|
Hemigalinae
The Hemigalinae are a subfamily of the viverrids denominated and first described by John Edward Gray in 1864. Hemigalinae species are native to Southeast Asia from southern China through Indochina, Malay Peninsula to Sumatra, Borneo and Sulawesi. Characteristics The tails of Hemigalinae species are ringed. The toes and the middle of the lower part of the tarsus are bald. The frenum, upper part, and sides of the lower part are hairy. The orbit is imperfect. Hemigalinae resemble the Viverrinae in having the scent glands present in both sexes and wholly perineal, but differing by their simpler structure, consisting in the male of a shallower, smaller pouch, with less tumid lips, situated midway between the scrotum and the penis, but not extending to either. In the female, the scent glands consist of a pair of swellings, each with a slit-like orifice, situated one on each side of the vulva and a little behind it and on a common eminence, the perineal area behind this eminence being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viverridae
Viverridae is a family of small to medium-sized, feliform mammals. The viverrids () comprise 33 species placed in 14 genera. This family was named and first described by John Edward Gray in 1821. Viverrids occur all over Africa, southern Europe, and South and Southeast Asia, across the Wallace Line. Their occurrence in Sulawesi and in some of the adjoining islands shows them to be ancient inhabitants of the Old World tropics. Characteristics Viverrids have four or five toes on each foot and half-retractile claws. They have six incisors in each jaw and molars with two tubercular grinders behind in the upper jaw, and one in the lower jaw. The tongue is rough with sharp prickles. A pouch or gland occurs beneath the anus, but there is no cecum. Viverrids are the most primitive of all the families of feliform Carnivora and clearly less specialized than the Felidae. In external characteristics, they are distinguished from the Felidae by the longer muzzle and tuft of facial vibrissae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viverrinae
The Viverrinae represent the largest subfamily within the Viverridae comprising five genera, which are subdivided into 22 species native to Africa and Southeast Asia. This subfamily was denominated and first described by John Edward Gray in 1864.Gray, J. E. (1864)''A revision of the genera and species of viverrine animals (Viverridae), founded on the collection in the British Museum'' Proceedings of the Zoological Society of London for the year 1864: 502–579. Classification Gray defined the Viverrinae as comprising the genera ''Proteles'', ''Viverra'', ''Bassaris'' and '' Viverricula''. He subordinated the genera '' Genetta'' and ''Fossa'' to the Genettina, the genera ''Prionodon'' and ''Poiana'' to the Prionodontinae. Reginald Innes Pocock suggested that the African genets (''Genetta'') are also most nearly related to the Viverrinae, but should perhaps form a separate subfamily.Pocock, R. I. (1939)''The fauna of British India, including Ceylon and Burma. Mammalia. – Volum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
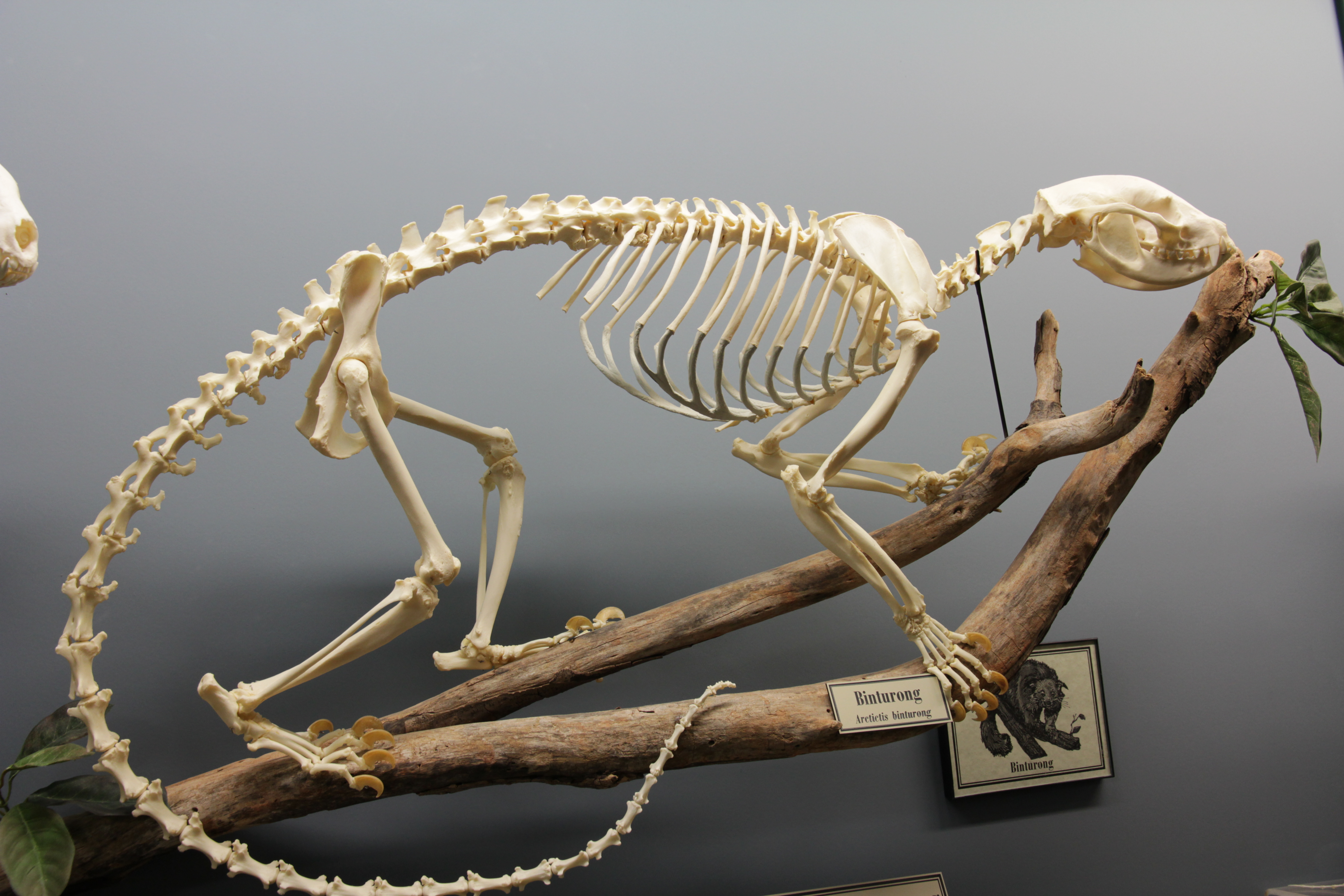
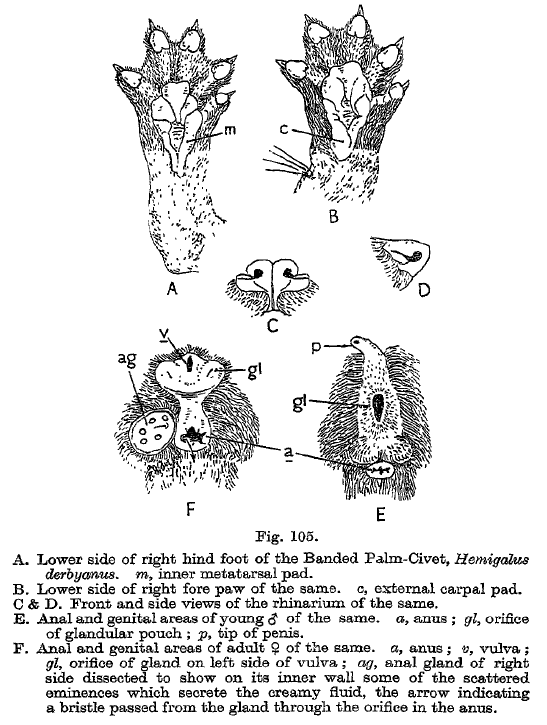
Banded Palm Civet
The banded palm civet (''Hemigalus derbyanus''), also called banded civet, is a viverrid native to Myanmar, Peninsular Malaysia, peninsular Thailand and the Sunda Islands of Sipura, Sumatra and Borneo. It is listed as Near Threatened on the IUCN Red List because of its large geographic and elevation range and tolerance to some habitat disturbance. ''Hemigalus'' is a monospecific genus that was first named and described by Claude Jourdan in 1837. Characteristics The banded palm civet has a long pointed face, reminiscent of insectivorous mammals. It has a long body set on short legs, and five toes on each foot with retractable claws. It looks very similar to Owston's palm civet (''Chrotogale owstoni''), except that it lacks spots on its body, and the hair on its neck points upwards instead of down along the neck. It is also similar to the rare Hose's palm civet (''Diplogale hosei''), an endemic of northern Borneo - they only differ in shape of muzzle and teeth and Hose's civet do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Claw
A claw is a curved, pointed appendage found at the end of a toe or finger in most amniotes (mammals, reptiles, birds). Some invertebrates such as beetles and spiders have somewhat similar fine, hooked structures at the end of the leg or tarsus for gripping a surface as they walk. The pincers of crabs, lobsters and scorpions, more formally known as their chelae, are sometimes called claws. A true claw is made of a hard protein called keratin. Claws are used to catch and hold prey in carnivorous mammals such as cats and dogs, but may also be used for such purposes as digging, climbing trees, self-defense and grooming, in those and other species. Similar appendages that are flat and do not come to a sharp point are called nails instead. Claw-like projections that do not form at the end of digits but spring from other parts of the foot are properly named spurs. Tetrapods In tetrapods, claws are made of keratin and consist of two layers. The unguis is the harder external layer, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hermann Schlegel
Hermann Schlegel (10 June 1804 – 17 January 1884) was a German ornithologist, herpetologist and ichthyologist. Early life and education Schlegel was born at Altenburg, the son of a brassfounder. His father collected butterflies, which stimulated Schlegel's interest in natural history. The discovery, by chance, of a buzzard's nest led him to the study of birds, and a meeting with Christian Ludwig Brehm. Schlegel started to work for his father, but soon tired of it. He travelled to Vienna in 1824, where, at the university, he attended the lectures of Leopold Fitzinger and Johann Jacob Heckel. A letter of introduction from Brehm to gained him a position at the Naturhistorisches Museum. Ornithological career One year after his arrival, the director of this natural history museum, Carl Franz Anton Ritter von Schreibers, recommended him to Coenraad Jacob Temminck, director of the natural history museum of Leiden, who was seeking an assistant. At first Schlegel worked mainly o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulawesi Palm Civet
The Sulawesi palm civet (''Macrogalidia musschenbroekii''), also known as Sulawesi civet, musang and brown palm civet is a little-known palm civet endemic to Sulawesi. It is listed as Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List due to population decline estimated to have been more than 30% over the last three generations (suspected to be 15 years) inferred from habitat destruction and degradation. ''Macrogalidia'' is a monospecific genus. It is the only carnivoran native to Sulawesi. Characteristics The Sulawesi civet has a light brownish-chestnut coloured soft and short coat with numerous light hairs intermixed. The underparts vary from fulvous to white; the breast is rufescent. There is a pair of indistinct longitudinal stripes and some faint spots on the hinder part of the back. The whiskers are mixed brown and white. The tail is marked with alternating rings of dark and pale brown, which are indistinct on the under surface, and disappear towards the dark tip. The length of head and bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Schwarz (zoologist)
Ernst Schwarz (1 December 1889 – 23 September 1962) was a German zoologist, mammalogist, and herpetologist. Schwarz was born in Frankfurt and studied zoology in Munich. He worked at the Museum of Natural History in Frankfurt and the Zoological Museum in Berlin. In 1929 he became professor of Zoology at the University of Greifswald. He worked at the Natural History Museum in London from 1933 to 1937, when he moved to the United States. He specialised in great ape species. He is often credited with having discovered the Bonobo in 1928. Schwarz also studied amphibians and reptiles, especially European and Mediterranean vipers The Viperidae (vipers) are a family of snakes found in most parts of the world, except for Antarctica, Australia, Hawaii, Madagascar, and various other isolated islands. They are venomous and have long (relative to non-vipers), hinged fangs tha ....Schwarz, Ernst. 1936. ''Untersuchungen über Systematik und Verbreitung der europäischen und mediterranen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
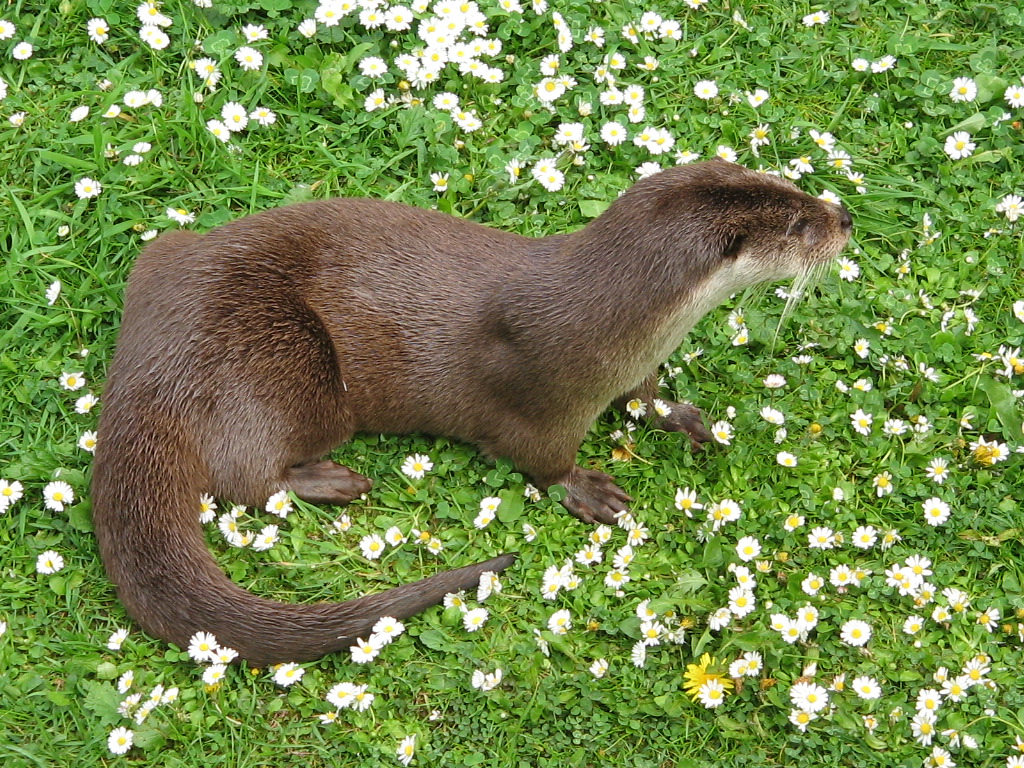
Otter Civet Area
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the Rank (zoology), subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic animal, aquatic, or Marine ecology, marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae Family (biology), family, which also includes weasels, badgers, mink, and wolverines, among other animals. Etymology The word ''otter'' derives from the Old English language, Old English word or . This, and cognate words in other Indo-European languages, ultimately stem from the Proto-Indo-European language root , which also gave rise to the English word "water". Terminology An otter's den is called a holt or couch. Male otters are called dogs or boars, females are called bitches or sows, and their offspring are called pups or cubs. The collective nouns for otters are bevy, family, lodge, romp (being descriptive of their often playful nature) or, when in water, raft. The feces of otters are typically identified by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
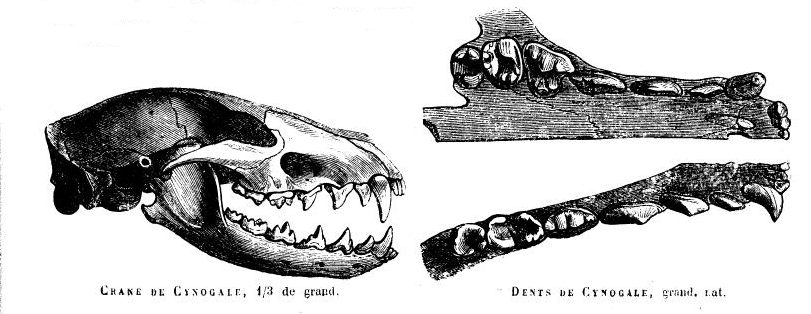
Otter Civet
The otter civet (''Cynogale bennettii'') is a semiaquatic viverrid native to Thailand, Malaysia, Indonesia and Brunei. It is listed as Endangered because of a serious ongoing population decline, estimated to be more than 50% over the past three generations (estimated to be 15 years), inferred from direct habitat destruction, and indirect inferred declines due to pollutants. ''Cynogale'' is a monospecific genus. Characteristics The otter civet possesses several adaptations to its habitat, including a broad mouth and webbed feet with naked soles and long claws. Its muzzle is long with numerous long whiskers. It is in many ways similar to the Hose's palm civet (''Diplogale hosei'') but has a shorter tail and no whitish underparts. Distribution and habitat Otter civets are distributed in Sumatra, Borneo and peninsular Thailand. Preferred habitat appears to be lowland primary forest, but they have also been recorded in secondary forest, bamboo and logged forest. The supposed ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |