|
Hartmut Ehrig
Hartmut Ehrig (born 6 December 1944 in Angermünde; died 17 March 2016) was a German computer scientist and professor of theoretical computer science and formal specification. He was a pioneer in algebraic specification of abstract data types, and in graph grammars. Vita In 1969, Ehrig received his diploma in mathematics from the Technical University (TU) of Berlin. In 1971, he earned his doctorate, and in 1974 his habilitation from the same university. Subsequently, he had research stays at the Thomas J. Watson Research Center, among others. In 1976, he became a lecturer at the TU Berlin, and the director of its Institute for Software Engineering and Theoretical Computer Science. In 1984, he was appointed full professor at the TU Berlin. Between 1981 and 1991, he was also Dean of its Department of Computer Science for several periods. He was EATCS The European Association for Theoretical Computer Science (EATCS) is an international organization with a European focus, founded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angermünde
Angermünde () is a town in the district of Uckermark in the state of Brandenburg, Germany. It is about northeast of Berlin, the capital of Germany. The population is about 14,000, but has been declining since its traditional industrial base, enamel-working, has declined. An administrative sub-centre of its district, it has several Protestant churches, a former Franciscan church, a number of schools of higher learning and a recently refurbished historic marketplace with an old town hall. Located in the game-filled forests of the Uckermark, with its many lakes, it now relies heavily on tourism and the sources of revenue linked to it. Since 2010, Angermünde is a federally declared resort town. Name The name Angermünde is an abbreviation of the older town of Tangermünde, for a while the town was named New-Tangermünde (''Neu-Tangermünde''), until it was changed to "Angermünde", with ''Anger'' being German for a central square in a town. Geography With an area of around 3 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technical University Of Berlin
The Technical University of Berlin (official name both in English and german: link=no, Technische Universität Berlin, also known as TU Berlin and Berlin Institute of Technology) is a public research university located in Berlin, Germany. It was the first German university to adopt the name "Technische Universität" (Technical University). The university alumni and professor list includes several US National Academies members, two National Medal of Science laureates and ten Nobel Prize laureates. TU Berlin is a member of TU9, an incorporated society of the largest and most notable German institutes of technology and of the Top International Managers in Engineering network, which allows for student exchanges between leading engineering schools. It belongs to the Conference of European Schools for Advanced Engineering Education and Research. The TU Berlin is home of two innovation centers designated by the European Institute of Innovation and Technology. The university is labeled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Computer Scientists
German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) **Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman times) * German language **any of the Germanic languages * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (other) * Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2016 Deaths
This is a list of deaths of notable people, organised by year. New deaths articles are added to their respective month (e.g., Deaths in ) and then linked here. 2022 2021 2020 2019 2018 2017 2016 2015 2014 2013 2012 2011 2010 2009 2008 2007 2006 2005 2004 2003 2002 2001 2000 1999 1998 1997 1996 1995 1994 1993 1992 1991 1990 1989 1988 1987 See also * Lists of deaths by day The following pages, corresponding to the Gregorian calendar, list the historical events, births, deaths, and holidays and observances of the specified day of the year: Footnotes See also * Leap year * List of calendars * List of non-standard ... * Deaths by year {{DEFAULTSORT:deaths by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1944 Births
Events Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix. January * January 2 – WWII: ** Free France, Free French General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny is appointed to command First Army (France), French Army B, part of the Sixth United States Army Group in North Africa. ** Landing at Saidor: 13,000 US and Australian troops land on Papua New Guinea, in an attempt to cut off a Japanese retreat. * January 8 – WWII: Philippine Commonwealth troops enter the province of Ilocos Sur in northern Luzon and attack Japanese forces. * January 11 ** President of the United States Franklin D. Roosevelt proposes a Second Bill of Rights for social and economic security, in his State of the Union address. ** The Nazi German administration expands Kraków-Płaszów concentration camp into the larger standalone ''Konzentrationslager Plaszow bei Krakau'' in occupied Poland. * January 12 – WWII: Winston Churchill and Charles de Gaulle begin a 2-day conference in Marrakech ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symposium On Switching And Automata Theory
The IEEE Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science (FOCS) is an academic conference in the field of theoretical computer science. FOCS is sponsored by the IEEE Computer Society. As writes, FOCS and its annual Association for Computing Machinery counterpart STOC (the Symposium on Theory of Computing) are considered the two top conferences in theoretical computer science, considered broadly: they “are forums for some of the best work throughout theory of computing that promote breadth among theory of computing researchers and help to keep the community together.” includes regular attendance at FOCS and STOC as one of several defining characteristics of theoretical computer scientists. Awards The Knuth Prize for outstanding contributions to theoretical computer science is presented alternately at FOCS and STOC. Works of the highest quality presented at the conference are awarded the Best Paper Award. In addition, the Machtey Award is presented to the best student- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EATCS
The European Association for Theoretical Computer Science (EATCS) is an international organization with a European focus, founded in 1972. Its aim is to facilitate the exchange of ideas and results among theoretical computer scientists as well as to stimulate cooperation between the theoretical and the practical community in computer science. The major activities of the EATCS are: * Organization of ICALP, the International Colloquium on Automata, Languages and Programming;Brauer, Ute; Brauer, WilfriedEuropean Association for Theoretical Computer Science / About the Association / Silver Jubilee of EATCS/ref> * Publication of the ''Bulletin of the EATCS''; * Publication of a series of monographs and texts on theoretical computer science; * Publication of the journal ''Theoretical Computer Science''; * Publication of the journal ''Fundamenta Informaticae''. EATCS Award Each year, the EATCS Award is awarded in recognition of a distinguished career in theoretical computer science. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas J
Clarence Thomas (born June 23, 1948) is an American jurist who serves as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States. He was nominated by President George H. W. Bush to succeed Thurgood Marshall and has served since 1991. After Marshall, Thomas is the second African American to serve on the Court and its longest-serving member since Anthony Kennedy's retirement in 2018. Thomas was born in Pin Point, Georgia. After his father abandoned the family, he was raised by his grandfather in a poor Gullah community near Savannah. Growing up as a devout Catholic, Thomas originally intended to be a priest in the Catholic Church but was frustrated over the church's insufficient attempts to combat racism. He abandoned his aspiration of becoming a clergyman to attend the College of the Holy Cross and, later, Yale Law School, where he was influenced by a number of conservative authors, notably Thomas Sowell, who dramatically shifted his worldview from progressive to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
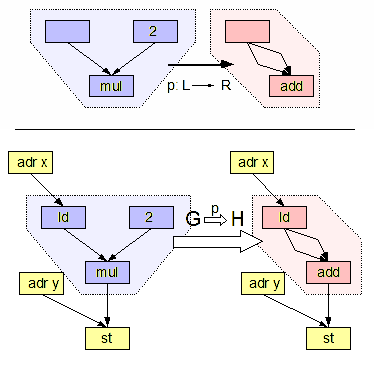
Graph Grammar
In computer science, graph transformation, or graph rewriting, concerns the technique of creating a new graph out of an original graph algorithmically. It has numerous applications, ranging from software engineering (software construction and also software verification) to layout algorithms and picture generation. Graph transformations can be used as a computation abstraction. The basic idea is that if the state of a computation can be represented as a graph, further steps in that computation can then be represented as transformation rules on that graph. Such rules consist of an original graph, which is to be matched to a subgraph in the complete state, and a replacing graph, which will replace the matched subgraph. Formally, a graph rewriting system usually consists of a set of graph rewrite rules of the form L \rightarrow R, with L being called pattern graph (or left-hand side) and R being called replacement graph (or right-hand side of the rule). A graph rewrite rule is applie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebraic Specification
Algebraic specification is a software engineering technique for formally specifying system behavior. It was a very active subject of computer science research around 1980. Overview Algebraic specification seeks to systematically develop more efficient programs by: # formally defining types of data, and mathematical operations on those data types # abstracting implementation details, such as the size of representations (in memory) and the efficiency of obtaining outcome of computations # formalizing the computations and operations on data types # allowing for automation by formally restricting operations to this limited set of behaviors and data types. An algebraic specification achieves these goals by defining one or more data types, and specifying a collection of functions that operate on those data types. These functions can be divided into two classes: # Constructor functions: Functions that create or initialize the data elements, or construct complex elements from simpler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abstract Data Type
In computer science, an abstract data type (ADT) is a mathematical model for data types. An abstract data type is defined by its behavior (Semantics (computer science), semantics) from the point of view of a ''User (computing), user'', of the data, specifically in terms of possible values, possible operations on data of this type, and the behavior of these operations. This mathematical model contrasts with data structures, which are concrete representations of data, and are the point of view of an implementer, not a user. Formally, an ADT may be defined as a "class of objects whose logical behavior is defined by a set of values and a set of operations"; this is analogous to an algebraic structure in mathematics. What is meant by "behaviour" varies by author, with the two main types of formal specifications for behavior being ''axiomatic (algebraic) specification'' and an ''abstract model;'' these correspond to axiomatic semantics and operational semantics of an abstract machine, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algebraic Specification
Algebraic specification is a software engineering technique for formally specifying system behavior. It was a very active subject of computer science research around 1980. Overview Algebraic specification seeks to systematically develop more efficient programs by: # formally defining types of data, and mathematical operations on those data types # abstracting implementation details, such as the size of representations (in memory) and the efficiency of obtaining outcome of computations # formalizing the computations and operations on data types # allowing for automation by formally restricting operations to this limited set of behaviors and data types. An algebraic specification achieves these goals by defining one or more data types, and specifying a collection of functions that operate on those data types. These functions can be divided into two classes: # Constructor functions: Functions that create or initialize the data elements, or construct complex elements from simpler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |