|
Henderson Molybdenum Mine
The Henderson molybdenum mine is a large underground molybdenum mine west of the town of Empire, Colorado, Empire in Clear Creek County, Colorado, USA. The Henderson mine, which has produced molybdenum since 1976, is owned by Freeport-McMoRan. The Henderson mine is North America's largest producer of primary molybdenum. 2007 production was 40 million pounds of molybdenum, with a value of $1.1 billion. History The Henderson mine is near the Urad mine, which produced molybdenum from 1914 to the 1960s, before exhausting its orebody. Owner Climax Molybdenum Co. recognized the potential for deeper orebodies in the area, and discovered the Henderson deposit in 1964. The mine was named after mining engineer Robert Henderson. Production began in 1976; on Jan. 4, 2010, workers mined the billionth pound of molybdenum. In 2006, remaining ore reserves were estimated to be 500 million pounds of recoverable molybdenum. It was considered by the National Science Foundation as one of the tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrite
The mineral pyrite (), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Iron, FeSulfur, S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral. Pyrite's metallic Luster (mineralogy), luster and pale brass-yellow hue give it a superficial resemblance to gold, hence the well-known nickname of ''fool's gold''. The color has also led to the nicknames ''brass'', ''brazzle'', and ''Brazil'', primarily used to refer to pyrite found in coal. The name ''pyrite'' is derived from the Greek language, Greek (), 'stone or mineral which strikes fire', in turn from (), 'fire'. In ancient Roman times, this name was applied to several types of stone that would create sparks when struck against steel; Pliny the Elder described one of them as being brassy, almost certainly a reference to what we now call pyrite. By Georgius Agricola's time, , the term had become a generic term for all of the pyrite group, sulfide minerals. Pyrite is usua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Madison, Iowa
Fort Madison is a city and a county seat of Lee County, Iowa, United States along with Keokuk. Of Iowa's 99 counties, Lee County is the only one with two county seats. The population was 10,270 at the time of the 2020 census. Located along the Mississippi River in the state's southeast corner, it lies between small bluffs along one of the widest portions of the river. History Fort Madison was founded as the location of the first U.S. military fort in the upper Mississippi region. — A biographical sketch of the first settler and founder of the new Fort Madison A replica of the fort stands along the river.Old Fort Madison: Sheaffer Pens were developed and made in Fort Madison for many years. The city is the location of the Iowa State Penitentiary—the state's maximum security prison for men. Fort Madison is the Mississippi river crossing and station stop for Amtrak's ''Southwest Chief''. Fort Madison has the last remaining double swing-span bridge on the Mississippi Riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Froth Flotation
Froth flotation is a process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. This is used in mineral processing, paper recycling and waste-water treatment industries. Historically this was first used in the mining industry, where it was one of the great enabling technologies of the 20th century. It has been described as "the single most important operation used for the recovery and upgrading of Sulfide#Geology, sulfide ores". The development of froth flotation has improved the recovery of valuable minerals, such as copper- and lead-bearing minerals. Along with mechanized mining, it has allowed the economic recovery of valuable metals from much lower grade ore than previously. Industries Froth flotation is applied to a wide range of separations. An estimated 1B tons of materials are processed in this manner annually. Mineral processing Froth flotation is a process for separating minerals from gangue by exploiting differences in their hydrophobicity. Hydrophob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parshall, Colorado
Parshall is an unincorporated town, a post office, and a census-designated place (CDP) located in and governed by Grand County, Colorado, United States. The Parshall post office has the ZIP Code 80468. At the United States Census 2010, the population of the Parshall CDP was 47, while the population of the 80468 ZIP Code Tabulation Area was 391 including adjacent areas. Geography Parshall is located along the south side of U.S. Route 40 between Hot Sulphur Springs and Kremmling, on the north bank of the Colorado River downstream from Byers Canyon. The Parshall CDP has an area of , all land. Climate This climate type is dominated by the winter season, a long, bitterly cold period with short, clear days, relatively little precipitation mostly in the form of snow, and low humidity. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Parshall has a subarctic climate, abbreviated "Dfc" on climate maps. Demographics The United States Census Bureau initially defined the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Divide (Atlantic/Pacific)
The Continental Divide of the Americas (also known as the Great Divide, the Western Divide or simply the Continental Divide; ) is the principal, and largely mountainous, hydrological divide of the Americas. The Continental Divide extends from the Bering Strait to the Strait of Magellan, and separates the watersheds that drain into the Pacific Ocean from those river systems that drain into the Atlantic and (in northern North America) Arctic oceans (including those that drain into the Gulf of Mexico, the Caribbean Sea and Hudson Bay). Although there are many other hydrological divides in the Americas, the Continental Divide is by far the most prominent of these because it tends to follow a line of high peaks along the main ranges of the Rocky Mountains and Andes, at a generally much higher elevation than the other hydrological divisions. Geography Beginning at the westernmost point of the Americas’ mainland (Cape Prince of Wales, just south of the Arctic Circle), the Contine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
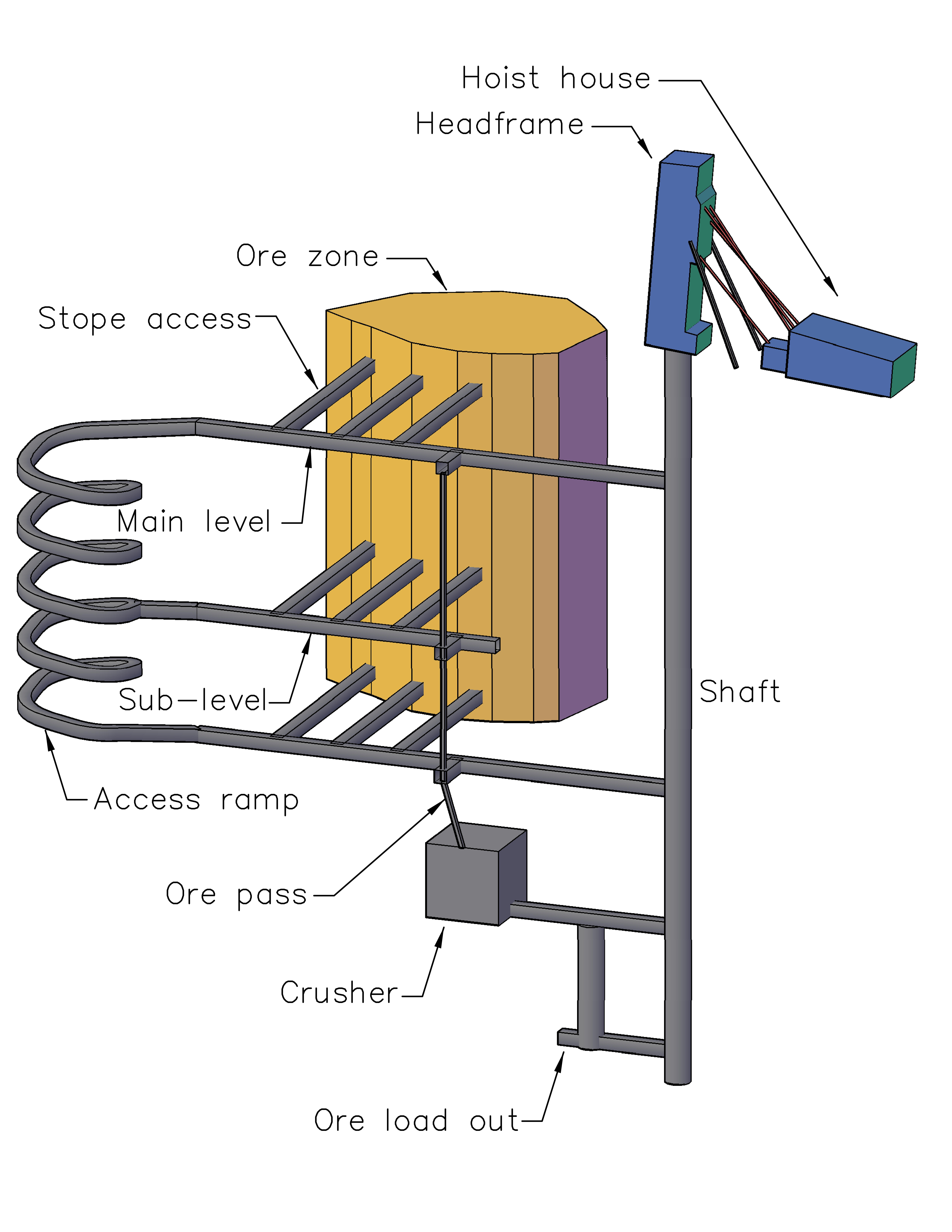
Glory Hole (mining)
Underground hard-rock mining refers to various underground mining techniques used to excavate "hard" minerals, usually those containing metals, such as ore containing gold, silver, iron, copper, zinc, nickel, tin, and lead. It also involves the same techniques used to excavate ores of gems, such as diamonds and rubies. Soft-rock mining refers to the excavation of softer minerals, such as salt, coal, and oil sands. Mine access Underground access Accessing underground ore can be achieved via a decline (ramp), inclined vertical shaft or adit. *Declines can be a spiral tunnel which circles either the flank of the deposit or circles around the deposit. The decline begins with a box cut, which is the portal to the surface. Depending on the amount of overburden and quality of bedrock, a galvanized steel culvert may be required for safety purposes. They may also be started into the wall of an open cut mine. *Shafts are vertical excavations sunk adjacent to an ore body. Shafts are sun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Block Caving
Underground hard-rock mining refers to various underground mining techniques used to excavate "hard" minerals, usually those containing metals, such as ore containing gold, silver, iron, copper, zinc, nickel, tin, and lead. It also involves the same techniques used to excavate ores of gems, such as diamonds and rubies. Soft-rock mining refers to the excavation of softer minerals, such as salt, coal, and oil sands. Mine access Underground access Accessing underground ore can be achieved via a decline (ramp), inclined vertical shaft or adit. *Declines can be a spiral tunnel which circles either the flank of the deposit or circles around the deposit. The decline begins with a box cut, which is the portal to the surface. Depending on the amount of overburden and quality of bedrock, a galvanized steel culvert may be required for safety purposes. They may also be started into the wall of an open cut mine. *Shafts are vertical excavations sunk adjacent to an ore body. Shafts are sun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durango, Colorado
Durango is a home rule municipality that is the county seat and the most populous municipality of La Plata County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 19,071 at the 2020 United States Census. Durango is the home of Fort Lewis College. History The town was organized from September 1880 to April 1881 by the Denver and Rio Grande Railroad (D&RG, later known as the Denver and Rio Grande Western railroad) as part of their efforts to reach Silverton, Colorado, and service the San Juan mining district, the goal of their "San Juan Extension" built from Alamosa Colorado. The D&RG chose a site in the Animas Valley close to the Animas River near what's now the Downtown Durango Historic Business District for its railroad facilities following a brief and most likely perfunctory negotiation with the other establishment in the area known as Animas City, two miles to the north. The city was named by ex-Colorado Governor Alexander C. Hunt, a friend of D&RG President William Jacks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulder, Colorado
Boulder is a home rule city that is the county seat and most populous municipality of Boulder County, Colorado, United States. The city population was 108,250 at the 2020 United States census, making it the 12th most populous city in Colorado. Boulder is the principal city of the Boulder, CO Metropolitan Statistical Area and an important part of the Front Range Urban Corridor. Boulder is located at the base of the foothills of the Rocky Mountains, at an elevation of above sea level. Boulder is northwest of the Colorado state capital of Denver. It is home of the main campus of the University of Colorado, the state's largest university. History On November 7, 1861, the Colorado General Assembly passed legislation to locate the University of Colorado in Boulder. On September 20, 1875, the first cornerstone was laid for the first building (Old Main) on the CU campus. The university officially opened on September 5, 1877. In 1907, Boulder adopted an anti- saloon ordinanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorado Mineral Belt
The Colorado Mineral Belt (CMB) is an area of ore deposits from the La Plata Mountains in Southwestern Colorado to near the middle of the state at Boulder, Colorado and from which over 25 million troy ounces (778 t) of gold were extracted beginning in 1858. The belt is a "northeast-striking zone defined by: a Proterozoic shear zone system (McCoy, 2001); a suite of Laramide-aged plutons and related ore deposits ( Tweto and Sims, 1963); a major gravity low (Isaacson and Smithson, 1976); low- crustal velocities; and high heat flow (Decker et al., 1988)." Mining districts includ *Central City-Idaho Springs district *Leadville mining district, named for Leadville, Colorado * Sneffels-Red Mountain-Telluride district The belt lies within a zone that has been geologically active at intervals beginning from near the time of crustal accretion in central Colorado at least 1.6 billion years ago until the present. Parts of the CMB follow shear zones of Precambrian age and the Paleozoic an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |