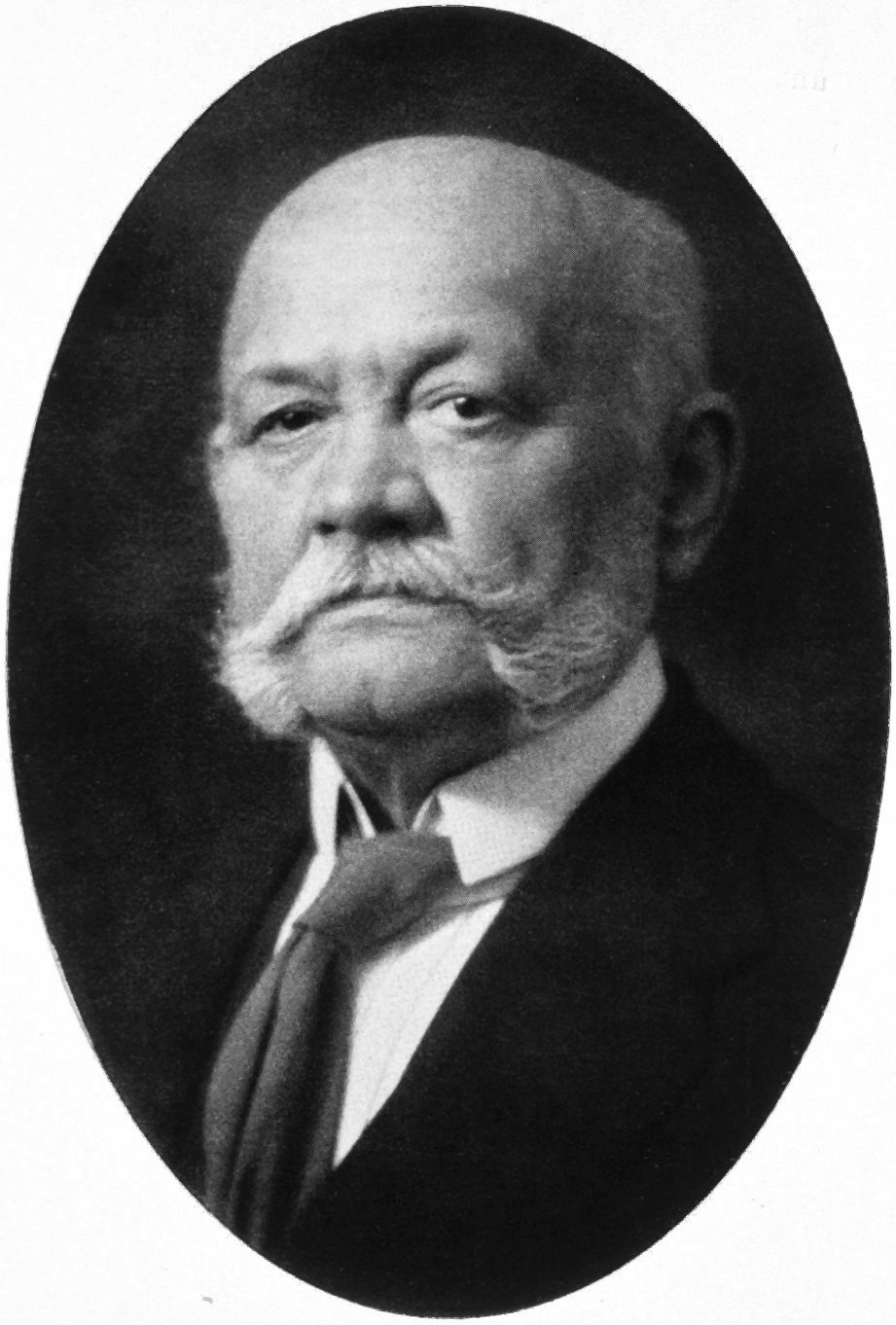|
Heinrich Theodor Höch
Heinrich Theodor Höch was a German businessman. Höch grew up in Ludwigshafen, then part of the Kingdom of Bavaria. In 1864, at the age of 19, Höch began his first venture which was to export Palatine tobacco to the Union during the American Civil War. When the war ended, Höch filed for bankruptcy. He continued to trade goods and acted as a broker. Höch entered the rail industry in the 1860s as a co-accordant in the construction of the Munich–Rosenheim railway line. Höch's businesses were successful in this era. In 1866, he moved to Munich where he dedicated himself to general trade and finance, from suspenders and walking sticks to investments in real estate business. Early life Höch grew up in Ludwigshafen, then part of the Kingdom of Bavaria. His father, Gottfried Höch, was the éminence grise in the founding of the community of Ludwigshafen and the economist show managed the estates of Stéphanie de Beauharnais. Business career Maxvorstadt Höch's understood t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackets
A bracket is either of two tall fore- or back-facing punctuation marks commonly used to isolate a segment of text or data from its surroundings. They come in four main pairs of shapes, as given in the box to the right, which also gives their names, that vary between British English, British and American English. "Brackets", without further qualification, are in British English the ... marks and in American English the ... marks. Other symbols are repurposed as brackets in specialist contexts, such as International Phonetic Alphabet#Brackets and transcription delimiters, those used by linguists. Brackets are typically deployed in symmetric pairs, and an individual bracket may be identified as a "left" or "right" bracket or, alternatively, an "opening bracket" or "closing bracket", respectively, depending on the Writing system#Directionality, directionality of the context. In casual writing and in technical fields such as computing or linguistic analysis of grammar, brackets ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
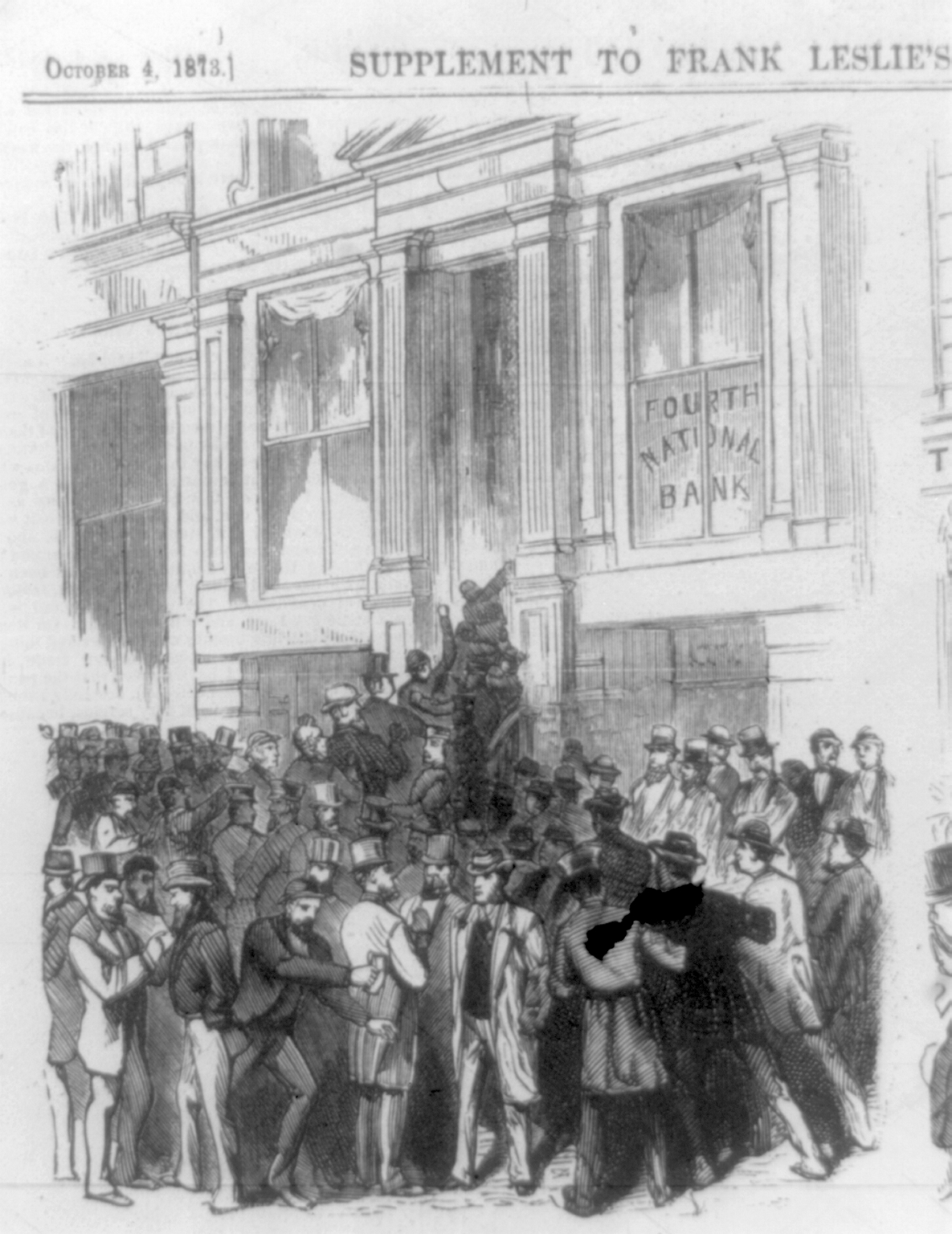
Panic Of 1873
The Panic of 1873 was a financial crisis that triggered an economic depression in Europe and North America that lasted from 1873 to 1877 or 1879 in France and in Britain. In Britain, the Panic started two decades of stagnation known as the "Long Depression" that weakened the country's economic leadership. In the United States, the Panic was known as the "Great Depression" until the events of 1929 and the early 1930s set a new standard. The Panic of 1873 and the subsequent depression had several underlying causes for which economic historians debate the relative importance. American inflation, rampant speculative investments (overwhelmingly in railroads), the demonetization of silver in Germany and the United States, ripples from economic dislocation in Europe resulting from the Franco-Prussian War (1870–1871), and major property losses in the Great Chicago Fire (1871) and the Great Boston Fire (1872) helped to place massive strain on bank reserves, which, in New York ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sendling
Sendling is a borough of Munich. It is located south-west of the city centre and spans the city boroughs Sendling and Sendling-Westpark. Sendling is subdivided into Obersendling, Mittersendling, and Untersendling. Untersendling and Mittersendling are located in the borough of Sendling, and Obersendling is located in the borough of Thalkirchen-Obersendling-Forstenried-Fürstenried-Solln. Overview Sendling is mainly a residential quarter, with shops and businesses straddling the ''Plinganserstraße'' around the historical core of Sendling. It is a multicultural quarter, with one of the largest rates of foreigners among the population. The proposed site for the new mosque in Sendling is located at ''Gotzinger Platz'', opposite ''St. Korbinian'' Church. Supposedly, this neighborhood boasts the best falafels in town, located in the Valleystrasse. ''Harras'', an urban square near the historical centre of Sendling, is the busiest square of the borough. A number of shops and busines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heilmann & Littmann
Heilmann & Littmann was a leading German contracting business. It was founded in 1871 by Jakob Heilmann (1846-1927) in Regensburg as "Baugeschäft J. Heilmann" (J. Heilmann building company), and, by 1876, specialized on railway construction, later on in building construction. In 1892, the architect Max Littmann (1862-1931), Heilmann's son-in-law, joined the company, thus forming an ordinary partnership ("Offene Handelsgesellschaft Heilmann & Littmann"). In 1897, Richard Reverdy became another partner and managing director, and the company was transformed into a limited liability company, specialising on the construction of theaters and other monumental structure, e.g. the present-day Munich Hofbräuhaus was erected during the years 1896 and 1897 by Heilmann & Littmann. After Jakob Heilmann's death in 1927, the construction businesses in Munich, Nuremberg and Berlin were taken over by the ''Heilmann'sche Immobilien-Gesellschaft AG'', creating the Heilmann & Littmann Bau-AG. Af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nymphenburg
The Nymphenburg Palace (, Palace of the Nymphs) is a Baroque palace situated in Munich's western district Neuhausen-Nymphenburg, in Bavaria, southern Germany. The Nymphenburg served as the main summer residence for the former rulers of Bavaria of the House of Wittelsbach. Combined with the adjacent Nymphenburg Palace Park it constitutes one of the premier royal palaces of Europe. Its frontal width of (north–south axis) even surpasses Versailles. History Building history The palace was commissioned by the electoral couple Ferdinand Maria and Henriette Adelaide of Savoy to the designs of the Italian architect Agostino Barelli in 1664 after the birth of their son Maximilian II Emanuel. During its construction Barelli was again replaced (1674) by Enrico Zuccalli. The concept for the mythological decorative programme was supplied by the scholar Emanuele Tesauro of Turin; the ceiling paintings were by Antonio Triva and Antonio Zanchi. The central pavilion was completed i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septic Drain Field
Septic drain fields, also called leach fields or leach drains, are subsurface wastewater disposal facilities used to remove contaminants and impurities from the liquid that emerges after anaerobic digestion in a septic tank. Organic materials in the liquid are catabolized by a microbial ecosystem. A septic drain field, a septic tank, and associated piping compose a septic system. The drain field typically consists of an arrangement of trenches containing perforated pipes and porous material (often gravel) covered by a layer of soil to prevent animals (and surface runoff) from reaching the wastewater distributed within those trenches. Primary design considerations are both ''hydraulic'' for the volume of wastewater requiring disposal and ''catabolic'' for the long-term biochemical oxygen demand of that wastewater. The land area that is set aside for the septic drain field may be called a septic reserve area (SRA). Sewage farms similarly dispose of wastewater through a series ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainer Maria Rilke
René Karl Wilhelm Johann Josef Maria Rilke (4 December 1875 – 29 December 1926), known as Rainer Maria Rilke, was an Austrian poet and novelist. Acclaimed as an Idiosyncrasy, idiosyncratic and expressive poet, he is widely recognized as a significant writer in the German language.Biography: Rainer Maria Rilke 1875–1926 Poetry Foundation website. Retrieved 2 February 2013. His work is viewed by critics and scholars as possessing undertones of mysticism, exploring themes of Subjectivity, subjective experience and disbelief. His writings include one novel, several collections of poetry, several volumes of correspondence and a few early novellas. Rilke traveled extensively throughout Europe, finally settling in Switzerland, which provided the inspiration for many of his poems. While Rilke is best ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Koch
Heinrich Hermann Robert Koch ( ; ; 11 December 1843 – 27 May 1910) was a German physician and microbiologist. As the discoverer of the specific causative agents of deadly infectious diseases including tuberculosis, cholera and anthrax, he is regarded as one of the main founders of modern bacteriology. As such he is popularly nicknamed the father of microbiology (with Louis Pasteur), and as the father of medical bacteriology. His discovery of the anthrax bacterium ('' Bacillus anthracis'') in 1876 is considered as the birth of modern bacteriology. Koch used his discoveries to establish that germs "could cause a specific disease" and directly provided proofs for the germ theory of diseases, therefore creating the scientific basis of public health, saving millions of lives. For his life's work Koch is seen as one of the founders of modern medicine. While working as a private physician, Koch developed many innovative techniques in microbiology. He was the first to use the oil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB), also known colloquially as the "white death", or historically as consumption, is a contagious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as inactive or latent tuberculosis. A small proportion of latent infections progress to active disease that, if left untreated, can be fatal. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with latent TB do not spread the disease. A latent infection is more likely to become active in those with weakened I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Von Soxhlet
Franz Ritter von Soxhlet (12 January 1848 – 5 May 1926) was a German agricultural chemist and inventor. Biography Franz von Soxhlet was born on 12 January 1848 in Brno, Moravia, Austrian Empire and migrated with his family to the German Confederation. He was the son of spinning industrialist Hubert Soxhlet, an immigrant from Dalhem near Liège (in the former Duchy of Brabant). He gained a PhD at Leipzig in 1872 with the dissertation ''Zur physiologischen Chemie der Milch''. In 1879, he became a professor of agricultural chemistry at the Technical University of Munich. He invented the Soxhlet extractor in 1879 and in 1886 he proposed pasteurization be applied to milk and other beverages in order to prevent disease and spoilage. Soxhlet is also known as the first scientist who fractionated the milk proteins in casein, albumin, globulin and lactoprotein. Furthermore, he described for the first time the sugar present in milk, lactose. The Soxhlet solution is an alternative t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombing Of Munich In World War II
The Bombing of Munich took place mainly in the later stages of World War II. Munich was, and is, a significant German city, as much culturally as industrially. Augsburg, to the west, was a main center of diesel engine production (and still is today), and was also heavily bombed during the war. Although some considerable distance from the United Kingdom, Munich is not a difficult city to find from the air due to both its size and proximity to the Austrian Alps to the south-east, which was used as a visual reference point. Munich was protected initially by its distance from the United Kingdom. After a small air raid in November 1940 the city got little attention from bombers until 1944. Munich was bombed by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and the United States Army Air Forces (USAAF). There were 74 air raids on Munich, with 6,632 people killed and 15,800 wounded. Around 90% of the old part of the city () was severely damaged due to the policy of carpet bombing (). Munich was conside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goetheplatz (Munich U-Bahn)
Goetheplatz is a U-Bahn station in Munich, Germany, in operation since 19 October 1971. It is used by the U3 and U6 lines, for which it originally was the southern terminus. History The tunnel from Sendlinger Tor to Goetheplatz (including the station) was completed between 1938 and 1941. It was originally part of a planned North-South S-Bahn line. However, construction was delayed due to World War II, that led to the tunnel being used as a bomb-shelter. This structural work was used later in the construction of the U-Bahn network.Schütz, Floria"Vorkriegstunnel Am Goetheplatz" 12 June 2007. Retrieved in January 2014. The station has an unusual length of and is longer than any other U-Bahn station. It is also one of the stations on Munich's U-Bahn network where classical music is played all day via loudspeakers. The largest part of the station lies below Lindwurmstraße and only the northern end is beneath Goetheplatz. At both ends, an intermediate floor can be reached by escala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |