|
Hellmuth Walter Kommanditgesellschaft
Hellmuth Walter Kommanditgesellschaft (HWK), Helmuth Walter Werke (HWM), or commonly known as the Walter-Werke, was a German company founded by Professor Hellmuth Walter to pursue his interest in engines using hydrogen peroxide as a fuel. Having experimented with torpedoes and submarines, Walter began to design rocket engines for aircraft and founded the HWK in Kiel in 1935. During World War II the HWK developed and built a variety of rocket engines for assisted take-off (RATO), and guided missiles, before developing main propulsion engines for rocket-powered interceptor aircraft, notably the Messerschmitt Me 163 ''Komet'' and the Bachem Ba 349 ''Natter''. HWM designed the steam catapult that launched the V-1 flying bomb. The steam was generated through the combination of T-Stoff and Z-Stoff. The company was wound up in 1945 and Walter subsequently continued his work in the United States. See also * C-Stoff – another chemical fuel developed by HWK * Walter HWK 109-500 – RA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hellmuth Walter
Hellmuth Walter (26 August 1900 – 16 December 1980) was a German engineer who pioneered research into rocket engines and gas turbines. His most noteworthy contributions were rocket motors for the Messerschmitt Me 163 and Bachem Ba 349 interceptor aircraft, so-called ''Starthilfe'' jettisonable rocket propulsion units used for a variety of Luftwaffe aircraft during World War II, and a revolutionary new propulsion system for submarines known as air-independent propulsion (AIP). Early life Walter began training as a machinist in 1917 in Hamburg and in 1921 commenced studies in mechanical engineering at the Technical University of Berlin. He left before completing these studies, however, in order to take up a position at the Stettiner Maschinenbau AG Vulcan, a major shipyard. Walter's experience with marine engines here led him to become interested in overcoming some of the limitations of the internal combustion engine. He reasoned that an engine powered by a fuel source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter HWK 109-500
The Walter HWK 109-500 was a liquid-fuelled rocket engine developed by Walter in Germany during the Second World War. Description The 109-500 is a self-contained, modular monopropellant ''Starthilfe'' (take-off assist) engine in a pod, able to produce thrust for thirty seconds. After the fuel was expended, the pod was jettisoned and it returned to earth by parachute, with the parachute packed externally, onto the blunt forward end of the pod. The T-Stoff monopropellant, stored in the large spherical tank within the ''Starthilfe'' module's forward end, needed to react with a catalyst to provide the boosting thrust for an aircraft on takeoff - this Z-Stoff sodium or calcium-based, alkaline permanganate-compound (in an aqueous solution) catalyst was provided in a small tank above the reaction chamber just forward of the exhaust nozzle, with compressed air from a network of five pressure tanks driving the monopropellant and catalyst together through the reaction chamber, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Meteorite
HMS ''Meteorite'' was an experimental U-boat developed in Germany, scuttled at the end of World War II, subsequently raised and commissioned into the Royal Navy. The submarine was originally commissioned into the '' Kriegsmarine'' on 13 March 1945 as ''U-1407''. She was built around a Walter engine fueled by high-test peroxide (HTP). History The three completed German Type XVIIB submarines were scuttled by their crews at the end of the Second World War, at Flensburg and and ''U-1407'' at Cuxhaven, all in the British Zone of Occupation. ''U-1406'' and ''U-1407'' were scuttled on 7 May 1945 by ''Oberleutnant zur See'' Gerhard Grumpelt even though a superior officer, ''Kapitän zur See'' Kurt Thoma, had prohibited such actions. Grumpelt was subsequently sentenced to seven years' imprisonment by a British military court. At the Potsdam Conference in July 1945 ''U-1406'' was allocated to the United States and ''U-1407'' to the United Kingdom, and both were soon salvaged. Roya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DFS 346
The DFS 346 (''Samolyot 346'') was a German rocket-powered swept-wing aircraft which began development during World War II in Germany. It was designed by Felix Kracht at the ''Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug'' (DFS), the "German Institute for Sailplane Flight". A prototype was constructed but did not reach completion before the end of the war. It was taken to the Soviet Union where it was completed, tested and flown (with indifferent success). Design The DFS-346 was a midwing design of all-metal construction. The front fuselage of the 346 was a body of rotation based on the NACA-Profile 0012-0,66-50. The middle part was approximately cylindrical and narrowed to the cut off to accommodate vertically arrayed nozzles in back. Probably for volume and weight reasons the DFS-346 was equipped with landing skids, both in the original German design and in the later Soviet prototypes; this caused trouble several times. The wings had a 45° swept NACA 0012-0,55-1,25 profile of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DFS 228
The DFS 228 was a rocket-powered, high-altitude reconnaissance aircraft designed by the ''Deutsche Forschungsanstalt für Segelflug'' (DFS - "German Research Institute for Sailplane Flight") during World War II. By the end of the war, the aircraft had only flown in the form of two unpowered prototypes. Design and development Initial design of the DFS 228 was undertaken before the outbreak of war as a research aircraft, the DFS 54, aimed at developing a high-altitude escape system for sailplanes. The project was suspended by the commencement of hostilities, but was revived in 1940 when the ''Reichsluftfahrtministerium'' (RLM - "Reich Aviation Ministry") delivered the DFS with a requirement for a rocket-powered reconnaissance aircraft. The advantages of a sailplane for aerial reconnaissance included its silence, its low speed relative to the ground (allowing for higher-quality photography), and its potential ability to loiter above an area of interest. The project gave the DFS th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
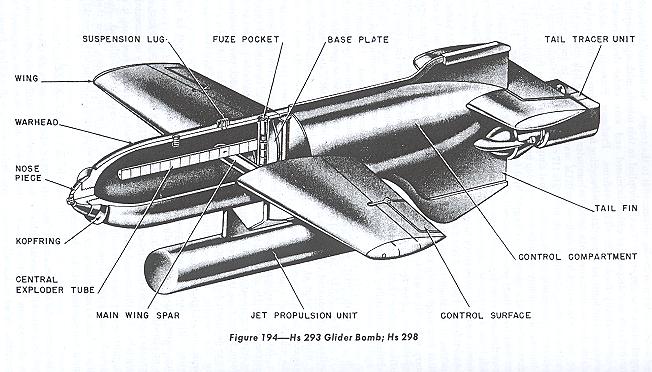
Henschel Hs 293
The Henschel Hs 293 was a World War II German radio-guided glide bomb. It is the first operational anti-shipping missile, first used unsuccessfully on 25 August 1943 and then with increasing success over the next year, ultimately damaging or sinking at least 25 ships. Allied efforts to jam the radio control link were increasingly successful despite German efforts to counter them. The weapon remained in use through 1944 when it was also used as an air-to-ground weapon to attack bridges to prevent the Allied breakout after D-Day, but proved almost useless in this role. Development The Hs 293 project was started in 1940, based on the "Gustav Schwartz Propellerwerke" pure glide bomb that was designed in 1939. The Schwartz design did not have a terminal guidance system; instead, it used an autopilot to maintain a straight course. It was intended to be launched from a bomber at sufficient distance to keep the aircraft out of range of anti-aircraft fire. A Henschel team, under Dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinkel He 176
The Heinkel He 176 was a German rocket-powered aircraft. It was the world's first aircraft to be propelled solely by a liquid-fueled rocket, making its first powered flight on 20 June 1939 with Erich Warsitz at the controls. It was a private venture by the Heinkel company in accordance with director Ernst Heinkel's emphasis on developing technology for high-speed flight. The performance of the He 176 was not spectacular, but it did provide "proof of concept" for rocket propulsion. All documents regarding the He 176 were destroyed during the war. The Warsitz biography suggests material is in the Soviet/Russian archives. The often quoted performance data of the aircraft, such as a speed reaching 750 km/h, or 800 km/h in Warsitz's biography, as well as some of the drawings, are not based on sound documents. Only two true pictures of the He 176 have survived which were probably taken in Peenemünde during tests.Volker Koos, ''Heinkel He 176 – Dichtung und Wahrheit,'' J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotha Go 242
The Gotha Go 242 was a transport glider used by the ''Luftwaffe The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German ''Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the ''Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabtei ...'' during World War II. It was an upgrade over the DFS 230 in both cargo/troop capacity and flight characteristics. It saw limited combat action. There were multiple variants. Development The Go 242 was designed by Albert Kalkert in response to a ''Reichsluftfahrtministerium'' (RLM) requirement for a heavy transport glider to replace the DFS 230 then in service. The requirement was for a glider capable of carrying 20 fully laden troops or the equivalent cargo. The aircraft was a high-wing monoplane with a simple square-section fuselage ending in clamshell doors used to load cargo. The empennage was mounted on twin booms linked by a tailplane. The fuselage was formed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walter HWK 109-509
The Walter HWK 109-509 was a German liquid-fuel bipropellant rocket engine that powered the Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet and Bachem Ba 349 aircraft. It was produced by Hellmuth Walter Kommanditgesellschaft (HWK) commencing in 1943, with licensed production by the Heinkel firm's facilities in Jenbach, Austria. Design and development Early versions of the Me 163 had been powered by an earlier design running on a "cold engine" fueled with Z-Stoff. This fuel tended to clog the jets in the combustion chamber, causing fluctuations in power and potentially explosions. Worse, however, was the fact that the engine could not be throttled, and when the aircraft leveled off after its climb to altitude it quickly accelerated to speeds that caused serious compressibility issues. The RLM demanded that a version be developed with a throttle. During this period Walter had also been working with a new fuel known as C-Stoff that gave off significant heat and was thus known as the "hot engine". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RATO
Rato is a village in the Cornillon commune in the Croix-des-Bouquets Arrondissement, Ouest department of Haiti Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and .... See also * Cornillon, for a list of other settlements in the commune. References Populated places in Ouest (department) {{Haiti-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-Stoff
C-Stoff (; "substance C") was a reductant used in bipropellant rocket fuels (as a fuel itself) developed by Hellmuth Walter Kommanditgesellschaft in Germany during World War II. It was developed for use with T-Stoff (a high-test peroxide) as an oxidizer, which together with C-Stoff as the fuel, forms a hypergolic mixture. The proportions of the components in C-Stoff were developed to catalyse the decomposition of T-Stoff, promote combustion with the oxygen released by the decomposition, and sustain uniform combustion through sufficient quantity of the highly reactive hydrazine. The combination of the C-Stoff, used as a rocket fuel, with the T-Stoff used as the oxidizer, often resulted in spontaneous explosion from their combined nature as a hypergolic fuel combination, necessitating strict hygiene in fueling operations; there were numerous catastrophic explosions of the Messerschmitt Me 163 aircraft that employed this fuel system. Another hazard was toxicity to humans of each o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-test Peroxide
High-test peroxide (HTP) is a highly concentrated (85 to 98%) solution of hydrogen peroxide, with the remainder consisting predominantly of water. In contact with a catalyst, it decomposes into a high-temperature mixture of steam and oxygen, with no remaining liquid water. It was used as a propellant of HTP rockets and torpedoes, and has been used for high-performance vernier engines. Properties Hydrogen peroxide works best as a propellant in extremely high concentrations (roughly over 70%). Although any concentration of peroxide will generate some hot gas (oxygen plus some steam), at concentrations above approximately 67%, the heat of decomposing hydrogen peroxide becomes large enough to completely vaporize all the liquid at standard pressure. This represents a safety and utilization turning point, since decomposition of any concentration above this amount is capable of transforming the liquid entirely to heated gas (the higher the concentration, the hotter the resulting gas). Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |