conditions. Pleomorphism has been observed in some members of the Deinococcaceae family of bacteria. The modern definition of pleomorphism in the context of bacteriology is based on ''variation'' of morphology or functional methods of the individual cell, rather than a heritable ''change'' of these characters as previously believed. Bacteria In the first decades of the 20th century, the term "pleomorphism" was used to refer to the idea that bacteria change morphology, biological systems, or reproductive methods dramatically according to environmental cues. This claim was controversial among microbiologists of the time, and split them into two schools: the monomorphists, who opposed the claim, and the pleomorphists such as Antoine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henipavirus Genome
''Henipavirus'' is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses in the family ''Paramyxoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales'' containing six established species, and numerous others still under study. Henipaviruses are naturally harboured by several species of small mammals, notably pteropid fruit bats (flying foxes), microbats of several species, and shrews. Henipaviruses are characterised by long genomes and a wide host range. Their recent emergence as zoonotic pathogens capable of causing illness and death in domestic animals and humans is a cause of concern. In 2009, RNA sequences of three novel viruses in phylogenetic relationship to known henipaviruses were detected in African straw-colored fruit bats (''Eidolon helvum'') in Ghana. The finding of these novel henipaviruses outside Australia and Asia indicates that the region of potential endemicity of henipaviruses may be worldwide. These African henipaviruses are slowly being characterised. ''Nipah'' and '' Hendra henipaviruses' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henipavirus Structure
''Henipavirus'' is a genus of negative-strand RNA viruses in the family ''Paramyxoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales'' containing six established species, and numerous others still under study. Henipaviruses are naturally harboured by several species of small mammals, notably pteropid fruit bats (flying foxes), microbats of several species, and shrews. Henipaviruses are characterised by long genomes and a wide host range. Their recent emergence as zoonotic pathogens capable of causing illness and death in domestic animals and humans is a cause of concern. In 2009, RNA sequences of three novel viruses in phylogenetic relationship to known henipaviruses were detected in African straw-colored fruit bats (''Eidolon helvum'') in Ghana. The finding of these novel henipaviruses outside Australia and Asia indicates that the region of potential endemicity of henipaviruses may be worldwide. These African henipaviruses are slowly being characterised. ''Nipah'' and '' Hendra henipaviruses' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Select Agent
Under United States law, Biological select agents or toxins (BSATs) — or simply select agents for short — are bio-agents which (since 1997) have been declared by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) or by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) to have the "potential to pose a severe threat to public health and safety". The agents are divided into (1) HHS select agents and toxins affecting humans; (2) USDA select agents and toxins affecting agriculture; and (3) overlap select agents and toxins affecting both. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) regulates the laboratories which may possess, use, or transfer select agents within the United States in its Select Agent Program (SAP) — also called the Federal Select Agent Program (FSAP) — since 2001. The SAP was established to satisfy requirements of the USA PATRIOT Act of 2001 and the Public Health Security and Bioterrorism Preparedness and Response Act of 2002, which were enacted in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
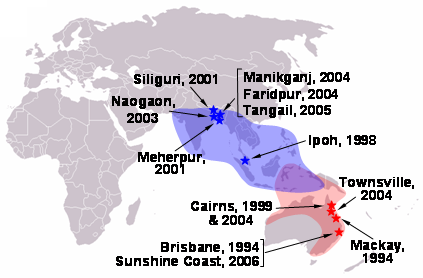
Hendra Virus
Hendra virus (HeV), scientific name ''Hendra henipavirus'', is a bat-borne virus that is associated with a highly fatal infection in horses and humans. Numerous disease outbreaks in Australia among horses have been caused by Hendra virus. The Hendra virus belongs to the genus ''Henipavirus'', which also contains the Nipah virus, which has also caused disease outbreaks. Pathology Flying foxes experimentally infected with the Hendra virus develop a viraemia and shed the virus in their urine, faeces and saliva for approximately one week. There is no other indication of an illness in them. Symptoms of Hendra virus infection of humans may be respiratory, including hemorrhage and edema of the lungs, or in some cases viral meningitis. In horses, infection usually causes one or more of pulmonary oedema, congestion and neurological signs. Ephrin B2 has been identified as the main receptor for the henipaviruses. Transmission Flying foxes have been identified as the reservoir host of Hend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nipah Virus
Nipah virus, scientific name ''Nipah henipavirus'', is a bat-borne virus that causes Nipah virus infection in humans and other animals, a disease with a high mortality rate. Numerous disease outbreaks caused by Nipah virus have occurred in South and Southeast Asia. Nipah virus belongs to the genus ''Henipavirus'' along with the Hendra virus, which has also caused disease outbreaks. Virology Like other henipaviruses, the Nipah virus genome is a single (nonsegmented) negative-sense, single-stranded RNA of over 18 kb, which is substantially longer than that of other paramyxoviruses. The enveloped virus particles are variable in shape, and can be filamentous or spherical; they contain a helical nucleocapsid. Six structural proteins are generated: N (nucleocapsid), P (phosphoprotein), M (matrix), F (fusion), G (glycoprotein) and L (RNA polymerase). The ''P'' open reading frame also encodes three nonstructural proteins, C, V and W. There are two envelope glycoproteins. The G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.gif)