|
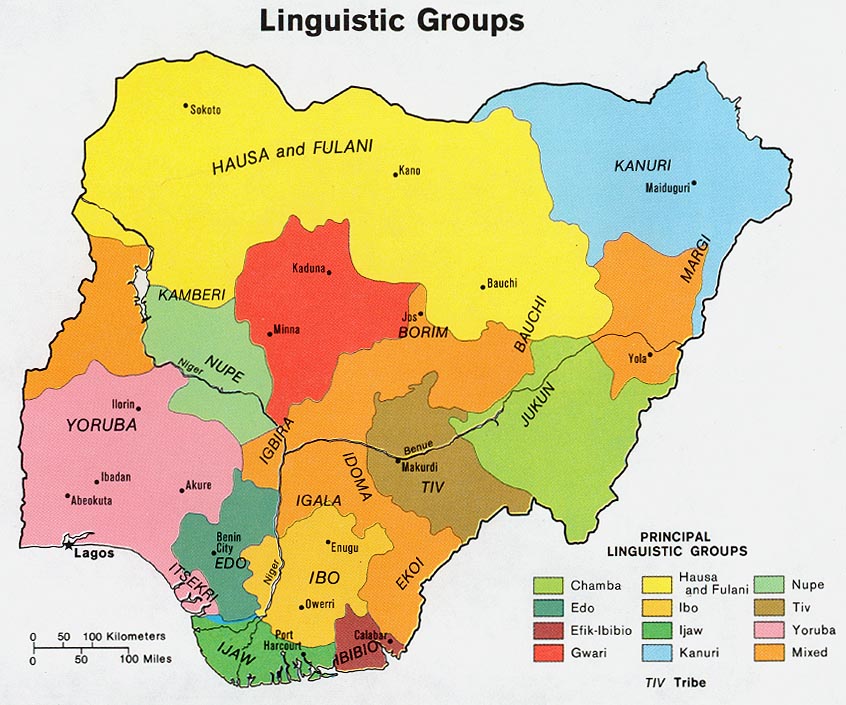
Hausa Braille
Several braille alphabets are used in Nigeria. For English, Unified English Braille has been adopted. Three other languages have been written in braille: Hausa language, Hausa, Igbo language, Igbo, and Yoruba language, Yoruba. All three alphabets are based on English readings, with the addition of letters particular to these languages. Punctuation is as in English Braille. : The letters of these languages beyond the ISO basic Latin alphabet, basic Latin alphabet are as follows: Hausa Braille Hausa includes from English ''q, sh, st, ed'' (international second ''d''), and three derived letters: Hausa is presumably written in braille in Niger as well, since ''Ethnologue'' 17 reports that Zarma language, Zarma is written in braille in that country. However, this need not mean it uses the same alphabet as Nigerian Hausa. Igbo Braille Igbo Braille has from English ''q, ch, gh, sh,'' and six other letters with common international braille, international/African values ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Braille
Braille (Pronounced: ) is a tactile writing system used by people who are visually impaired, including people who are blind, deafblind or who have low vision. It can be read either on embossed paper or by using refreshable braille displays that connect to computers and smartphone devices. Braille can be written using a slate and stylus, a braille writer, an electronic braille notetaker or with the use of a computer connected to a braille embosser. Braille is named after its creator, Louis Braille, a Frenchman who lost his sight as a result of a childhood accident. In 1824, at the age of fifteen, he developed the braille code based on the French alphabet as an improvement on night writing. He published his system, which subsequently included musical notation, in 1829. The second revision, published in 1837, was the first binary form of writing developed in the modern era. Braille characters are formed using a combination of six raised dots arranged in a 3 × 2 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igbo Alphabet
The modern Igbo alphabet (Igbo: ''Mkpụrụ Edemede Igbo''), otherwise known as the Igbo alphabet (Igbo: ''Mkpụrụ Edemede'' ''Igbo''), is the alphabet of the Igbo language, it is one of the three national languages of Nigeria. The modern Igbo alphabet is made up of 36 letters, which includes only a 23-letter set of the ISO basic Latin alphabet minus C, Q, and X, which are not part of Abidịị Igbo. The alphabet uses the dot above on the letter Ṅ, and the dot below on Ị, Ọ and Ụ. There are numerous Igbo dialects, some of which are not mutually intelligible. The standard written form of Igbo is based on the Owerri and Umuahia dialects. A ''New Standard Orthography'' has been proposed for Igbo, and it was used, for example, in the 1998 ''Igbo English Dictionary'' by Michael Echeruo, but it has not been otherwise widely adopted. In this orthography, diaeresis replaces the dot below (ï ö ü), and the ch digraph is not used. Letters The 36-letter alphabet is ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Braille
The goal of braille uniformity is to unify the braille alphabets of the world as much as possible, so that literacy in one braille alphabet readily transfers to another. Unification was first achieved by a convention of the ''International Congress on Work for the Blind'' in 1878, where it was decided to replace the mutually incompatible national conventions of the time with the French values of the basic Latin alphabet, both for languages that use Latin-based alphabets and, through their Latin equivalents, for languages that use other scripts. However, the unification did not address letters beyond these 26, leaving French and German Braille partially incompatible and as braille spread to new languages with new needs, national conventions again became disparate. A second round of unification was undertaken under the auspices of UNESCO in 1951, setting the foundation for international braille usage today. Numerical order Braille arranged his characters in decades (groups of ten) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yoruba Alphabet
The Yoruba alphabet (Yoruba: ''Álífábẹ́ẹ̀tì Yorùbá'') is either of two Latin alphabets used to write the Yoruba language, one in Nigeria and one in neighboring Benin. The Nigerian Yoruba alphabet is made up of 25 letters, without C Q V X Z but with the additions of Ẹ, Ọ, Ṣ and Gb. However, many of the excluded consonants are present in several dialectal forms of Yoruba, including V, Z, and other digraphs (like ch, gh, and gw). Central Yoruba dialects also have 2 extra vowels that are allophones of I and U. It is somewhat unusual in that the letter P usually transcribes , being only in restricted situations like onomatopoeia. The Beninese alphabet has the letters Ɛ and Ɔ, and previously had C. Sounds The nasal vowels are written with digraphs: , , , , , unless they come after . Long vowels are written double, as in (). The high and low tones are written with acute and grave accents (á, à), while mid tone is unmarked (a), except for disambiguation on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabiye Braille
Kabye may refer to: * Kabye people * Kabye language Kabiye (; also rendered ''Kabiyé'', ''Kabiyè'', ''Kabye'', ''Kabyé'', ''Kabyè'', ''Cabrai'' or ''Cabrais'') is an Eastern Gurunsi Gur language spoken primarily in northern Togo. Throughout the 20th century, there was extensive migration to ... {{disambig Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Braille
The goal of braille uniformity is to unify the braille alphabets of the world as much as possible, so that literacy in one braille alphabet readily transfers to another. Unification was first achieved by a convention of the ''International Congress on Work for the Blind'' in 1878, where it was decided to replace the mutually incompatible national conventions of the time with the French values of the basic Latin alphabet, both for languages that use Latin-based alphabets and, through their Latin equivalents, for languages that use other scripts. However, the unification did not address letters beyond these 26, leaving French and German Braille partially incompatible and as braille spread to new languages with new needs, national conventions again became disparate. A second round of unification was undertaken under the auspices of UNESCO in 1951, setting the foundation for international braille usage today. Numerical order Braille arranged his characters in decades (groups of ten) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zarma Language
Zarma (also spelled Djerma, Jerma, Dyabarma, Dyarma, Dyerma, Adzerma, Zabarma, Zarbarma, Zarmaci or Zerma) is one of the Songhay languages. It is the leading indigenous language of the southwestern lobe of the West African nation of Niger, where the Niger River flows and the capital city, Niamey, is located. Zarma is the second-most common language in the country, after Hausa, which is spoken in south-central Niger. With over 2 million speakers, Zarma is easily the most widely spoken Songhay language. In earlier decades, Zarma was rendered ''Djerma'', using French orthography, but it is usually now 'Zarma', the form that the Zarma people use in their language. Geographic distribution The majority of people who speak Zarma live in Southwestern Niger. It is also spoken in other parts of Niger and in neighbouring countries. Cities where Zarma is spoken include Tillaberi, Dosso, Niamey, Tahoua and Agadez. In Nigeria, where the Zarma people are usually referred to as Zabarma or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unified English Braille
Unified English Braille Code (UEBC, formerly UBC, now usually simply UEB) is an English language Braille code standard, developed to permit representing the wide variety of literary and technical material in use in the English-speaking world today, in uniform fashion. Background on why the new encoding standard was developed Standard 6-dot braille only provides 63 distinct characters (not including the space character), and thus, over the years a number of distinct rule-sets have been developed to represent literary text, mathematics, scientific material, computer software, the @ symbol used in email addresses, and other varieties of written material. Different countries also used differing encodings at various times: during the 1800s American Braille competed with English Braille and New York Point in the ''War of the Dots''. As a result of the expanding need to represent technical symbolism, and divergence during the past 100 years across countries, braille users who desi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hausa Alphabet
Hausa (; /; Ajami: ) is a Chadic language spoken by the Hausa people in the northern half of Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Benin and Togo, and the southern half of Niger, Chad and Sudan, with significant minorities in Ivory Coast. Hausa is a member of the Afroasiatic language family and is the most widely spoken language within the Chadic branch of that family. Ethnologue estimated that it was spoken as a first language by some 47 million people and as a second language by another 25 million, bringing the total number of Hausa speakers to an estimated 72 million. In Nigeria, the Hausa-speaking film industry is known as Kannywood. Classification Hausa belongs to the West Chadic languages subgroup of the Chadic languages group, which in turn is part of the Afroasiatic language family. Geographic distribution Native speakers of Hausa, the Hausa people, are mostly found in southern Niger and northern Nigeria. The language is used as a lingua franca by non-native speak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Braille
English Braille, also known as ''Grade 2 Braille'', is the braille alphabet used for English. It consists of around 250 letters ( phonograms), numerals, punctuation, formatting marks, contractions, and abbreviations ( logograms). Some English Braille letters, such as , correspond to more than one letter in print. There are three levels of complexity in English Braille. Grade 1 is a nearly one-to-one transcription of printed English and is restricted to basic literacy. Grade 2, which is nearly universal beyond basic literacy materials, abandons one-to-one transcription in many places (such as the letter ) and adds hundreds of abbreviations and contractions. Both Grade 1 and Grade 2 have been standardized. "Grade 3" is any of various personal shorthands that are almost never found in publications. Most of this article describes the 1994 American edition of Grade 2 Braille, which is largely equivalent to British Grade 2 Braille. Some of the differences with Unified English Br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |