|
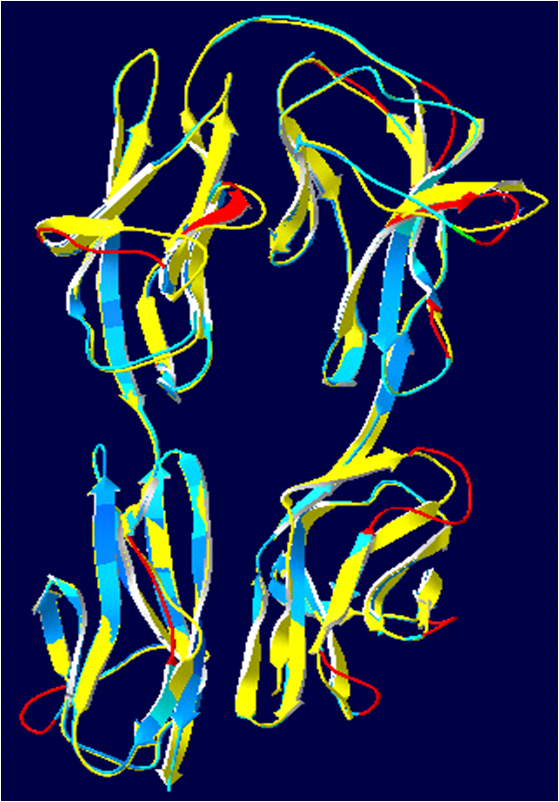
Hemolin And Neuroglian 3D
Hemolin is an immunoglobulin-like protein exclusively found in Lepidoptera (moths and butterflies). It was first discovered in immune-challenged pupae of ''Hyalophora cecropia'' and ''Manduca sexta''. Hemolin has a horseshoe crystal structure with four domains and resembles the developmental protein neuroglian. Hemolin increases 18-fold up to 7 mg/ml following injection of bacteria in ''H. cecropia''. Induction of Hemolin in moths after bacterial injection have been shown in several species including ''Antheraea pernyi'', ''Bombyx mori'', ''Helicoverpa zea'', ''Heliothis virescens'', ''Hyphantria cunea'', and ''Samia cynthia''. Hemolin has also been suggested to participate in the immune response to virus infection and shown to bind to virus particles. It is expressed in response to dsRNA in a dose-dependent manner. ''Galleria mellonella, Galleria melonella'' responds to caffeine intake by increased Hemolin protein expression. Hemolin is thought to be a gene duplication ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin
An antibody (Ab), also known as an immunoglobulin (Ig), is a large, Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen, called an antigen. Each tip of the "Y" of an antibody contains a paratope (analogous to a lock) that is specific for one particular epitope (analogous to a key) on an antigen, allowing these two structures to bind together with precision. Using this binding mechanism, an antibody can ''tag'' a microbe or an infected cell for attack by other parts of the immune system, or can neutralize it directly (for example, by blocking a part of a virus that is essential for its invasion). To allow the immune system to recognize millions of different antigens, the antigen-binding sites at both tips of the antibody come in an equally wide variety. In contrast, the remainder of the antibody is relatively constant. It only occurs in a few vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samia Cynthia
''Samia cynthia'', the ailanthus silkmoth, is a saturniid moth, used to produce silk fabric but not as domesticated as the silkworm, ''Bombyx mori''. The moth has very large wings of , with a quarter-moon shaped spot on both the upper and lower wings, whitish and yellow stripes and brown background. There are eyespots on the outer forewings. The species was first described by Dru Drury in 1773. Eri silk The common name, ailanthus silkmoth, refers to the host plant ''Ailanthus''. There is a subspecies, ''S. cynthia ricini'' in India and Thailand that feeds upon the leaves of castor bean, and is known for the production of eri silk, and is often referred to by the common name eri silkmoth. The eri silk worm is the only completely domesticated silkworm other than ''Bombyx mori''. The silk is extremely durable, but cannot be easily reeled off the cocoon and is thus spun like cotton or wool. Range Peigler & Naumann (2003),Peigler, R.S. & Naumann, S., 2003. ''A Revision of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innate Immune System
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the dominant immune system response found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms (see Beyond vertebrates).. The major functions of the innate immune system are to: * recruit immune cells to infection sites by producing chemical factors, including chemical mediators called cytokines * activate the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells * identify and remove foreign substances present in organs, tissues, blood and lymph, by specialized white blood cells * activate the adaptive immune system through antigen presentation * act as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents; via physical measures such as skin and chemical measures such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNAi
RNA interference (RNAi) is a biological process in which RNA molecules are involved in sequence-specific suppression of gene expression by double-stranded RNA, through translational or transcriptional repression. Historically, RNAi was known by other names, including ''co-suppression'', ''post-transcriptional gene silencing'' (PTGS), and ''quelling''. The detailed study of each of these seemingly different processes elucidated that the identity of these phenomena were all actually RNAi. Andrew Fire and Craig C. Mello shared the 2006 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their work on RNAi in the nematode worm ''Caenorhabditis elegans'', which they published in 1998. Since the discovery of RNAi and its regulatory potentials, it has become evident that RNAi has immense potential in suppression of desired genes. RNAi is now known as precise, efficient, stable and better than antisense therapy for gene suppression. Antisense RNA produced intracellularly by an expression vector ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymantria Dispar
''Lymantria dispar'', also known as the gypsy moth or the spongy moth, is a species of moth in the family Erebidae. ''Lymantria dispar'' is subdivided into several subspecies, with subspecies such as ''L. d. dispar'' and ''L. d. japonica'' being clearly identifiable without ambiguity. ''Lymantria dispar'' has been introduced to several continents and is now found in Europe, Africa, Asia, North America and South America. The polyphagous larvae live on a variety of deciduous and coniferous trees and can cause severe damage in years of mass reproduction. Due to these features, ''Lymantria dispar'' is listed among the world's 100 worst invasive alien species. Etymology The name “gypsy moth” does not have conclusive origins, however it has been in use since 1908. Moths of the subfamily Lymantriinae are commonly called tussock moths due to the tussock-like tufts of hair on the caterpillars.The Gypsy Moth: Research Toward Integrated Pest Management, United States Department of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
20-Hydroxyecdysone
20-Hydroxyecdysone (ecdysterone or 20E) is a naturally occurring ecdysteroid hormone which controls the ecdysis (moulting) and metamorphosis of arthropods. It is therefore one of the most common moulting hormones in insects, crabs, etc. It is also a phytoecdysteroid produced by various plants, including ''Cyanotis vaga'', ''Ajuga turkestanica'' and ''Rhaponticum carthamoides'' where its purpose is presumably to disrupt the development and reproduction of insect pests. In arthropods, 20-hydroxyecdysone acts through the ecdysone receptor. Although mammals lack this receptor, 20-hydroxyecdysone may affect mammalian (including human) biological systems ''in vitro'', but there is uncertainty whether any ''in vivo'' or physiological effects occur. 20-Hydroxyecdysone is an ingredient of some supplements that aim to enhance physical performance. In humans, it is hypothesized to bind to the estrogen receptor beta (ERβ) protein-coding gene. Sources in arthropods The primary sources of 20-h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pupa
A pupa ( la, pupa, "doll"; plural: ''pupae'') is the life stage of some insects undergoing transformation between immature and mature stages. Insects that go through a pupal stage are holometabolous: they go through four distinct stages in their life cycle, the stages thereof being egg, larva, pupa, and imago. The processes of entering and completing the pupal stage are controlled by the insect's hormones, especially juvenile hormone, prothoracicotropic hormone, and ecdysone. The act of becoming a pupa is called pupation, and the act of emerging from the pupal case is called eclosion or emergence. The pupae of different groups of insects have different names such as ''chrysalis'' for the pupae of butterflies and ''tumbler'' for those of the mosquito family. Pupae may further be enclosed in other structures such as cocoons, nests, or shells. Position in life cycle The pupal stage follows the larval stage and precedes adulthood (''imago'') in insects with complete metamorphosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine class. It is mainly used recreationally as a cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional performance. Caffeine acts by blocking binding of adenosine to the adenosine A1 receptor, which enhances release of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Caffeine has a three-dimensional structure similar to that of adenosine, which allows it to bind and block its receptors. Caffeine also increases cyclic AMP levels through nonselective inhibition of phosphodiesterase. Caffeine is a bitter, white crystalline purine, a methylxanthine alkaloid, and is chemically related to the adenine and guanine bases of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). It is found in the seeds, fruits, nuts, or leaves of a number of plants native to Africa, East Asia and South America, and helps to protect them against herbivores and from competition by preventing the germination of nearby seeds, as well as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galleria Mellonella
''Galleria mellonella'', the greater wax moth or honeycomb moth, is a moth of the family Pyralidae. ''G. mellonella'' is found throughout the world. It is one of two species of wax moths, with the other being the lesser wax moth. ''G. mellonella'' eggs are laid in the spring, and they have four life stages. Males are able to generate ultrasonic sound pulses, which, along with pheromones, are used in mating. The larvae of ''G. mellonella'' are also often used as a model organism in research. The greater wax moth is well known for its Parasitism, parasitization of honeybees and their hives. Because of the economic loss caused by this species, several control methods including heat treatment and chemical fumigants such as carbon dioxide have been used. The caterpillar of ''G. mellonella'' has attracted interest for its ability to degrade Polyethylene, polyethylene plastic. Geographic range ''G. mellonella'' was first reported as a pest in Asia, but then spread to northern Africa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DsRNA
Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and deoxyribonucleic acid ( DNA) are nucleic acids. Along with lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, nucleic acids constitute one of the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA, RNA is found in nature as a single strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (''mRNA'') to convey genetic information (using the nitrogenous bases of guanine, uracil, adenine, and cytosine, denoted by the letters G, U, A, and C) that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome. Some RNA molecules play an active role within cells by catalyzing biological reactions, controlling gene expression, or sensing and communicating responses to cellular signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyphantria Cunea
The fall webworm (''Hyphantria cunea'') is a moth in the family Erebidae known principally for its larval stage, which creates the characteristic webbed nests on the tree limbs of a wide variety of hardwoods in the late summer and fall. It is considered a pest but, does not harm otherwise healthy trees. It is well known to commercial tree services and arboriculturists. Description The adult fall webworm has a wingspan of approximately 30 mm and is generally white-colored, although some individuals may have dark-colored marks. Distribution The moth is native to North America, ranging from Canada to Mexico and has been introduced into other continents. Introduced to what was formerly Yugoslavia in the 1940s (firstly recorded in 1949), it now has occupied probably its entire range in Europe from France to the Caspian Sea in the east as well as penetrated into Central Asia: Turkmenistan (from 1990 to 1993), Uzbekistan (Fergana valley from 1996 to 1997), Kyrgyzstan, and sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lepidoptera
Lepidoptera ( ) is an order (biology), order of insects that includes butterfly, butterflies and moths (both are called lepidopterans). About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera are described, in 126 Family (biology), families and 46 Taxonomic rank, superfamilies, 10 percent of the total described species of living organisms. It is one of the most widespread and widely recognizable insect orders in the world. The Lepidoptera show many variations of the basic body structure that have evolved to gain advantages in lifestyle and distribution. Recent estimates suggest the order may have more species than earlier thought, and is among the four most wikt:speciose, speciose orders, along with the Hymenoptera, fly, Diptera, and beetle, Coleoptera. Lepidopteran species are characterized by more than three derived features. The most apparent is the presence of scale (anatomy), scales that cover the torso, bodies, wings, and a proboscis. The scales are modified, flattened "hairs", and give ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |