|
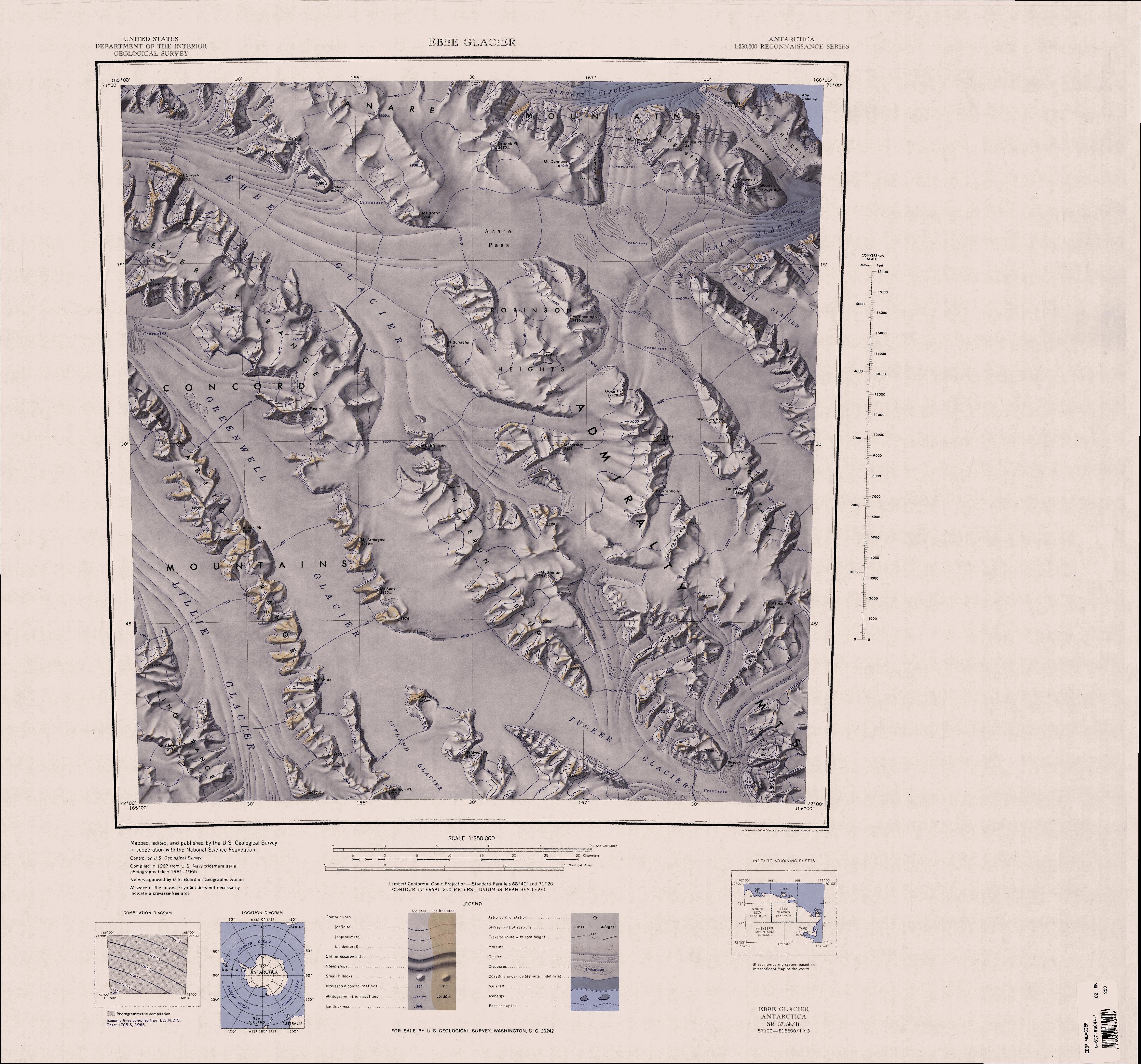
Hedgpeth Heights
The Hedgpeth Heights () are mainly snow-covered heights, long and with peaks rising to , located southwest of the Quam Heights in the Anare Mountains of Victoria Land, Antarctica. Exploration and naming The Hedgpeth Heights was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and United States Navy air photos, 1960–63, and was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Joel Hedgpeth, a United States Antarctic Research Program (USARP) biologist at McMurdo Station, 1967–68, and Palmer Station, 1968–69. Location The Hedgpeth Heights are towards the east of the Anare Mountains. The Barnett Glacier runs east along the north side, and the Dennistoun Glacier runs east along its south side. The Douglas Gap to the east connects the two glaciers and separates the Hedgpeth Heights from the Quam Heights Quam Heights () is a mostly snow-covered heights, 15 miles (24 km) long and 4 miles (6 km) wide, ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Victoria Land
Victoria Land is a region in eastern Antarctica which fronts the western side of the Ross Sea and the Ross Ice Shelf, extending southward from about 70°30'S to 78°00'S, and westward from the Ross Sea to the edge of the Antarctic Plateau. It was discovered by Captain James Clark Ross in January 1841 and named after Queen Victoria. The rocky promontory of Minna Bluff is often regarded as the southernmost point of Victoria Land, and separates the Scott Coast to the north from the Hillary Coast of the Ross Dependency to the south. The region includes ranges of the Transantarctic Mountains and the McMurdo Dry Valleys (the highest point being Mount Abbott in the Northern Foothills), and the flatlands known as the Labyrinth. The Mount Melbourne is an active volcano in Victoria Land. Early explorers of Victoria Land include James Clark Ross and Douglas Mawson. In 1979, scientists discovered a group of 309 meteorites in Antarctica, some of which were found near the Allan Hills in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Thomas Troubridge
Rear Admiral Sir Edward Thomas Troubridge, 2nd Baronet, ( – 7 October 1852) was an officer of the British Royal Navy who served in the French Revolutionary, Napoleonic and War of 1812. He later served for fifteen years as the member of parliament for Sandwich, Kent. Biography Family background and early life Troubridge was the only son of Rear-Admiral Sir Thomas Troubridge, Bt., and Frances Northall, the daughter of Captain John Northall. He was educated at Dr. Charles Burney's school at Greenwich.Fisher (2009) Wartime naval career Troubridge entered the Navy on 21 January 1797 as a volunteer on board the ship , the guard ship at Plymouth under the command of Captain Richard Boger. He was discharged in April 1799, and in January 1801 joined the ship , Captain George Murray, as a midshipman. He followed Murray into the , seeing action at the battle of Copenhagen on 2 April 1801, and subsequently into , until transferred in May 1802 to , Captain James Oughton, for a sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Pechell
Rear-Admiral Sir Samuel John Brooke Pechell, 3rd Baronet CB, KCH, FRS (1 September 1785 – 3 November 1849) was a prominent British Royal Navy officer of the early nineteenth century. Although he served in several celebrated naval actions of the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars his most important achievements were made while serving as a Lord of the Admiralty, pioneering the science and instruction of rapid and accurate gunnery in the Royal Navy through training facilities and manuals. In addition to his work at the Admiralty, Pechell served in the House of Commons for two constituencies and was on good terms with King William IV, who supported his efforts to improve standards of gunnery and returned him to the Admiralty in 1839 after a five-year absence caused by his support for the Whig government. In 1826 he inherited the Pechell Baronetcy from his father, but died childless and the title passed to his brother George. Life Pechell was born in Ireland in 1785, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Clark Ross
Sir James Clark Ross (15 April 1800 – 3 April 1862) was a British Royal Navy officer and polar explorer known for his explorations of the Arctic, participating in two expeditions led by his uncle John Ross, and four led by William Edward Parry, and, in particular, for his own Antarctic expedition from 1839 to 1843. Biography Early life Ross was born in London, the son of George Ross and nephew of John Ross, under whom he entered the Royal Navy on 5 April 1812. Ross was an active participant in the Napoleonic Wars, being present at an action where HMS ''Briseis'', commanded by his uncle, captured ''Le Petit Poucet'' (a French privateer) on 9 October 1812. Ross then served successively with his uncle on HMS ''Actaeon'' and HMS ''Driver''. Arctic exploration Ross participated in John's unsuccessful first Arctic voyage in search of a Northwest Passage in 1818 aboard ''Isabella''. Between 1819 and 1827 Ross took part in four Arctic expeditions under William Ed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Douglas Gap
Douglas Gap () is a glacier-filled gap, 1.5 nautical miles (3 km) wide, between the Hedgpeth Heights and the Quam Heights in the Anare Mountains of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–63, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Donald S. Douglas, a United States Antarctic Research Program biologist at Hallett Station, 1959–60 and 1960–61. This mountain pass lies situated on the Pennell Coast, a portion of Antarctica lying between Cape Williams and Cape Adare Cape Adare is a prominent cape of black basalt forming the northern tip of the Adare Peninsula and the north-easternmost extremity of Victoria Land, East Antarctica. Description Marking the north end of Borchgrevink Coast and the west e .... References Mountain passes of Victoria Land Pennell Coast {{VictoriaLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dennistoun Glacier
The Dennistoun Glacier is a glacier, long, draining the northern slopes of Mounts Black Prince, Royalist and Adam in the Admiralty Mountains of Victoria Land in Antarctica. It flows northwest between the Lyttelton Range and Dunedin Range, turning east on rounding the latter range to enter the sea south of Cape Scott. The coastal extremity of the glacier was charted in 1911–12 by the Northern Party, led by Victor Campbell, of the British Antarctic Expedition, 1910–13. The geographical feature lies situated on the Pennell Coast, a portion of Antarctica lying between Cape Williams and Cape Adare. The glacier is named after Jim Dennistoun, a New Zealand alpinist who was in charge of the mules on board the '' Terra Nova'' on her way to Antarctica. The entire extent of the glacier was mapped by the U.S. Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy aerial photography, 1960–63. The name Fowlie Glacier, which in fact refers to a tributary glacier, has sometimes been inadvertently ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barnett Glacier
Barnett Glacier () is a large glacier in the Anare Mountains that flows east along the south side of Tapsell Foreland into Smith Inlet, northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Exploration and naming Barnett Glacier was mapped by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and from United States Navy air photos, 1960–63. It was named by the United States Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) after Donald C. Barnett, USGS topographic engineer, a member of USGS Topo East and West, 1962–63, in which the expedition extended geodetic control from the area of Cape Hallett to the Wilson Hills (Topo West) and from the foot of Beardmore Glacier through the Horlick Mountains (Topo East). Location Barnett Glacier rises in the Anare Mountains to the northeast of Drabek Peak, and flows east. It passes Mount Dalmeny, Hedgpeth Heights, the Douglas Gap and Quam Heights to the south. It is fed by McElroy Glacier from Tapsell Foreland to the north, and flows past the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palmer Station
Palmer Station is a United States research station in Antarctica located on Anvers Island, the only US station located north of the Antarctic Circle. Initial construction of the station finished in 1968. The station, like the other U.S. Antarctic stations, is operated by the United States Antarctic Program (USAP) of the National Science Foundation. The base is about as distant from the equator as Fairbanks, Alaska. Description The station is named for Nathaniel B. Palmer, usually recognized as the first American to see Antarctica. The maximum population that Palmer Station can accommodate is 46 people. The normal austral summer contingent varies, but it is generally around 40 people. Palmer is staffed year-round; however, the population drops to 15-20 people for winter maintenance after the conclusion of the summer research season. There are science labs located in the Bio-Lab building (pictured), the other main building is GWR (Garage, Warehouse, and Recreation). Webcam image ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quam Heights
Quam Heights () is a mostly snow-covered heights, 15 miles (24 km) long and 4 miles (6 km) wide, rising over 1,000 m and forming the coastline between the Barnett and Dennistoun Glaciers in northern Victoria Land, Antarctica. Mapped by United States Geological Survey (USGS) from surveys and U.S. Navy aerial photography, 1960–63. The site was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Louis O. Quam, chief scientist of the National Science Foundation The National Science Foundation (NSF) is an independent agency of the United States government that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National I ...'s Office of Polar Programs, 1967–72. Mountains of Victoria Land Pennell Coast {{VictoriaLand-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McMurdo Station
McMurdo Station is a United States Antarctic research station on the south tip of Ross Island, which is in the New Zealand-claimed Ross Dependency on the shore of McMurdo Sound in Antarctica. It is operated by the United States through the United States Antarctic Program (USAP), a branch of the National Science Foundation. The station is the largest community in Antarctica, capable of supporting up to 1,258 residents, and serves as one of three year-round United States Antarctic science facilities. All personnel and cargo going to or coming from Amundsen–Scott South Pole Station first pass through McMurdo. By road, McMurdo is 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) from New Zealand's smaller Scott Base. History The station takes its name from its geographic location on McMurdo Sound, named after Lieutenant Archibald McMurdo of . The ''Terror'', commanded by Irish explorer Francis Crozier, along with expedition flagship ''Erebus'' under command of James Clark Ross, first charted the area ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Antarctic Research Program
The United States Antarctic Program (or USAP; formerly known as the United States Antarctic Research Program or USARP and the United States Antarctic Service or USAS) is an organization of the United States government which has presence in the Antarctica continent. Founded in 1959, the USAP manages all U.S. scientific research and related logistics in Antarctica as well as aboard ships in the Southern Ocean. United States Antarctic Program The United States established the U.S. Antarctic Research Program (USARP) in 1959—the name was later changed to the U.S. Antarctic Program—immediately following the success of the International Geophysical Year (IGY). Today, the National Science Foundation (NSF) has a Presidential Mandate to manage the United States Antarctic Program, through which it operates three year-round research stations and two research vessels, coordinates all U.S. science on the southernmost continent, and works with other federal agencies, the U.S. military, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |