|
Hebridean Terrane
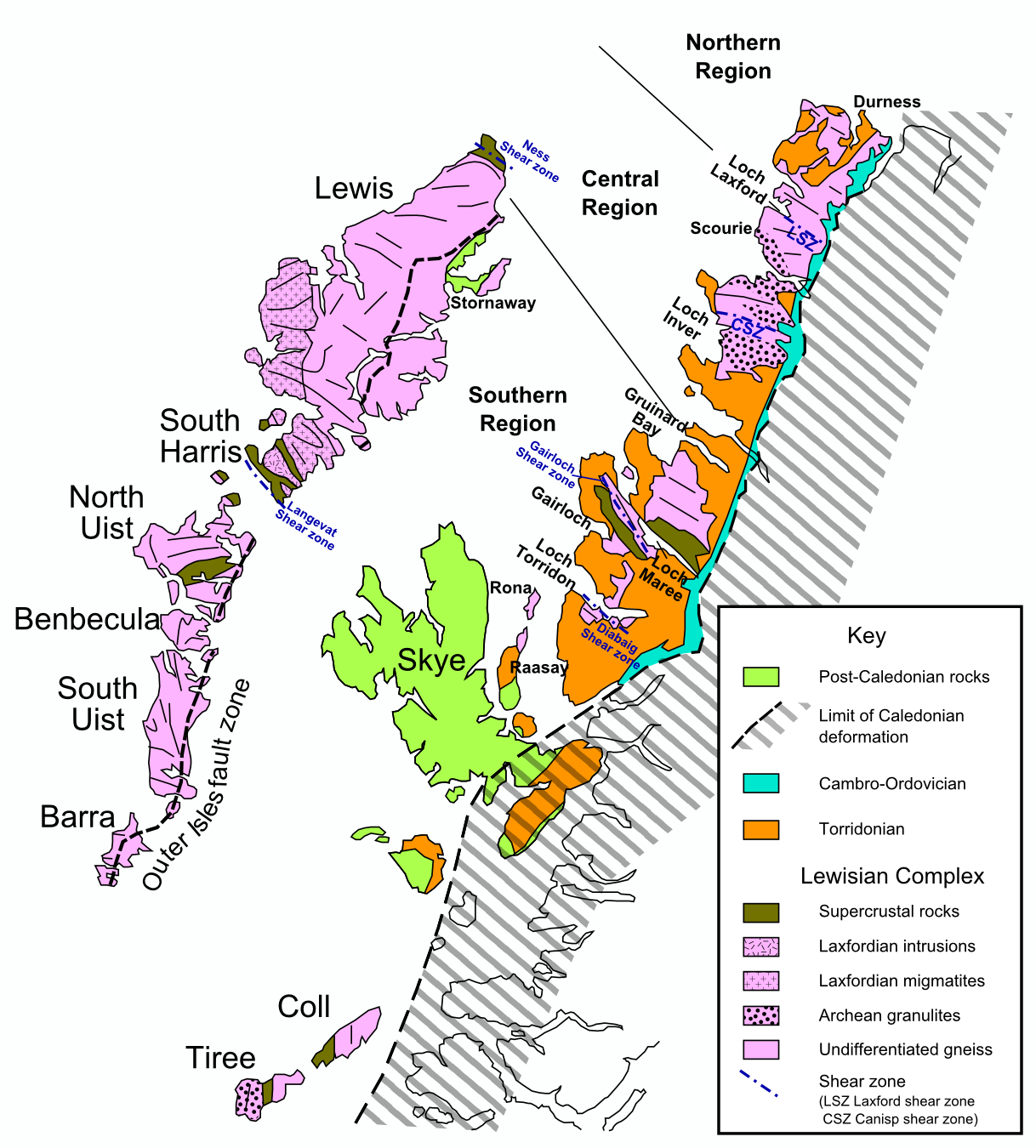
The Hebridean Terrane is one of the terranes that form part of the Caledonian orogenic belt in northwest Scotland. Its boundary with the neighbouring Northern Highland Terrane is formed by the Moine Thrust Belt. The basement is formed by Archaean and Paleoproterozoic gneisses of the Lewisian complex, unconformably overlain by the Neoproterozoic Torridonian sediments, which in turn are unconformably overlain by a sequence of Cambro–Ordovician sediments. It formed part of the Laurentian foreland during the Caledonian continental collision. Extent The Hebridean Terrane forms the westernmost strip of mainland Scotland, most of the Inner Hebrides and all of the Outer Hebrides. Similar rocks are also thought to be present in Shetland and have been proved west and north of the Outer Hebrides by BGS shallow boreholes and hydrocarbon exploration wells. The full extent of this terrane to the west is obscured by the effects of Mesozoic rifting. Rock units Lewisian complex The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hebridean Terrane
The Hebridean Terrane is one of the terranes that form part of the Caledonian orogenic belt in northwest Scotland. Its boundary with the neighbouring Northern Highland Terrane is formed by the Moine Thrust Belt. The basement is formed by Archaean and Paleoproterozoic gneisses of the Lewisian complex, unconformably overlain by the Neoproterozoic Torridonian sediments, which in turn are unconformably overlain by a sequence of Cambro–Ordovician sediments. It formed part of the Laurentian foreland during the Caledonian continental collision. Extent The Hebridean Terrane forms the westernmost strip of mainland Scotland, most of the Inner Hebrides and all of the Outer Hebrides. Similar rocks are also thought to be present in Shetland and have been proved west and north of the Outer Hebrides by BGS shallow boreholes and hydrocarbon exploration wells. The full extent of this terrane to the west is obscured by the effects of Mesozoic rifting. Rock units Lewisian complex The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
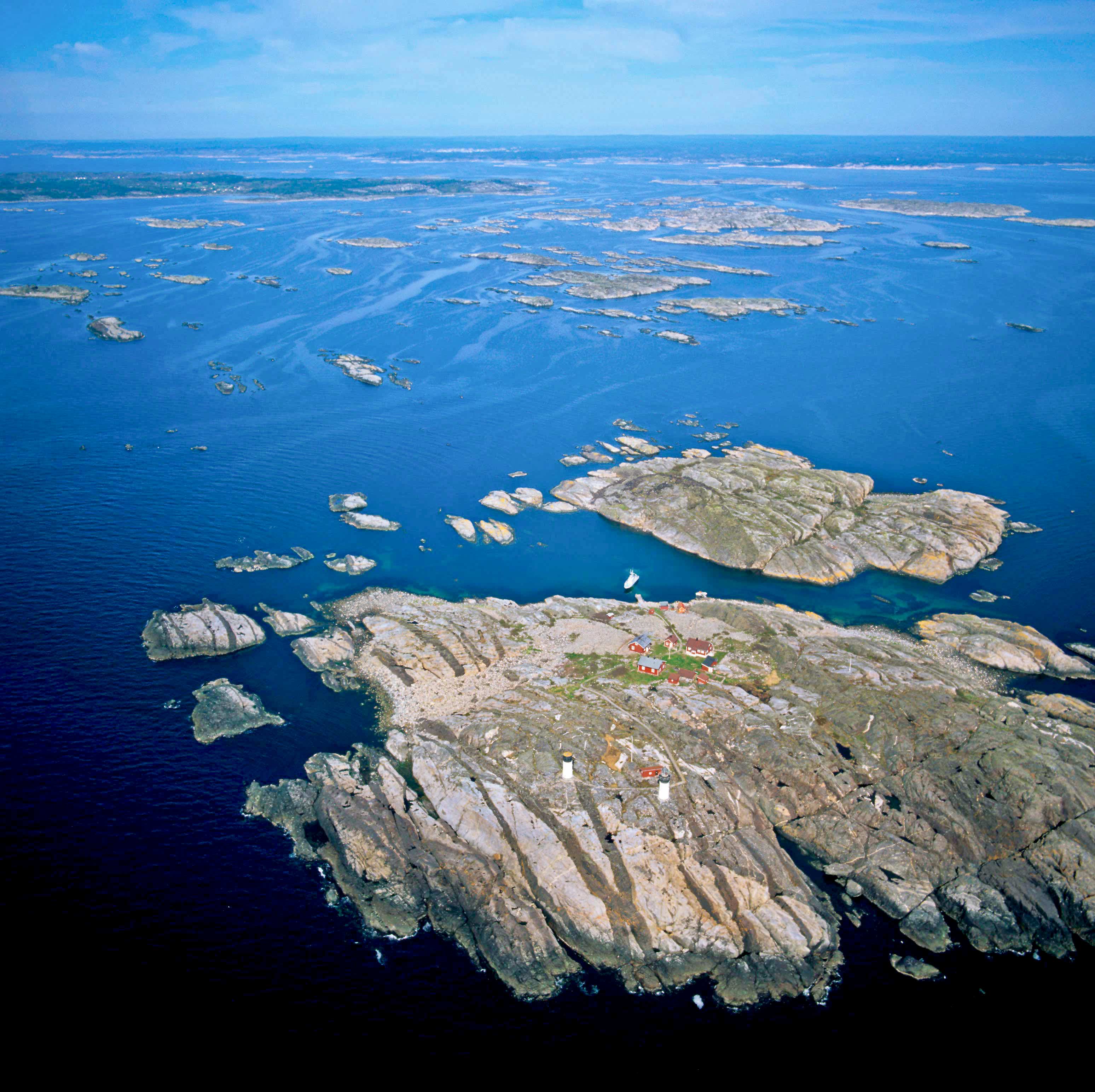
Outer Hebrides
The Outer Hebrides () or Western Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Siar or or ("islands of the strangers"); sco, Waster Isles), sometimes known as the Long Isle/Long Island ( gd, An t-Eilean Fada, links=no), is an island chain off the west coast of mainland Scotland. The islands are geographically coextensive with , one of the 32 unitary council areas of Scotland. They form part of the archipelago of the Hebrides, separated from the Scottish mainland and from the Inner Hebrides by the waters of the Minch, the Little Minch, and the Sea of the Hebrides. Scottish Gaelic is the predominant spoken language, although in a few areas English speakers form a majority. Most of the islands have a bedrock formed from ancient metamorphic rocks, and the climate is mild and oceanic. The 15 inhabited islands have a total population of and there are more than 50 substantial uninhabited islands. The distance from Barra Head to the Butt of Lewis is roughly . There are various important prehisto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
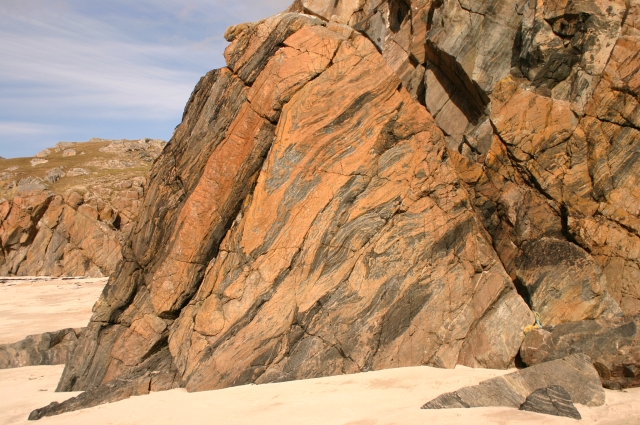
Granulite
Granulites are a class of high-grade metamorphic rocks of the granulite facies that have experienced high-temperature and moderate-pressure metamorphism. They are medium to coarse–grained and mainly composed of feldspars sometimes associated with quartz and anhydrous ferromagnesian minerals, with granoblastic texture and gneissose to massive structure.D.R. Bowes (1989), ''The Encyclopedia of Igneous and Metamorphic Petrology''; Van Nostrand Reinhold They are of particular interest to geologists because many granulites represent samples of the deep continental crust. Some granulites experienced decompression from deep in the Earth to shallower crustal levels at high temperature; others cooled while remaining at depth in the Earth. The minerals present in a granulite will vary depending on the parent rock of the granulite and the temperature and pressure conditions experienced during metamorphism. A common type of granulite found in high-grade metamorphic rocks of the continent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Year
A year or annus is the orbital period of a planetary body, for example, the Earth, moving in its orbit around the Sun. Due to the Earth's axial tilt, the course of a year sees the passing of the seasons, marked by change in weather, the hours of daylight, and, consequently, vegetation and soil fertility. In temperate and subpolar regions around the planet, four seasons are generally recognized: spring, summer, autumn and winter. In tropical and subtropical regions, several geographical sectors do not present defined seasons; but in the seasonal tropics, the annual wet and dry seasons are recognized and tracked. A calendar year is an approximation of the number of days of the Earth's orbital period, as counted in a given calendar. The Gregorian calendar, or modern calendar, presents its calendar year to be either a common year of 365 days or a leap year of 366 days, as do the Julian calendars. For the Gregorian calendar, the average length of the calendar year (t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granitic
A granitoid is a generic term for a diverse category of coarse-grained igneous rocks that consist predominantly of quartz, plagioclase, and alkali feldspar. Granitoids range from plagioclase-rich tonalites to alkali-rich syenites and from quartz-poor monzonites to quartz-rich quartzolites. As only two of the three defining mineral groups (quartz, plagioclase, and alkali feldspar) need to be present for the rock to be called a granitoid, foid-bearing rocks, which predominantly contain feldspars but no quartz, are also granitoids. The terms ''granite'' and ''granitic rock'' are often used interchangeably for granitoids; however, granite is just one particular type of granitoid. Granitoids are diverse; no classification system for granitoids can give a complete and unique characterization of the origin, compositional evolution, and geodynamic environment for the genesis of a granitoid. Accordingly, multiple granitoid classification systems have been developed such as those based ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protolith
A protolith () is the original, unmetamorphosed rock from which a given metamorphic rock is formed. For example, the protolith of a slate is a shale or mudstone. Metamorphic rocks can be derived from any other kind of non-metamorphic rock and thus there is a wide variety of protoliths. Identifying a protolith is a major aim of metamorphic geology. Protoliths are non-metamorphic rocks and have no protoliths themselves. The non-metamorphic rocks fall into two classes: sedimentary rocks, formed from sediment, and igneous rocks, formed from magma. The source of the sediment of a sedimentary rock is termed its provenance. Magmatic protoliths can be further divided into three categories: ultramafic rock, mafic rock, and quartzo-feldspathic rock. Similarly, sedimentary protoliths can be classified as quartzo-feldspathic, pelitic, carbonate rocks, or some mixture of the three. On a geological time scale, the first protoliths were first formed shortly after the formation of the Earth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dyke Swarm
A dike swarm (American spelling) or dyke swarm (British spelling) is a large geological structure consisting of a major group of parallel, linear, or radially oriented magmatic dikes intruded within continental crust or central volcanoes in rift zones. Examples exist in Iceland and near other large volcanoes, (stratovolcanoes, calderas, shield volcanoes and other fissure systems) around the world. They consist of several to hundreds of dikes emplaced more or less contemporaneously during a single intrusive event, are magmatic and stratigraphic, and may form a large igneous province. The occurrence of mafic dike swarms in Archean and Paleoproterozoic terrains is often cited as evidence for mantle plume activity associated with abnormally high mantle potential temperatures. Dike swarms may extend over in width and length. The largest dike swarm known on Earth is the Mackenzie dike swarm in the western half of the Canadian Shield in Canada, which is more than wide and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is nearly alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics. Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben with normal faulting and rift-flank uplifts mainly on one side. Where rifts remain above sea level they form a rift valley, which may be filled by water forming a rift lake. The axis of the rift area may contain volcanic rocks, and active volcanism is a part of many, but not all, active rift systems. Major rifts occur along the central axis of most mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust and lithosphere is created along a divergent boundary between two tectonic plates. ''Failed rifts'' are the result of continental rifting that failed to continue to the point of break-up. Typically the transition from rifting to spreading develops at a triple junction where three converging rifts meet over a hotspot. Two of these evolve to the poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian reptiles, like the dinosaurs; an abundance of conifers and ferns; a hot Greenhouse and icehouse earth, greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since Cambrian explosion, complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic. The era began in the wake of the Permian–Triassic extinction event, the largest well-documented mass extinction in Earth's history, and ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, another mass extinction whose victims included the non-avian dinosaurs, Pterosaur, pterosaurs, Mosasaur, mosasaurs, and Plesiosaur, plesiosaurs. The Mesozoic was a time of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oil Well
An oil well is a drillhole boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas may be termed a gas well. Wells are created by drilling down into an oil or gas reserve that is then mounted with an extraction device such as a pumpjack which allows extraction from the reserve. Creating the wells can be an expensive process, costing at least hundreds of thousands of dollars, and costing much more when in hard to reach areas, e.g., when creating offshore oil platforms. The process of modern drilling for wells first started in the 19th century, but was made more efficient with advances to oil drilling rigs during the 20th century. Wells are frequently sold or exchanged between different oil and gas companies as an asset – in large part because during falls in price of oil and gas, a well may be unproductive, but if price ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |