|
Hay–Herbert Treaty
The Alaska boundary dispute was a territorial dispute between the United States and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, which then controlled Canada's foreign relations. It was resolved by arbitration in 1903. The dispute had existed between the Russian Empire and Britain since 1821, and was inherited by the United States as a consequence of the Alaska Purchase in 1867. The final resolution favored the American position, as Canada did not get an all-Canadian outlet from the Yukon gold fields to the sea. The disappointment and anger in Canada was directed less at the United States, and more at the British government for betraying Canadian interests in favor of healthier United Kingdom–United States relations, Anglo-American relations. Background 1825–1897 In 1825 Russia and the United Kingdom signed a treaty to define the borders of their respective colonial possessions, the Treaty of Saint Petersburg (1825), Anglo-Russian Convention of 1825. Part of the wordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian-American Company
The Russian-American Company Under the High Patronage of His Imperial Majesty was a state-sponsored chartered company formed largely on the basis of the Shelikhov-Golikov Company, United American Company. Emperor Paul I of Russia chartered the company in the Ukase of 1799. It had the mission of establishing new settlements in Russian America, conducting trade with natives, and carrying out an expanded Russian colonization of the Americas, colonization program. Russia's first joint-stock company, it came under the direct authority of the Ministry of Commerce of the Russian Empire, Ministry of Commerce of Imperial Russia. Count Nikolay Rumyantsev, Nikolai Petrovich Rumyantsev (Minister of Commerce from 1802 to 1811; Minister of Foreign Affairs from 1808 to 1814) exercised a pivotal influence upon the early activities of the company. In 1801 the company's headquarters moved from Irkutsk to Saint Petersburg, and the merchants who were initially the major stockholders were soon replac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klondike River
The Klondike River () is a tributary of the Yukon River in Canada that gave its name to the Klondike Gold Rush and the Klondike region of the Yukon Territory. The Klondike River rises in the Ogilvie Mountains and flows into the Yukon River at Dawson City. Its name comes from the Hän word () meaning ''hammerstone'', a tool which was used to hammer down stakes used to set salmon nets. Gold was discovered in tributaries of the Klondike River in 1896, which started the Klondike Gold Rush, and is still being mined today. In Jack London's story " A Relic of the Pliocene" (''Collier's Weekly'', 1901), this river was mentioned as "Reindeer River". (See Reindeer Lake.) Gallery File:Dawson City Rivers Lookout 3264px.jpg, Klondike River (left) flowing into the Yukon River The Yukon River is a major watercourse of northwestern North America. From its source in British Columbia, it flows through Canada's territory of Yukon (itself named after the river). The lower half of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haines, Alaska
Haines (Tlingit: ''Deishú'') is a census-designated place located in Haines Borough, Alaska, United States. It is in the northern part of the Alaska Panhandle and near Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve. As of the 2020 census, the population of the Haines CDP was 1,657, down from 1,713 in 2010; it has 79.6% of Haines Borough's total population. History The original Native name for Haines was Deishú, meaning "end of the trail"; it was named by the Chilkat group of the Tlingit. The name is derived from the fact that they could portage (carry) their canoes from the trail they used to trade with the interior. The trail began at the outlet of the Chilkat River and went to Dtehshuh; portaging saved of rowing around the Chilkat Peninsula. The first European, George Dickinson, an agent for the North West Trading Company, settled at Dtehshuh in 1879. In 1881, the Chilkat asked Sheldon Jackson to send missionaries to the area. John Muir and Samuel Hall Young, a Presby ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William McKinley
William McKinley (January 29, 1843September 14, 1901) was the 25th president of the United States, serving from 1897 until Assassination of William McKinley, his assassination in 1901. A member of the Republican Party (United States), Republican Party, he led a realignment that made Republicans History of the Republican Party (United States), largely dominant in the industrial states and nationwide for decades. McKinley successfully led the U.S. in the Spanish–American War and oversaw a period of Manifest destiny, American expansionism, with the annexations of Hawaii, Puerto Rico, Guam, the Philippines, and American Samoa. McKinley was the last president to have served in the American Civil War; he was the only one to begin his service as an enlisted soldier, enlisted man and ended it as a brevet (military), brevet major. After the war, he settled in Canton, Ohio, where he practiced law and married Ida Saxton. In 1876, McKinley was elected to Congress, where he became the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada. Situated in the Pacific Northwest between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains, the province has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, forests, lakes, mountains, inland deserts and grassy plains. British Columbia borders the province of Alberta to the east; the territories of Yukon and Northwest Territories to the north; the U.S. states of Washington (state), Washington, Idaho and Montana to the south, and Alaska to the northwest. With an estimated population of over 5.7million as of 2025, it is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, third-most populous province. The capital of British Columbia is Victoria, British Columbia, Victoria, while the province's largest city is Vancouver. Vancouver and its suburbs together make up List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, the third-largest metropolit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian America
Russian(s) may refer to: *Russians (), an ethnic group of the East Slavic peoples, primarily living in Russia and neighboring countries *A citizen of Russia *Russian language, the most widely spoken of the Slavic languages *''The Russians'', a book by Hedrick Smith *Russian (comics), fictional Marvel Comics supervillain from ''The Punisher'' series *Russian (solitaire), a card game *Russians (song), "Russians" (song), from the album ''The Dream of the Blue Turtles'' by Sting *"Russian", from the album ''Tubular Bells 2003'' by Mike Oldfield *"Russian", from the album ''Robot Face, '' by Caravan Palace *Nik Russian, the perpetrator of a con committed in 2002 See also * *Russia (other) *Rus (other) *Rossiysky (other) *Russian River (other) *Rushen (other) {{Disambiguation Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puget Sound Agricultural Company
The Puget Sound Agricultural Company (PSAC), with common variations of the name including Puget Sound or Puget's Sound, was a subsidiary joint stock company formed in 1840 by the Hudson's Bay Company (HBC). Its stations operated within the Pacific Northwest, in the HBC administrative division of the Columbia Department. The RAC-HBC Agreement was signed in 1839 between the Russian-American Company and the HBC, with the British to now supply the various trade posts of Russian America. It was hoped by the HBC governing committee that independent American merchants, previously a major source of foodstuffs for the RAC, would be shut out of the Russian markets and leave the Maritime fur trade. Because its monopoly license granted by the British Government forbade any activity besides the fur trade, the HBC created the PSAC to sidestep this issue. The PSAC was formed to produce or manufacture enough agricultural and livestock products to meet the Russian supply demands. In correspondence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monopoly
A monopoly (from Greek language, Greek and ) is a market in which one person or company is the only supplier of a particular good or service. A monopoly is characterized by a lack of economic Competition (economics), competition to produce a particular thing, a lack of viable substitute goods, and the possibility of a high monopoly price well above the seller's marginal cost that leads to a high monopoly profit. The verb ''monopolise'' or ''monopolize'' refers to the ''process'' by which a company gains the ability to raise prices or exclude competitors. In economics, a monopoly is a single seller. In law, a monopoly is a business entity that has significant market power, that is, the power to charge Monopoly price, overly high prices, which is associated with unfair price raises. Although monopolies may be big businesses, size is not a characteristic of a monopoly. A small business may still have the power to raise prices in a small industry (or market). A monopoly may als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fur Trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of a world fur market in the early modern period, furs of boreal ecosystem, boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most valued. Historically the trade stimulated the exploration and colonization of Siberia, northern North America, and the South Shetland Islands, South Shetland and South Sandwich Islands. Today the importance of the fur trade has diminished; it is based on pelts produced at fur farms and regulated fur-bearer trapping, but has become controversial. Animal rights organizations oppose the fur trade, citing that animals are brutally killed and sometimes skinned alive. Fur has been replaced in some clothing by synthetic fiber, synthetic imitations, for example, as in ruffs on hoods of parkas. Continental fur trade Russian fur trade Before the European colonization of the Americas, Russia was a major supplier of fur pelts to W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
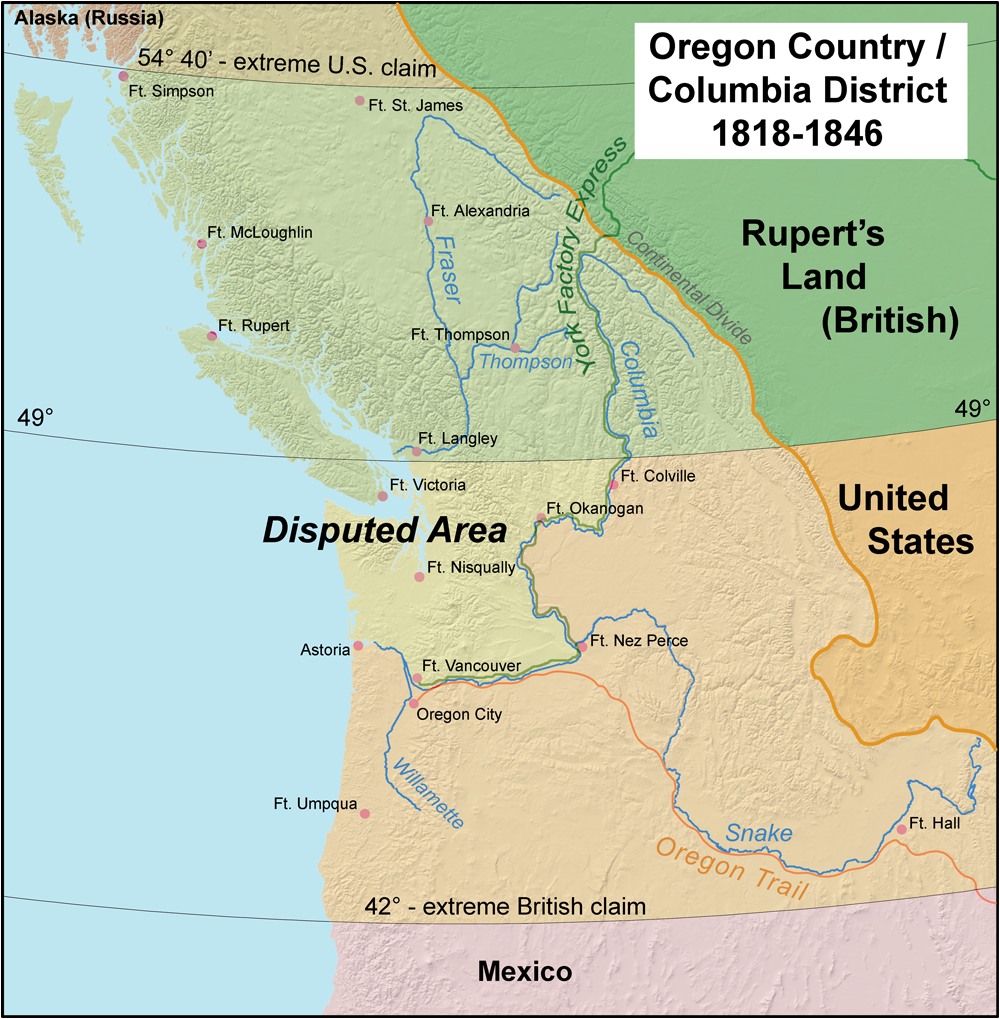
Parallel 54°40′ North
The Oregon boundary dispute or the Oregon Question was a 19th-century territorial dispute over the political division of the Pacific Northwest of North America between several nations that had competing territorial and commercial aspirations in the region. Expansionist competition into the region began in the 18th century, with participants including the Russian Empire, Great Britain, Spain, and the United States. After the War of 1812, the Oregon dispute took on increased importance for diplomatic relations between the British Empire and the fledgling American republic. In the mid-1820s, the Russians signed the Russo-American Treaty of 1824 and the Russo-British Treaty of 1825, and the Spanish signed the Adams–Onís Treaty of 1819, by which Russia and Spain formally withdrew their respective territorial claims in the region, and the British and the Americans acquired residual territorial rights in the disputed area. But the question of sovereignty over a portion of the Nort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |