|
Helioscope (horse)
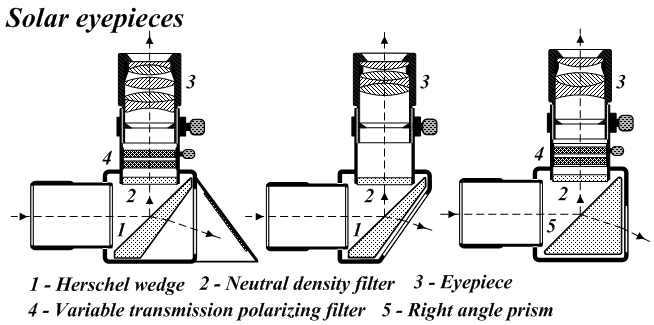
A helioscope is an instrument used in observing the Sun and sunspots. The helioscope was first used by Benedetto Castelli (1578-1643) and refined by Galileo Galilei (1564–1642). The method involves projecting an image of the sun onto a white sheet of paper suspended in a darkened room with the use of a telescope. The first ''machina helioscopica'' or helioscope was designed by Christoph Scheiner (1575 –1650) to assist his sunspot observations. (Latin) In the context of modern astroparticle physics, the term ''helioscope'' can also refer to an experiment that seeks to observe hypothetical particles (such as the axion) produced inside the sun. Examples of such helioscope experiments searching for axions include the CERN Axion Solar Telescope and International Axion Observatory. See also *Solar telescope * Heliometer * Spectroheliograph *Spectrohelioscope A spectrohelioscope is a type of solar telescope designed by George Ellery Hale in 1924 to allow the Sun to be viewed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunspot Instrument Of Christoph Scheiner (1573-1650)
Sunspots are phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as temporary spots that are darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. Sunspots appear within active regions, usually in pairs of opposite magnetic polarity. Their number varies according to the approximately 11-year solar cycle. Individual sunspots or groups of sunspots may last anywhere from a few days to a few months, but eventually decay. Sunspots expand and contract as they move across the surface of the Sun, with diameters ranging from to . Larger sunspots can be visible from Earth without the aid of a telescope. They may travel at relative speeds, or proper motions, of a few hundred meters per second when they first emerge. Indicating intense magnetic activity, sunspots accompany other active region phenomena such as coronal loops, prominences, and reconnection events. Most solar flares and coronal mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunspot
Sunspots are phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as temporary spots that are darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. Sunspots appear within active regions, usually in pairs of opposite magnetic polarity. Their number varies according to the approximately 11-year solar cycle. Individual sunspots or groups of sunspots may last anywhere from a few days to a few months, but eventually decay. Sunspots expand and contract as they move across the surface of the Sun, with diameters ranging from to . Larger sunspots can be visible from Earth without the aid of a telescope. They may travel at relative speeds, or proper motions, of a few hundred meters per second when they first emerge. Indicating intense magnetic activity, sunspots accompany other active region phenomena such as coronal loops, prominences, and reconnection events. Most solar flares and coronal mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benedetto Castelli
Benedetto Castelli (1578 – 9 April 1643), born Antonio Castelli, was an Italian mathematician. Benedetto was his name in religion on entering the Benedictine Order in 1595. Life Born in Brescia, Castelli studied at the University of Padua and later became an abbot at the Benedictine monastery in Monte Cassino. He was a long-time friend and supporter of his teacher, Galileo Galilei, and in turn teacher to Galileo's son. He assisted Galileo's study of sunspots and participated in the examination of the theories of Nicolaus Copernicus. Castelli was interested in mathematics and hydraulics. He was appointed as a mathematician to the University of Pisa, replacing Galileo, and later at the University of Rome La Sapienza. Castelli introduced Bonaventura Cavalieri to Galileo, leading to an extensive correspondence between the latter; Galileo was instrumental in procuring a position for Cavalieri at the University of Bologna in 1629. Castelli was involved in the discovery of the phase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was born in the city of Pisa, then part of the Duchy of Florence. Galileo has been called the "father" of observational astronomy, modern physics, the scientific method, and modern science. Galileo studied speed and velocity, gravity and free fall, the principle of relativity, inertia, projectile motion and also worked in applied science and technology, describing the properties of pendulums and "hydrostatic balances". He invented the thermoscope and various military compasses, and used the telescope for scientific observations of celestial objects. His contributions to observational astronomy include telescopic confirmation of the phases of Venus, observation of the four largest satellites of Jupiter, observation of Saturn's rings, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christoph Scheiner
Christoph Scheiner SJ (25 July 1573 (or 1575) – 18 June 1650) was a Jesuit priest, physicist and astronomer in Ingolstadt. Biography Augsburg/Dillingen: 1591–1605 Scheiner was born in Markt Wald near Mindelheim in Swabia, earlier markgravate Burgau, possession of the House of Habsburg. He attended the Jesuit St. Salvator Grammar School in Augsburg from May 1591 until 24 October 1595. He graduated as a "rhetor" and entered the Jesuit Order in Landsberg am Lech on 26 October 1595. At the local seminary, he served his biennial novitiate (1595–1597) under the tutelage of Novice Master Father Rupert Reindl SJ. From 1597 to 1598, he finished his lower studies of rhetoric in Augsburg. He took his first vows before Father Melchior Stör, SJ and received the minor orders from the Augsburg suffragan bishop Sebastian Breuning. He spent the years 1598–1601 in Ingolstadt studying philosophy (metaphysics and mathematics). In 1603, Scheiner invented the pantograph, "Lake Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sunspot
Sunspots are phenomena on the Sun's photosphere that appear as temporary spots that are darker than the surrounding areas. They are regions of reduced surface temperature caused by concentrations of magnetic flux that inhibit convection. Sunspots appear within active regions, usually in pairs of opposite magnetic polarity. Their number varies according to the approximately 11-year solar cycle. Individual sunspots or groups of sunspots may last anywhere from a few days to a few months, but eventually decay. Sunspots expand and contract as they move across the surface of the Sun, with diameters ranging from to . Larger sunspots can be visible from Earth without the aid of a telescope. They may travel at relative speeds, or proper motions, of a few hundred meters per second when they first emerge. Indicating intense magnetic activity, sunspots accompany other active region phenomena such as coronal loops, prominences, and reconnection events. Most solar flares and coronal mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axion
An axion () is a hypothetical elementary particle postulated by the Peccei–Quinn theory in 1977 to resolve the strong CP problem in quantum chromodynamics (QCD). If axions exist and have low mass within a specific range, they are of interest as a possible component of cold dark matter. History Strong CP problem As shown by Gerard 't Hooft, strong interactions of the standard model, QCD, possess a non-trivial vacuum structure that in principle permits violation of the combined symmetries of charge conjugation and parity, collectively known as CP. Together with effects generated by weak interactions, the effective periodic strong CP-violating term, , appears as a Standard Model input – its value is not predicted by the theory, but must be measured. However, large CP-violating interactions originating from QCD would induce a large electric dipole moment (EDM) for the neutron. Experimental constraints on the currently unobserved EDM implies CP violation from QCD must be e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CERN Axion Solar Telescope
The CERN Axion Solar Telescope (CAST) is an experiment in astroparticle physics to search for axions originating from the Sun. The experiment, sited at CERN in Switzerland, was commissioned in 1999 and came online in 2002 with the first data-taking run starting in May 2003. The successful detection of solar axions would constitute a major discovery in particle physics, and would also open up a brand new window on the astrophysics of the solar core. CAST is currently the most sensitive axion helioscope. Theory and operation If the axions exist, they may be produced in the Sun's core when X-rays scatter off electrons and protons in the presence of strong electric fields. The experimental setup is built around a 9.26 m long decommissioned test magnet for the LHC capable of producing a field of up to . This strong magnetic field is expected to convert solar axions back into X-rays for subsequent detection by X-ray detectors. The telescope observes the Sun for about 1.5&nb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Axion Observatory
The International Axion Observatory (IAXO) is a next-generation axion helioscope for the search of solar axions and axion-like particles. It is the follow-up of the CERN Axion Solar Telescope (CAST), which has been operating since 2003. The IAXO will be set up by implementing the helioscope concept used in the CAST experiment to its largest possible size. The Letter of Intent for International Axion Observatory was submitted to the CERN SPS committee in August 2013. IAXO formally founded in July 2017 and received an advanced grant from the European Research Council in October 2018. The near-term goal of the collaboration is to build a scaled-down prototype version of the experiment, called Baby-IAXO, which is under discussion for a possible location at DESY, Germany. Baby IAXO Baby IAXO is a prototype, scaled-down version of all the subsystems of the IAXO. The prototype is a testing version and will serve as an intermediate step to explore further possible improvements to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Telescope
A solar telescope is a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph. Professional solar telescopes Solar telescopes need optics large enough to achieve the best possible diffraction limit but less so for the associated light-collecting power of other astronomical telescopes. However, recently newer narrower filters and higher framerates have also driven solar telescopes towards photon-starved operations. Both the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope as well as the proposed European Solar Telescope (EST) have larger apertures not only to increase the resolution, but also to increase the light-collecting power. Because solar telescopes operate during the day, seeing is generally worse than for night-time telescopes, because the ground around the telescope is heated which causes turbulence and degrades the res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliometer
A heliometer (from Greek ἥλιος ''hḗlios'' "sun" and ''measure'') is an instrument originally designed for measuring the variation of the sun's diameter at different seasons of the year, but applied now to the modern form of the instrument which is capable of much wider use. The basic concept is to introduce a split element into a telescope's optical path so as to produce a double image. If one element is moved using a screw micrometer, precise angle measurements can be made. The simplest arrangement is to split the object lens in half, with one half fixed and the other attached to the micrometer screw and slid along the cut diameter. To measure the diameter of the sun, for example, the micrometer is first adjusted so that the two images of the solar disk coincide (the "zero" position where the split elements form essentially a single element). The micrometer is then adjusted so that diametrically opposite sides of the two images of the solar disk just touch each other. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroheliograph
The spectroheliograph is an instrument used in astronomy which captures a photographic image of the Sun at a single wavelength of light, a monochromatic image. The wavelength is usually chosen to coincide with a spectral wavelength of one of the chemical elements present in the Sun. It was developed independently by George Ellery Hale and Henri-Alexandre Deslandres in the 1890s and further refined in 1932 by Robert R. McMath to take motion pictures. The instrument comprises a prism or diffraction grating and a narrow slit that passes a single wavelength (a monochromator). The light is focused onto a photographic medium and the slit is moved across the disk of the Sun to form a complete image. It is now possible to make a filter that transmits a narrow band of wavelengths which produces a similar image, but spectroheliographs remain in use. See also * Spectrohelioscope * Helioscope * Heliometer A heliometer (from Greek ἥλιος ''hḗlios'' "sun" and ''measure'') is an in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_2007-04-30_T001456.gif)