|
Hasan Tahsin Pasha
Hasan Tahsin Pasha (1845–1918), also known as Hasan Tahsin Mesarea, was a senior Ottoman military officer, who served in the Greco-Turkish War of 1897, and in the First Balkan War. Biography and career Hasan Tahsin was an Albanian, born in Mesare (located in Albania on the border with Greece), which at the time was part of the ''kaza'' of Leskovik. During his youth, he attended and graduated from the Greek Zosimaia School at Ioannina, and spoke Greek fluently. He began service as a gendarme ca. 1870 in Katerini, and later joined the Ottoman Army as an NCO. He soon received a commission as an officer, and by 1881 he commanded the Ottoman Gendarmerie at Ioannina. During the Greco-Turkish War of 1897, he commanded the 6th Trabzon Division, and around 1900, he was placed as garrison commander of Thessaloniki. In 1908–1910, he served as the governor of Yemen before returning to Thessaloniki, where he assumed the post of commanding officer of the III Corps with the rank of ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Çarçovë
Çarçovë (also Çarshovë; el, Τσαρτσόβα ''Tsartsova'' or Κεράσοβο/''Kerasovo''; rup, Ciarshova) is a village, a municipal unit and a former municipality in the Gjirokastër County, southern Albania. Demographics The population of the former municipality at the 2011 census was 918. The total number of registered citizens of Çarçovë is 2.969 as of 2019. At the 2015 local government reform it became a subdivision of the municipality Përmet. The municipal unit consists of the villages Çarçovë, Vllaho-Psilloterë, Biovizhdë, Zhepë, Draçovë, Iliar-Munushtir, Strëmbec, Pëllumbar and Kanikol. The town of Çarçovë also has Greek and Aromanian communities. Two villages in the former municipality of Çarçovë are predominantly Greek speaking, in particular: Biovizhdë and Vllaho-Psilloterë. In Biovizhdë there is a significant Aromanian minority population. Their presence was originally temporary, related to their transhumant lifestyle, before becomi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Gendarmerie
The Ottoman Gendarmerie ( tr, Jandarma), also known as ''zaptı'', was a security and public order organization (a precursor to law enforcement) in the 19th-century Ottoman Empire. The first official gendarmerie organization was founded in 1869. History After the abolition of the Janissary corps of the Ottoman Empire in 1826, military organizations called ''Asâkir-i Muntazâma-i Mansûre'', ''Asâkir-i Muntazâma-i Hâssa'', and, in 1834, ''Asâkir-i Redîfe'' were established to deliver security and public order services in Anatolia and in some provinces of Rumelia. Since the term Gendarmerie was noticed only in the Assignment Decrees published in the years following the declaration of Tanzimat in 1839, it is assumed that the Gendarmerie organization was founded after that year, but the exact date of foundation has not yet been determined. Therefore, taking the June 14 of "June 14, 1869", on which ''Asâkir-i Zaptiye Nizâmnâmesi'' was adopted, June 14, 1839 was accepted as th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gefyra, Thessaloniki
Gefyra ( el, Γέφυρα, literally meaning "Bridge", until 1926 ''Τοψίν''/''Topsin'', bg, Топчиево/''Topchievo'', tr, Topçin) is a village and a community of the Chalkidona municipality, about 20 km northwest from Thessaloniki. Before the 2011 local government reform it was part of the municipality of Agios Athanasios, of which it was a municipal district. The 2011 census recorded 3,059 inhabitants in the community. The community of Gefyra covers an area of 29.836 km2. There is a highway junction near Gefyra, where the European route E75 and E86 meets. History The village is the site of the surrender of the Ottoman garrison of Thessaloniki under Hasan Tahsin Pasha to the Greek army under Crown Prince Constantine during the First Balkan War (1912). The villa where the surrender took place now houses the Balkan Wars Museum. See also * List of settlements in the Thessaloniki regional unit This is a list of settlements in the Thessaloniki regional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottomans Surrender In Salonique 1912 2
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922). Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, but they take their Turkish name, ''Osmanlı'' ("Osman" became altered in some European languages as "Ottoman"), from the house of Osman I (reigned 1299–1326), the founder of the House of Osman, the ruling dynasty of the Ottoman Empire for its entire 624 years. Expanding from its base in Söğüt, the Ottoman principality began incorporating other Turkish-speaking Muslims and non-Turkish Christians. Crossing into Europe from the 1350s, coming to dominate the Mediterranean Sea and, in 1453, invading Constantinople (the capital city of the Byzantine Empire), the Ottoman Turks blocked all major land routes between Asia and Europe. Western Europeans had to find other ways to trade with the East. Brief history The "Ottomans" first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th Rila Infantry Division
7 (seven) is the natural number following 6 and preceding 8. It is the only prime number preceding a cube. As an early prime number in the series of positive integers, the number seven has greatly symbolic associations in religion, mythology, superstition and philosophy. The seven Classical planets resulted in seven being the number of days in a week. It is often considered lucky in Western culture and is often seen as highly symbolic. Unlike Western culture, in Vietnamese culture, the number seven is sometimes considered unlucky. It is the first natural number whose pronunciation contains more than one syllable. Evolution of the Arabic digit In the beginning, Indians wrote 7 more or less in one stroke as a curve that looks like an uppercase vertically inverted. The western Ghubar Arabs' main contribution was to make the longer line diagonal rather than straight, though they showed some tendencies to making the digit more rectilinear. The eastern Arabs developed the digit fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
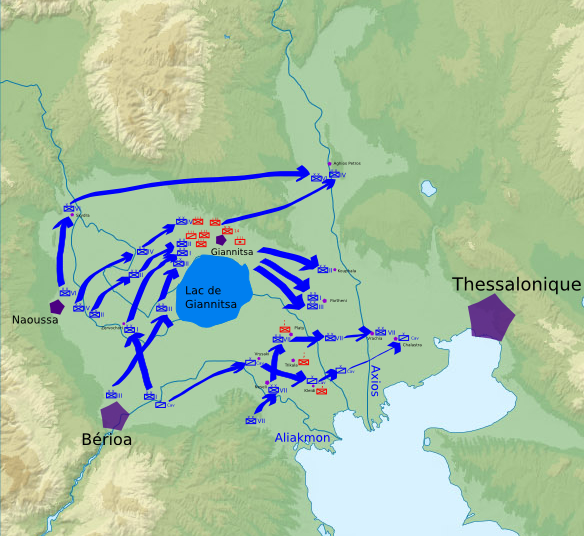
Battle Of Yenidje
The Battle of Yenidje, also transliterated as Yenice ( el, Μάχη των Γιαννιτσών, Battle of Giannitsa), was a major battle between Greek forces under Crown Prince Constantine and Ottoman forces under General Hasan Tahsin Pasha and took place between October 19–20 ( O.S.), 1912 during the First Balkan War. The battle began when the Greek army attacked the Ottoman fortified position at Yenidje (now Giannitsa, Greece), which was the last line of defense for the city of Thessaloniki. The rough and swampy terrain surrounding Yenidje significantly complicated the advance of the Greek army, most notably its artillery. In the early morning of 20 October, an infantry charge by the Greek 9th Evzone Battalion caused the Greek army to gain momentum, leading to the collapse of the entire western wing of the Ottomans. Ottoman morale plunged and the bulk of the defenders began fleeing two hours later. The Greek victory at Yenidje opened the way for the capture of Thessaloniki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Sarantaporo
The Battle of Sarantaporo, also variously transliterated as Sarantaporon or Sarandaporon ( el, Μάχη του Σαρανταπόρου, tr, Sarantaporo Muharebesi, links=no), took place on 9–10 October, 1912. It was the first major battle fought between Greek forces under Crown Prince Constantine and Ottoman forces under General Hasan Tahsin Pasha during the First Balkan War. The battle began when the Greek army attacked the Ottoman defensive line at the Sarantaporo pass, which connected Thessaly with central Macedonia. Despite being perceived as impregnable by its defenders, the main body of the Greek forces managed to advance deep inside the pass, while auxiliary units broke through the Ottoman flanks. The Ottomans abandoned their defensive line during the night, fearing encirclement. The Greek victory at Sarantaporo opened the way for the capture of Servia and Kozani. Background Following the conclusion of the Greek War of Independence, the Megali Idea (Great Idea) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constantine I Of Greece
Constantine I ( el, Κωνσταντίνος Αʹ, ''Konstantínos I''; – 11 January 1923) was King of Greece from 18 March 1913 to 11 June 1917 and from 19 December 1920 to 27 September 1922. He was commander-in-chief of the Hellenic Army during the unsuccessful Greco-Turkish War of 1897 and led the Greek forces during the successful Balkan Wars of 1912–1913, in which Greece expanded to include Thessaloniki, doubling in area and population. He succeeded to the throne of Greece on 18 March 1913, following his father's assassination. Constantine’s disagreement with Eleftherios Venizelos over whether Greece should enter World War I led to the National Schism. He forced Venizelos to resign twice, but in 1917 he left Greece, after threats by the Entente forces to bombard Athens; his second son, Alexander, became king. After Alexander's death, Venizelos' defeat in the 1920 legislative elections, and a plebiscite in favor of his return, Constantine was reinstated. He abd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of Thessaly
The Army of Thessaly ( el, Στρατιά Θεσσαλίας) was a field army of Greece, activated in Thessaly during the Greco-Turkish War of 1897 and the First Balkan War in 1912, both times against the Ottoman Empire and commanded by Crown Prince Constantine. 1897 In preparation for the war, two of the three infantry divisions in the Hellenic Army, 1st Infantry Division under Major General Nikolaos Makris and 2nd Infantry Division under Colonel Georgios Mavromichalis were mobilized and moved to Larissa and Trikala respectively. On 25 March, Crown Prince Constantine was named commander-in-chief of the Army of Thessaly, comprising these two divisions and support units, with Colonel Konstantinos Sapountzakis as his chief of staff. The Army of Thessaly comprised 36,000 men, 500 cavalry and 96 guns. When hostilities broke out on 18 April, the Army of Thessaly was defeated in successive battles on the border passes, the Battle of Farsala and the Battle of Domokos. By the time o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VIII Corps (Ottoman Empire)
The VIII Corps of the Ottoman Empire (Turkish: ''8 nci Kolordu'' ''or'' ''Sekizinci Kolordu'') was one of the corps of the Ottoman Army. It was formed in the early 20th century as part of the Ottoman military reforms. Formation Order of Battle, 1911 With further reorganizations of the Ottoman Army, to include the creation of corps level headquarters, by 1911 the VIII Corps was headquartered in Damascus. The Corps before the First Balkan War in 1911 was structured as such:Edward J. Erickson, ''Defeat in Detail, The Ottoman Army in the Balkans, 1912–1913'', Westport, Praeger, 2003, p. 379. *VIII Corps, Damascus ** 25th Division, Dera ***73rd Infantry Regiment, Dera ***74th Infantry Regiment, Suveydiye ***75th Infantry Regiment, Kerek ***25th Rifle Battalion, Maan ***25th Division Band, Dera ** 26th Division, Halep ***76th Infantry Regiment, Halep ***77th Infantry Regiment, Maraş ***78th Infantry Regiment, Adana ***26th Rifle Battalion, Halep ***26th Field Artillery Regim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balkan League
The League of the Balkans was a quadruple alliance formed by a series of bilateral treaties concluded in 1912 between the Eastern Orthodox kingdoms of Greece, Bulgaria, Serbia and Montenegro, and directed against the Ottoman Empire, which at the time still controlled much of Southeastern Europe. The Balkans had been in a state of turmoil since the early 1900s, with years of guerrilla warfare in Macedonia followed by the Young Turk Revolution, the protracted Bosnian Crisis, and several Albanian Uprisings. The outbreak of the Italo-Turkish War in 1911 had further weakened the Ottomans and emboldened the Balkan states. Under Russian influence, Serbia and Bulgaria settled their differences and signed an alliance, originally directed against Austria-Hungary on 13 March 1912,Crampton (1987) but by adding a secret chapter to it essentially redirected the alliance against the Ottoman Empire. Serbia then signed a mutual alliance with Montenegro, while Bulgaria did the same with Greece. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)