|
Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory
Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory (german: Landessternwarte Heidelberg-Königstuhl) is a historic astronomical observatory located near the summit of the Königstuhl hill in the city of Heidelberg in Germany. The predecessor of the current observatory was originally opened in 1774 in the nearby city of Mannheim but degradation of observational conditions there resulted in a relocation to the Königstuhl in 1898.This article incorporates information from the German Wikipedia. The observatory forms part of the Center of Astronomy of the University of Heidelberg. The Max Planck Institute for Astronomy opened on an adjacent site in 1967. Prof. Dr. Andreas Quirrenbach is the observatory's director since 2005. History The instrumentation of the observatory originated from the Mannheim Observatory, founded in 1774. In 1880 the observatory was provisionally moved to Karlsruhe because the astronomical/atmospherical seeing conditions worsened. In subsequent years, three oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysical, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. Historically, observatories were as simple as containing an astronomical sextant (for measuring the distance between stars) or Stonehenge (which has some alignments on astronomical phenomena). Astronomical observatories Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space-based, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Ground-based observatories Ground-based observatories, located on the surface of Earth, are used to make observations in the radio and visible light portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Most optical telescopes are housed within a dome or similar structure, to protect the delicate instruments from the elements. Telescope domes have a slit or other opening in the roof that can be opened during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catherine Wolfe Bruce
Catherine Wolfe Bruce (January 22, 1816, New York – March 13, 1900, New York) was a noted American philanthropist and patron of astronomy. Early life Bruce was born on January 22, 1816. She was the daughter of the George Bruce (1781–1866), a famous type founder who was born in Edinburgh, and Catherine Wolfe (1785–1861), the daughter of David Wolfe (1748–1836) of New York City. Her brother was David Wolfe Bruce (1824–1895), who, along with David Wolfe Bishop, inherited the fortune of their cousin, Catharine Lorillard Wolfe. Career She studied painting, learned Latin, German, French and Italian, and was familiar with the literature of those languages. In 1890, she wrote and published a translation of the "'' Dies Irae''." Personal life Due to an ever-increasing illness, she was confined to her home and died on March 13, 1900 at 810 Fifth Avenue in New York City. Philanthropy In 1877, she donated $50,000 for the construction of a library building and the purchase o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Astronomical Observatories
This is a list of astronomical observatories ordered by name, along with initial dates of operation (where an accurate date is available) and location. The list also includes a final year of operation for many observatories that are no longer in operation. While other sciences, such as volcanology and meteorology, also use facilities called observatories for research and observations, this list is limited to observatories that are used to observe celestial objects. Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space-based, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Many modern telescopes and observatories are located in space to observe astronomical objects in wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that cannot penetrate the Earth's atmosphere (such as ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays) and are thus impossible to observe using ground-based telescopes. Being above the atmosphere, these space observatories can also avoid the effects of atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere. Of the roughly one million known asteroids the greatest number are located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, approximately 2 to 4 AU from the Sun, in the main asteroid belt. Asteroids are generally classified to be of three types: C-type, M-type, and S-type. These were named after and are generally identified with carbonaceous, metallic, and silicaceous compositions, respectively. The size of asteroids varies greatly; the largest, Ceres, is almost across and qualifies as a dwarf planet. The total mass of all the asteroids combined is only 3% that of Earth's Moon. The majority of main belt asteroids follow slightly elliptical, stable orbits, revolving in the same direction as the Earth and taking from three to six years to comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karl Wilhelm Reinmuth
Karl Wilhelm Reinmuth (4 April 1892 in Heidelberg – 6 May 1979 in Heidelberg) was a German astronomer and a prolific discoverer of 395 minor planets. Scientific career From 1912 to 1957, Reinmuth was working as an astronomer at the Heidelberg Observatory (german: Landessternwarte Heidelberg-Königstuhl) an astronomical observatory on the Königstuhl hill above Heidelberg in southern Germany. He was a member at the minor planet studies group at Astronomisches Rechen-Institut between 1947 and 1950, and later became "Oberobservator" or chief-observer at Heidelberg Observatory until his retirement in 1957. Reinmuth obtained more than 12,500 precise astrometric measurements of minor planets' positions on photographic plates, an enormous accomplishment before computer-based assistance existed. Honours The outer main-belt asteroid 1111 Reinmuthia, discovered by himself at Heidelberg in 1912, was named in his honour (). Discoveries Among his most notable discoveries are th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Heidelberg
} Heidelberg University, officially the Ruprecht Karl University of Heidelberg, (german: Ruprecht-Karls-Universität Heidelberg; la, Universitas Ruperto Carola Heidelbergensis) is a public research university in Heidelberg, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Founded in 1386 on instruction of Pope Urban VI, Heidelberg is Germany's oldest university and one of the world's oldest surviving universities; it was the third university established in the Holy Roman Empire. Heidelberg is one of the most prestigious and highly ranked universities in Europe and the world. Heidelberg has been a coeducational institution since 1899. The university consists of twelve faculties and offers degree programmes at undergraduate, graduate and postdoctoral levels in some 100 disciplines. The language of instruction is usually German, while a considerable number of graduate degrees are offered in English as well as some in French. As of 2021, 57 Nobel Prize winners have been affiliated with the city o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomical Calculation Institute (University Of Heidelberg)
The Astronomical Calculation Institute (german: Astronomisches Rechen-Institut; ARI) is a research institute in Heidelberg, Germany, dating from the 1700s. Beginning in 2005, the ARI became part of the Center for Astronomy at Heidelberg University (', ). Previously, the institute directly belonged to the state of Baden-Württemberg. Description The ARI has a rich history. It was founded in 1700 in Berlin-Dahlem by Gottfried Kirch. It had its origin in a patent application by Frederick I of Prussia, who introduced a monopoly on publishing star catalogs in Prussia. In 1945 the Institute was moved by the Americans nearer to the United States Army Garrison Heidelberg. On January 1, 2005 the combined Center for Astronomy institute formed by combining ARI, with the Institute of Theoretical Astrophysics (', ITA) and the Landessternwarte Heidelberg-Königstuhl ("Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory", LSW). The ARI has been responsible among other things for the Gliese catal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institute Of Theoretical Astrophysics (University Of Heidelberg)
The Faculty of Physics and Astronomy is one of twelve faculties at the University of Heidelberg. It comprises the Kirchhoff Institute of Physics, the Institute of Physics, Theoretical Physics, Environmental Physics and Theoretical Astrophysics. Kirchhoff Institute of Physics The Kirchhoff-Institut für Physik (Kirchhoff Institute of Physics, KIP), built in 2002, is a research institute located in Heidelberg, Germany. It shares faculty with the physics and astronomy departments at the University of Heidelberg. The institute is named after Gustav Kirchhoff, who collaborated in Heidelberg in 1854 with Robert Bunsen in spectroscopic work. The scope of its research is broad. Many projects exist, from low temperature physics and neuronal information processing to surface physics. Facilities include (apart from several laboratories) a cleanroom, an ASIC laboratory, an experimental hall and, as it is also serves undergraduates, there are 2 auditoriums with a capacity of over 300 pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
588 Achilles
Achilles ( minor planet designation: 588 Achilles) is a large Jupiter trojan asteroid of the Greek camp. Achilles was the first Jupiter trojan to be discovered, and was discovered by Max Wolf at the Heidelberg Observatory in 1906. Wolf named the minor planet after the legendary hero Achilles from Greek mythology. The dark D-type asteroid measures approximately in diameter which makes it one of the 10 largest Jupiter trojans. It has a rotation period of 7.3 hours and possibly a spherical shape. Discovery ''Achilles'' was discovered on 22 February 1906, by the German astronomer Max Wolf at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in southern Germany. It was the first discovery of a Jupiter trojan, although had been observed as ' two years previously. This body, however, remained unconfirmed as the observation period was not long enough to calculate an orbit. August Kopff, a colleague of Wolf at Heidelberg, then discovered 617 Patroclus eight months after ''Achilles'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trojan Asteroid
In astronomy, a trojan is a small celestial body (mostly asteroids) that shares the orbit of a larger body, remaining in a stable orbit approximately 60° ahead of or behind the main body near one of its Lagrangian points and . Trojans can share the orbits of planets or of large moons. Trojans are one type of co-orbital object. In this arrangement, a star and a planet orbit about their common barycenter, which is close to the center of the star because it is usually much more massive than the orbiting planet. In turn, a much smaller mass than both the star and the planet, located at one of the Lagrangian points of the star–planet system, is subject to a combined gravitational force that acts through this barycenter. Hence the smallest object orbits around the barycenter with the same orbital period as the planet, and the arrangement can remain stable over time. In the Solar System, most known trojans share the orbit of Jupiter. They are divided into the Greek camp at (ah ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asteroids
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere. Of the roughly one million known asteroids the greatest number are located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, approximately 2 to 4 AU from the Sun, in the main asteroid belt. Asteroids are generally classified to be of three types: C-type, M-type, and S-type. These were named after and are generally identified with carbonaceous, metallic, and silicaceous compositions, respectively. The size of asteroids varies greatly; the largest, Ceres, is almost across and qualifies as a dwarf planet. The total mass of all the asteroids combined is only 3% that of Earth's Moon. The majority of main belt asteroids follow slightly elliptical, stable orbits, revolving in the same direction as the Earth and taking from three to six years to comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
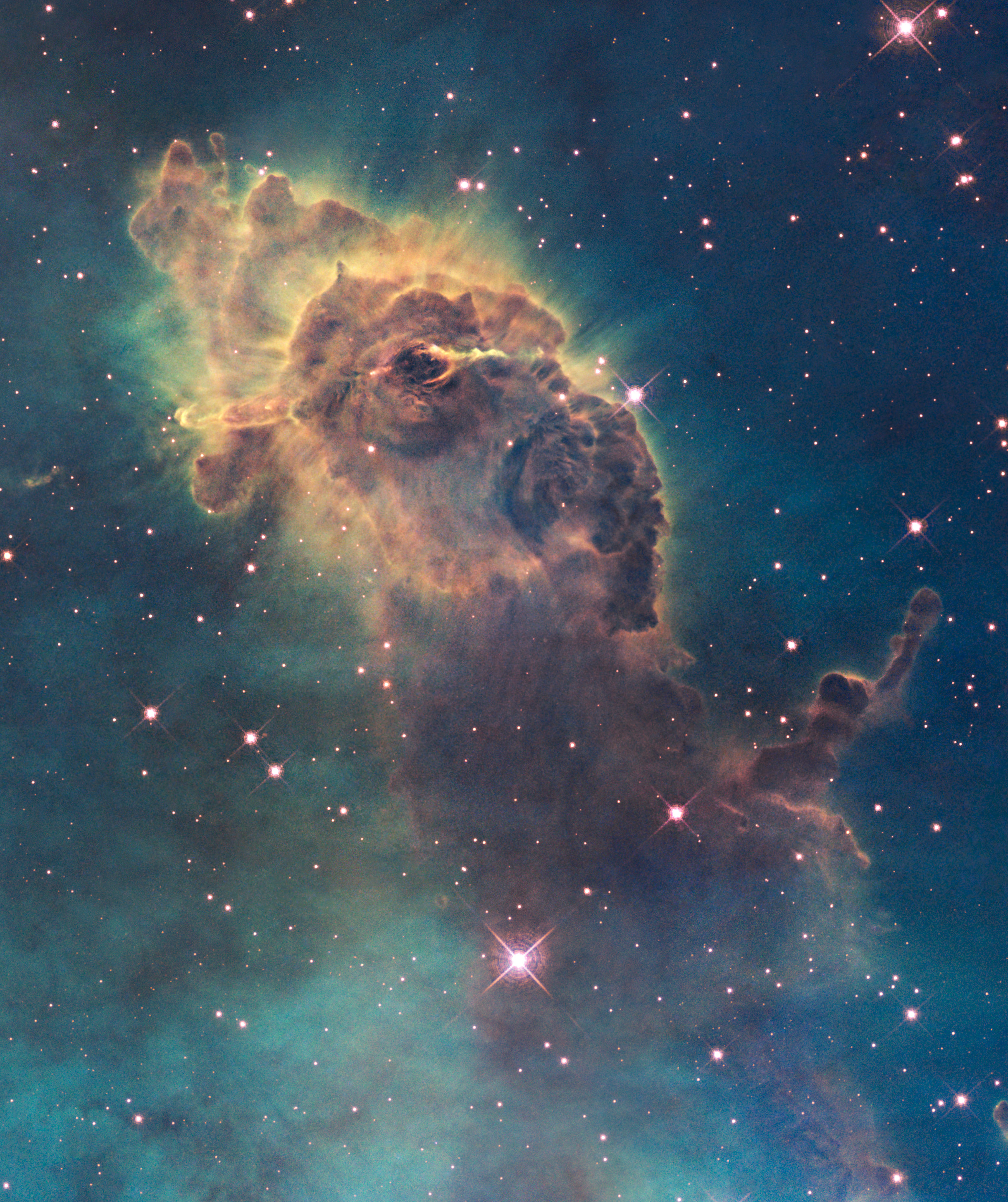
Nebula
A nebula ('cloud' or 'fog' in Latin; pl. nebulae, nebulæ or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the "Pillars of Creation" in the Eagle Nebula. In these regions, the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form denser regions, which attract further matter, and eventually will become dense enough to form stars. The remaining material is then thought to form planets and other planetary system objects. Most nebulae are of vast size; some are hundreds of light-years in diameter. A nebula that is visible to the human eye from Earth would appear larger, but no brighter, from close by. The Orion Nebula, the brightest nebula in the sky and occupying an area twice the angular diameter of the full Moon, can be viewed with the naked eye but was missed by early astronomers. Although denser than the space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |