|
Havelland FHSW
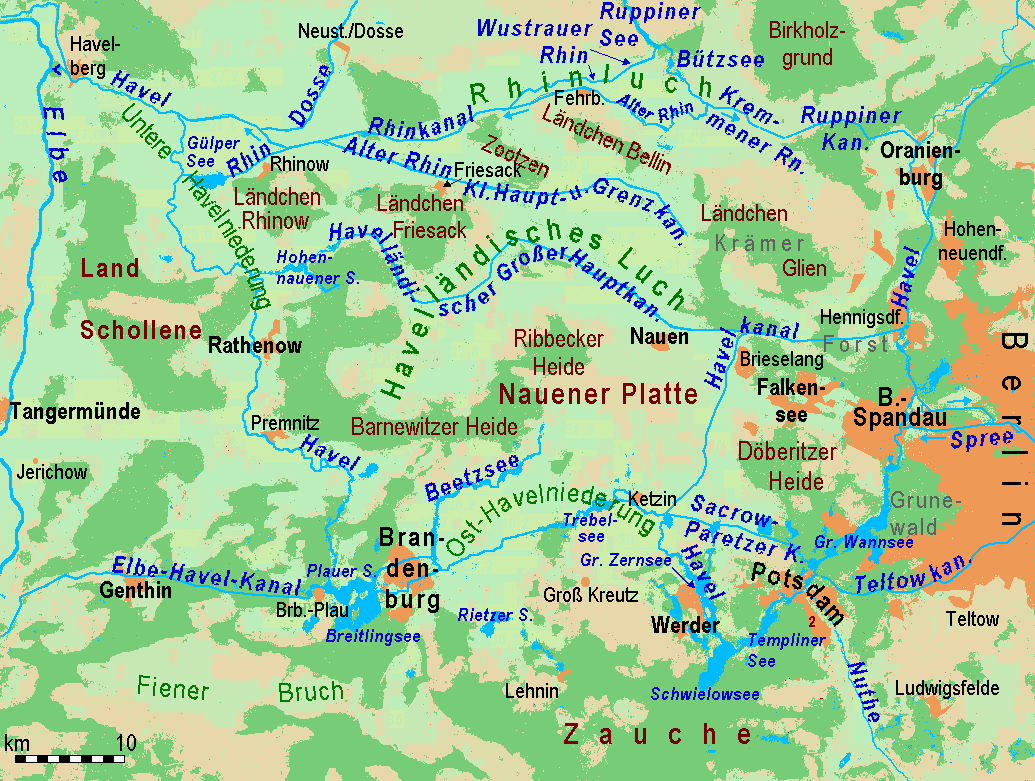
Geographically, the Havelland is the region around which the River Havel flows in a U-shape between Oranienburg to the northeast and Rhinow to the northwest. The northern boundary of the Havelland is formed by the River Rhin and the Rhin Canal. In the history of Brandenburg, the Havelland represents a historic region. In the heart of the Havelland is the Landkreis Havelland, county of the same name. In addition the Havelland includes the south of Ruppin Land with the Rhinluch, the western part of Berlin's Spandau, parts of Potsdam, the town of Brandenburg an der Havel and several villages in the county of Potsdam-Mittelmark. The Tourist Association of Havelland has chosen a rather different boundary. It covers the county of Havelland, the town of Brandenburg an der Havel and the northern part of the county of Potsdam-Mittelmark, including communities south of the Havel river, that belong to the region of Zauche. The writer Theodor Fontane described the Havelland as well as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Havelland FHSW
Geographically, the Havelland is the region around which the River Havel flows in a U-shape between Oranienburg to the northeast and Rhinow to the northwest. The northern boundary of the Havelland is formed by the River Rhin and the Rhin Canal. In the history of Brandenburg, the Havelland represents a historic region. In the heart of the Havelland is the Landkreis Havelland, county of the same name. In addition the Havelland includes the south of Ruppin Land with the Rhinluch, the western part of Berlin's Spandau, parts of Potsdam, the town of Brandenburg an der Havel and several villages in the county of Potsdam-Mittelmark. The Tourist Association of Havelland has chosen a rather different boundary. It covers the county of Havelland, the town of Brandenburg an der Havel and the northern part of the county of Potsdam-Mittelmark, including communities south of the Havel river, that belong to the region of Zauche. The writer Theodor Fontane described the Havelland as well as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herr Von Ribbeck Auf Ribbeck Im Havelland (Fontane)
Herr von Ribbeck auf Ribbeck im Havelland is a popular literary ballad written by the German poet and novelist Theodor Fontane in 1889. Up to today, the poem is published in German anthologies and learned in schools. Content The poem tells of a member of the German lower ''Uradel'' nobility, named in the title (Squire ''von Ribbeck,'' his family name; ''auf Ribbeck,'' residing on Ribbeck manor (today part of Nauen); ''im Havelland,'' in the Havelland region). Von Ribbeck is described as gentle and generous; he often gives away pears from his pear trees to children passing by, addressing them in a friendly Brandenburgisch dialect. But he knows his son and heir to be a scrooge; so when von Ribbeck feels his end near, he asks that a pear be put into his grave. This pear quickly grows into a pear-tree, which now provides free pears to the children, thus preserving the heritage of the late von Ribbeck. History The Ribbeck family of Brandenburgian nobles has been attested since 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at Last Glacial Maximum, the Laurentide Ice Sheet covered much of North America, the Weichselian ice sheet covered Northern Europe and the Patagonian Ice Sheet covered southern South America. Ice sheets are bigger than ice shelves or alpine glaciers. Masses of ice covering less than 50,000 km2 are termed an ice cap. An ice cap will typically feed a series of glaciers around its periphery. Although the surface is cold, the base of an ice sheet is generally warmer due to geothermal heat. In places, melting occurs and the melt-water lubricates the ice sheet so that it flows more rapidly. This process produces fast-flowing channels in the ice sheet — these are ice streams. The present-day polar ice sheets are relatively young in geol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weichsel Glaciation (born 1943), American bridge player
{{disambig ...
Weichsel may refer to: * Vistula river (Weichsel in German) * Weichselian glaciation * Peter Weichsel Peter M. Weichsel (born 1943) is an American professional bridge player from Encinitas, California. College and war years Early Weichsel started playing bridge at home with his family, but did not get hooked until 1963 when he was a student at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saale Glaciation
The Saale glaciation or Saale Glaciation, sometimes referred to as the Saalian glaciation, Saale cold period (german: Saale-Kaltzeit), Saale complex (''Saale-Komplex'') or Saale glacial stage (''Saale-Glazial'', colloquially also the ''Saale-Eiszeit'' or ''Saale-Zeit''), covers the middle of the three large glaciations in Northern Europe and the northern parts of Eastern, Central and Western Europe by the Scandinavian Inland Ice Sheet between the older Elster glaciation and the younger Weichselian glaciation, also called the Last Glacial Period. Age and definitions It succeeded the Holstein interglacial and was followed by the Eemian interglacial. The Saale complex is currently estimated, depending on the source, as existing from around 300,000 to 130,000 years ago or 347,000 to 128,000 years ago (duration: around 219,000 years), roughly contemporaneous with the glaciation of the Riss Glacial in the Alpine region. The actual "ice age" includes only part of the Saale glaciation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End Moraine
A terminal moraine, also called end moraine, is a type of moraine that forms at the terminal (edge) of a glacier, marking its maximum advance. At this point, debris that has accumulated by plucking and abrasion, has been pushed by the front edge of the ice, is driven no further and instead is deposited in an unsorted pile of sediment. Because the glacier acts very much like a conveyor belt, the longer it stays in one place, the greater the amount of material that will be deposited. The moraine is left as the marking point of the terminal extent of the ice. Formation As a glacier moves along its path, the surrounding area is continuously eroding. Loose rock and pieces of bedrock are constantly being picked up and transported with the glacier. Fine sediment and particles are also incorporated into the glacial ice. The accumulation of these rocks and sediment together form what is called glacial till when deposited. Push moraines are formed when a glacier retreats from a previou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Moraine
A moraine is any accumulation of unconsolidated debris (regolith and rock), sometimes referred to as glacial till, that occurs in both currently and formerly glaciated regions, and that has been previously carried along by a glacier or ice sheet. It may consist of partly rounded particles ranging in size from boulders (in which case it is often referred to as boulder clay) down to gravel and sand, in a groundmass of finely-divided clayey material sometimes called glacial flour. Lateral moraines are those formed at the side of the ice flow, and terminal moraines were formed at the foot, marking the maximum advance of the glacier. Other types of moraine include ground moraines (till-covered areas forming sheets on flat or irregular topography) and medial moraines (moraines formed where two glaciers meet). Etymology The word ''moraine'' is borrowed from French , which in turn is derived from the Savoyard Italian ("mound of earth"). ''Morena'' in this case was derived from ProvenĂ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides have deep hills or escarpments. Plateaus can be formed by a number of processes, including upwelling of volcanic magma, extrusion of lava, and erosion by water and glaciers. Plateaus are classified according to their surrounding environment as intermontane, piedmont, or continental. A few plateaus may have a small flat top while others have wide ones. Formation Plateaus can be formed by a number of processes, including upwelling of volcanic magma, extrusion of lava, Plate tectonics movements and erosion by water and glaciers. Volcanic Volcanic plateaus are produced by volcanic activity. The Columbia Plateau in the north-western United States is an example. They may be formed by upwelling of volcanic magma or extrusion of lava. The un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urstromtal
An ''urstromtal'' (plural: ''Urstromtäler'') is a type of broad glacial valley, for example, in northern Central Europe, that appeared during the ice ages, or individual glacial periods of an ice age, at the edge of the Scandinavian ice sheet and was formed by meltwaters that flowed more or less parallel to the ice margin. ''Urstromtäler'' are an element of the glacial series. The term is German and means "ancient stream valley". Although often translated as "glacial valley", it should not be confused with a valley carved out by a glacier. More accurately some sources call them "meltwater valleys" or "ice-marginal valleys". Emergence and structure Important for the emergence of the ''Urstromtäler'' is the fact that the general lie of the land on the North German Plain and in Poland slopes down from south to north. Thus the ice sheet that advanced from Scandinavia flowed into a rising terrain. The meltwaters could therefore only flow for a short distance southwards over the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhin Wassersuppe
The Rhin is a long river in Brandenburg, Germany, right tributary to the river Havel. It flows through the city Neuruppin and several lakes. A few kilometres downstream from Rhinow it flows into the Havel, about upstream from where the Havel meets the Elbe. File:Zermuetzel_bridge_Rhin.jpg, In Neuruppin-ZermĂĽtzel File:Wustrau_Wustrauer_Rhin.jpg, Wustrauer Rhin in Fehrbellin Fehrbellin is a municipality in Germany, located 60 km NW of Berlin. It had 9,310 inhabitants as of 2005, but has since declined to 8,606 inhabitants in 2012. History In 1675, the Battle of Fehrbellin was fought there, in which the troops o ...-Wustrau File:Fehrbellin_Wustrauer_Rhin.jpg, Wustrauer Rhin in Fehrbellin File:Fehrbellin_Wall_bridge.jpg, BĂĽtzrhin near Fehrbellin-Wall Rivers of Brandenburg Rivers of Germany {{Brandenburg-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |