|
Head Gasket
In an internal combustion engine, a head gasket provides the seal between the engine block and cylinder head(s). Its purpose is to seal the combustion gases within the cylinders and to avoid coolant or engine oil leaking into the cylinders. Leaks in the head gasket can cause poor engine running and/or overheating. Purpose Within a water-cooled internal combustion engine, there are three fluids which travel between the engine block and the cylinder head: # Combustion gases (unburned air/fuel mixture and exhaust gases) in each cylinder # Water-based coolant in the coolant passages # Lubricating oil in the oil galleries Correct operation of the engine requires that each of these circuits do not leak or lose pressure at the junction of the engine block and the cylinder head. The head gasket is the seal that prevents these leaks and pressure losses. Types * Multi-Layer Steel (MLS): Most modern engines are produced with MLS gaskets. These consist of two to five (typically three) th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head Gasket On Block
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals may not have a head, but many bilaterally symmetric forms do, regardless of size. Heads develop in animals by an evolutionary trend known as cephalization. In bilaterally symmetrical animals, nervous tissue concentrate at the anterior region, forming structures responsible for information processing. Through biological evolution, sense organs and feeding structures also concentrate into the anterior region; these collectively form the head. Human head The human head is an anatomical unit that consists of the skull, hyoid bone and cervical vertebrae. The term "skull" collectively denotes the mandible (lower jaw bone) and the cranium (upper portion of the skull that houses the brain). Sculptures of human heads are generally based on a sk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrolock
Hydrolock (a shorthand notation for hydrostatic lock or hydraulic lock) is an abnormal condition of any device which is designed to compress a gas by mechanically restraining it; most commonly the reciprocating internal combustion engine, the case this article refers to unless otherwise noted. Hydrolock occurs when a volume of liquid greater than the volume of the cylinder at its minimum (end of the piston's stroke) enters the cylinder. Since liquids are nearly incompressible the piston cannot complete its travel; either the engine must stop rotating or a mechanical failure must occur. Symptoms and damage If an engine hydrolocks while at speed, a mechanical failure is likely. Common damage modes include bent or broken connecting rods, a fractured crank, a fractured head, a fractured block, crankcase damage, damaged bearings, or any combination of these. Forces absorbed by other interconnected components may cause additional damage. Physical damage to metal parts can manif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seals (mechanical)
Seals may refer to: * Pinniped, a diverse group of semi-aquatic marine mammals, many of which are commonly called seals, particularly: ** Earless seal, or "true seal" ** Fur seal * Seal (emblem), a device to impress an emblem, used as a means of authentication, on paper, wax, clay or another medium (the impression is also called a seal) * Seal (mechanical), a device which helps prevent leakage, contain pressure, or exclude contamination where two systems join In military: * United States Navy SEALs, the U.S. Navy's principal special operations force * Royal Thai Navy SEALs, part of the Royal Thai Navy In sport: * Florida Seals, a minor league ice hockey team from 2002 and 2007 * California Golden Seals, originally ''California Seals'', a former NHL ice hockey team * San Francisco Seals (baseball), a minor league baseball team in the Pacific Coast League from 1903 until 1957 * San Francisco Seals (ice hockey), a minor league hockey team in the Western Hockey League from 1961 unti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rocker Cover Gasket
Rocker covers are covers that are bolted on over rocker arms in an internal combustion engine. They are called valve covers in the United States, Canada, and in situations where Rocker Arms are not present, such as some Overhead Cam, and most Dual Overhead Cam engines. and rocker boxes in the United Kingdom. On modern engines without rocker arms they are internationally known as "valve cover" but are sometimes referred to as a "cam cover" or "timing cover" if they also cover the timing gear(s) and belt or chain. V engines ( V6, V8, etc.) usually have two rocker covers, one for each bank of cylinders, while straight engines ( I4, I6, etc.) and single-cylinder engines usually have one rocker cover. Very large multi-cylinder engines, such as those used in a ship or in aviation, may have one rocker cover for each cylinder, to make removal and installation more manageable. History In early engines, these covers did not exist. As the rocker arms are critical to having the intake a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motor Oil
Motor oil, engine oil, or engine lubricant is any one of various substances used for the lubrication of internal combustion engines. They typically consist of base oils enhanced with various additives, particularly antiwear additives, detergents, dispersants, and, for multi-grade oils, viscosity index improvers. The main function of motor oil is to reduce friction and wear on moving parts and to clean the engine from sludge (one of the functions of dispersants) and varnish (detergents). It also neutralizes acids that originate from fuel and from oxidation of the lubricant (detergents), improves sealing of piston rings, and cools the engine by carrying heat away from moving parts. In addition to the aforementioned basic constituents, almost all lubricating oils contain corrosion and oxidation inhibitors. Motor oil may be composed of only a lubricant base stock in the case of non- detergent oil, or a lubricant base stock plus additives to improve the oil's detergency, extreme p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Combustion Engine Cooling
Internal combustion engine cooling uses either air or liquid to remove the waste heat from an internal combustion engine. For small or special purpose engines, cooling using air from the atmosphere makes for a lightweight and relatively simple system. Watercraft can use water directly from the surrounding environment to cool their engines. For water-cooled engines on aircraft and surface vehicles, waste heat is transferred from a closed loop of water pumped through the engine to the surrounding atmosphere by a radiator. Water has a higher heat capacity than air, and can thus move heat more quickly away from the engine, but a radiator and pumping system add weight, complexity, and cost. Higher-power engines generate more waste heat, but can move more weight, meaning they are generally water-cooled. Radial engines allow air to flow around each cylinder directly, giving them an advantage for air cooling over straight engines, flat engines, and V engines. Rotary engines have a sim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Tuning
Engine tuning is the adjustment or modification of the internal combustion engine or Engine Control Unit (ECU) to yield optimal performance and increase the engine's power output, economy, or durability. These goals may be mutually exclusive; an engine may be de-tuned with respect to output power in exchange for better economy or longer engine life due to lessened stress on engine components. Tuning can include a wide variety of adjustments and modifications, such as the routine adjustment of the carburetor and ignition system to significant engine overhauls. Performance tuning of an engine can involve revising some of the design decisions taken during the development of the engine. Setting the idle speed, air-fuel ratio, carburetor balance, spark plug and distributor point gaps, and ignition timing were regular maintenance tasks for older engines and are the final but essential steps in setting up a racing engine. On modern engines equipped with electronic ignition and fuel i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignition System
An ignition system generates a spark or heats an electrode to a high temperature to ignite a fuel-air mixture in spark ignition internal combustion engines, oil-fired and gas-fired boilers, rocket engines, etc. The widest application for spark ignition internal combustion engines is in petrol (gasoline) road vehicles such as cars and motorcycles. Compression ignition Diesel engines ignite the fuel-air mixture by the heat of compression and do not need a spark. They usually have glowplugs that preheat the combustion chamber to allow starting in cold weather. Other engines may use a flame, or a heated tube, for ignition. While this was common for very early engines it is now rare. The first electric spark ignition was probably Alessandro Volta's toy electric pistol from the 1780s. Siegfried Marcus patented his "Electrical igniting device for gas engines" on 7 October 1884. History Magneto systems The simplest form of spark ignition is that using a magneto. The engine spins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air–fuel Ratio
Air–fuel ratio (AFR) is the mass ratio of air to a solid, liquid, or gaseous fuel present in a combustion process. The combustion may take place in a controlled manner such as in an internal combustion engine or industrial furnace, or may result in an explosion (e.g., a dust explosion, gas or vapor explosion or in a thermobaric weapon). The air–fuel ratio determines whether a mixture is combustible at all, how much energy is being released, and how much-unwanted pollutants are produced in the reaction. Typically a range of fuel to air ratios exists, outside of which ignition will not occur. These are known as the lower and upper explosive limits. In an internal combustion engine or industrial furnace, the air–fuel ratio is an important measure for anti-pollution and performance-tuning reasons. If exactly enough air is provided to completely burn all of the fuel, the ratio is known as the stoichiometric mixture, often abbreviated to stoich. Ratios lower than stoichiometri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Knocking
In spark ignition internal combustion engines, knocking (also knock, detonation, spark knock, pinging or pinking) occurs when combustion of some of the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder does not result from propagation of the flame front ignited by the spark plug, but one or more pockets of air/fuel mixture explode outside the envelope of the normal combustion front. The fuel-air charge is meant to be ignited by the spark plug only, and at a precise point in the piston's stroke. Knock occurs when the peak of the combustion process no longer occurs at the optimum moment for the four-stroke cycle. The shock wave creates the characteristic metallic "pinging" sound, and cylinder pressure increases dramatically. Effects of engine knocking range from inconsequential to completely destructive. Knocking should not be confused with pre-ignition—they are two separate events. However, pre-ignition can be followed by knocking. The phenomenon of detonation was described in November 1914 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
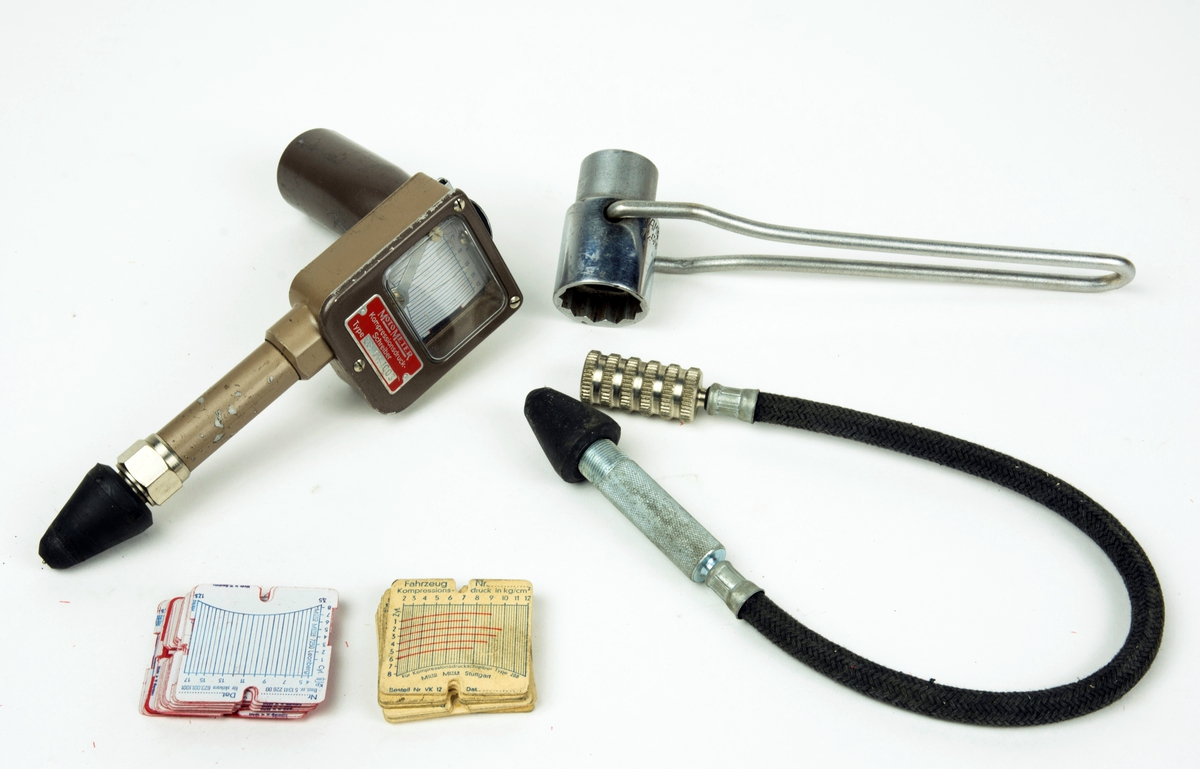
Leak-down Tester
A leak-down tester is a measuring instrument used to determine the condition of internal combustion engines by introducing compressed air into the cylinder and measuring the rate at which it leaks out. Compression testing is a crude form of leak-down testing which also includes effects due to compression ratio, valve timing, cranking speed, and other factors. Compression tests should normally be done with all spark plugs removed to maximize cranking speed. Cranking compression is a dynamic test of the actual low-speed pumping action, where peak cylinder pressure is measured and stored. Leak-down testing is a static test. Leak-down tests cylinder leakage paths. Leak-down primarily tests pistons and rings, seated valve sealing, and the head gasket. Leak-down will not show valve timing and movement problems, or piston movement related sealing problems. Any test should include both compression and leak-down. Testing is done on an engine which is not running, and normally with the tes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
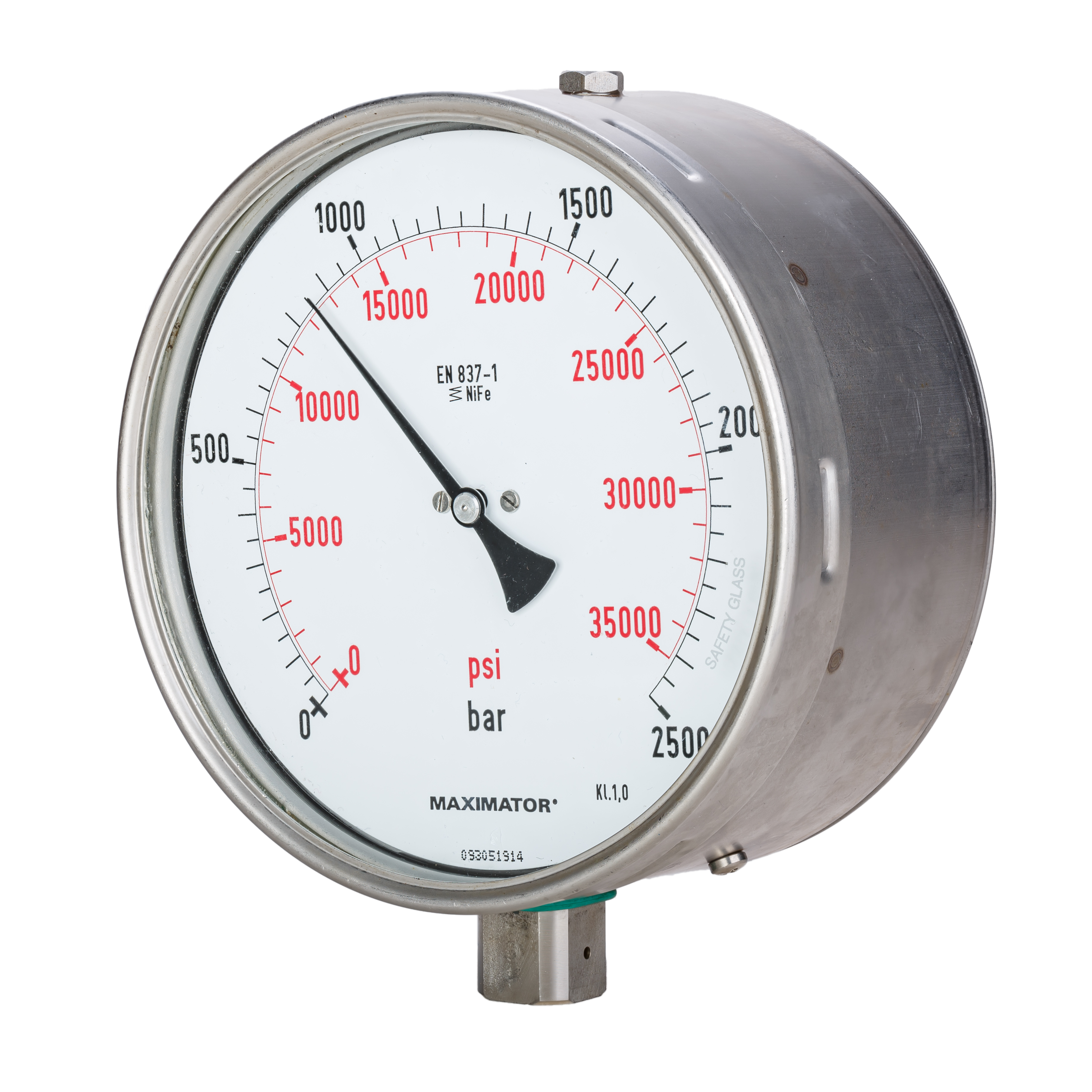
Pressure Gauge
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure mechanically are called pressure gauges, vacuum gauges or compound gauges (vacuum & pressure). The widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge. A vacuum gauge is used to measure pressures lower than the ambient atmospheric pressure, which is set as the zero point, in negative values (for instance, −1 bar or −760 mmHg equals total vacuum). Most gauges measure pressure relative to atmospheric pressure as the zero point, so this form of reading is simply referred to as "gauge pressure". However, anything greater than total vacuum is technically a form of pressure. For very low press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |