|
Hartlepool Borough Hall
Hartlepool Borough Hall is municipal building, which served as the meeting place of the old Hartlepool Borough Council, before it amalgamated with West Hartlepool County Borough Council. It is located on the Headland, Hartlepool in County Durham, England and is a Grade II listed building. History Following significant population growth, largely associated with its status as a seaport, Hartlepool became a municipal borough in 1850. In this context, the new civic leaders decided to commission a new market hall for the old part of the town, also known as the Headland: the site they chose was a street known as Johnny's Close. The foundation stone for the new building was laid on 10 August 1865. It was designed by Charles J. Adams in the Italianate style, built in red brick with stone dressings at a cost of £5,000 and was officially opened by the mayor, James Groves, on 4 October 1866. The design involved a symmetrical main frontage with eleven bays facing onto Middlegate; the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headland, Hartlepool
Headland is a civil parish in the borough of Hartlepool, County Durham, in the North East of England. The parish covers old Hartlepool and nearby villages. History The Heugh Battery, one of three constructed to protect the port of Hartlepool in 1860, is located in the area along with a museum. The area made national headlines in July 1994 in connection with the murder of Rosie Palmer, a local toddler. On 19 March 2002 the Time Team searched for an Anglo-Saxon monastery. See also * St Mary's Church, Hartlepool St Mary's Church or the Church of the Immaculate Conception is a Roman Catholic Parish church in Headland, Hartlepool, County Durham, England. It was built in 1850 and designed by Joseph Hansom in the Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival st ... References External links Civil parishes in County Durham Hartlepool {{Hartlepool-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonette
A colonnette is a small slender column, usually decorative, which supports a beam or lintel. Colonettes have also been used to refer to a feature of furnishings such as a dressing table and case clock, and even studied by archeologists in Roman ceramics. Architectural colonnettes are typically found in "a group in a parapet, balustrade, or cluster pier". The term columnette has also been used to refer to thin columns. In Khmer art, the colonnette designates in particular the columns which frame the doors of the sanctuaries and which are one of the dating elements of their style. Summits of complexity were attained in the development of the Khmer colonnette, according to Philippe Stern: Etymology The -''ette'' suffix, from French language, is a diminutive, which can also have a condescending connotation: in our case, it shifts the meaning from column to small column or fake columns. In the field of Angkorian archeology, Edme Casimir de Croizier was the first to use the name o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City And Town Halls In County Durham
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Buildings Completed In 1866
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state. In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is a means by which organizational policies are enforced, as well as a mechanism for determining policy. In many countries, the government has a kind of constitution, a statement of its governing principles and philosophy. While all types of organizations have governance, the term ''government'' is often used more specifically to refer to the approximately 200 independent national governments and subsidiary organizations. The major types of political systems in the modern era are democracies, monarchies, and authoritarian and totalitarian regimes. Historically prevalent forms of government include monarchy, aristocracy, timocracy, oligarchy, democracy, theocracy, and tyranny. These forms are not always mutually exclusive, and mixed governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Question Time (TV Programme)
''Question Time'' is a topical debate programme, typically broadcast on BBC One at 10:45 pm on Thursdays. It is usually repeated on BBC Two (with sign language) and on BBC Parliament, later in the week. If there is a Leaders special, it would be simulcasted on BBC News. ''Question Time'' is also available on BBC iPlayer. Fiona Bruce currently chairs the show having succeeded David Dimbleby as presenter in January 2019. Mentorn has produced the programme since 1998. Origins ''Question Time'' was first broadcast on Tuesday 25 September 1979, based on the BBC Radio 4 programme '' Any Questions?''. The first panel consisted of Labour MP Michael Foot, author Edna O'Brien, Conservative politician Teddy Taylor, and the Archbishop of Liverpool Derek Worlock. Format ''Question Time'' panels are typically composed of five public figures, "nearly always ncludinga representative from the UK government and the official opposition." The panel also features "representatives from oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morrissey
Steven Patrick Morrissey (; born 22 May 1959), known professionally as Morrissey, is an English singer and songwriter. He came to prominence as the frontman and lyricist of rock band the Smiths, who were active from 1982 to 1987. Since then, he has pursued a successful solo career. Morrissey's music is characterised by his baritone voice and distinctive lyrics with recurring themes of emotional isolation, sexual longing, self-deprecating and dark humour, and anti-establishment stances. Born to working-class Irish immigrants in Davyhulme, Lancashire, Morrissey grew up in nearby Manchester. As a child, he developed a love of literature, kitchen sink realism, and 1960s pop music. In the late 1970s, he fronted punk rock band the Nosebleeds with little success before beginning a career in music journalism and writing several books on music and film in the early 1980s. He formed the Smiths with Johnny Marr in 1982 and the band soon attracted national recognition for their e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hansard
''Hansard'' is the traditional name of the transcripts of parliamentary debates in Britain and many Commonwealth countries. It is named after Thomas Curson Hansard (1776–1833), a London printer and publisher, who was the first official printer to the Parliament at Westminster. Origins Though the history of the ''Hansard'' began in the British parliament, each of Britain's colonies developed a separate and distinctive history. Before 1771, the British Parliament had long been a highly secretive body. The official record of the actions of the House was publicly available but there was no record of the debates. The publication of remarks made in the House became a breach of parliamentary privilege, punishable by the two Houses of Parliament. As the populace became interested in parliamentary debates, more independent newspapers began publishing unofficial accounts of them. The many penalties implemented by the government, including fines, dismissal, imprisonment, and investiga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Hartlepool Town Hall
West Hartlepool Town Hall is a municipal building in Raby Road, Hartlepool, County Durham, England. The town hall, which was the meeting place of West Hartlepool County Borough Council, is a Grade II listed building. History The development of West Hartlepool was an initiative of Ralph Ward Jackson, who founded the West Hartlepool Dock Company and opened the Coal Dock to the south west of Old Hartlepool in 1847. By the 1880s West Hartlepool was over twice the size of Old Hartlepool and the Town Improvement Commissioners decided to procure a town hall dedicated to West Hartlepool: the site they selected was open land to the west of Hart Lane (subsequently renamed Raby Road). The foundation stone for the new building was laid by Councillor George Pyman on 18 December 1895. It was designed by Henry Cheers in the English Gothic style, built in red brick with stone dressings and was officially opened as West Hartlepool Town Hall on 1 October 1897. It was built in conjunction with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
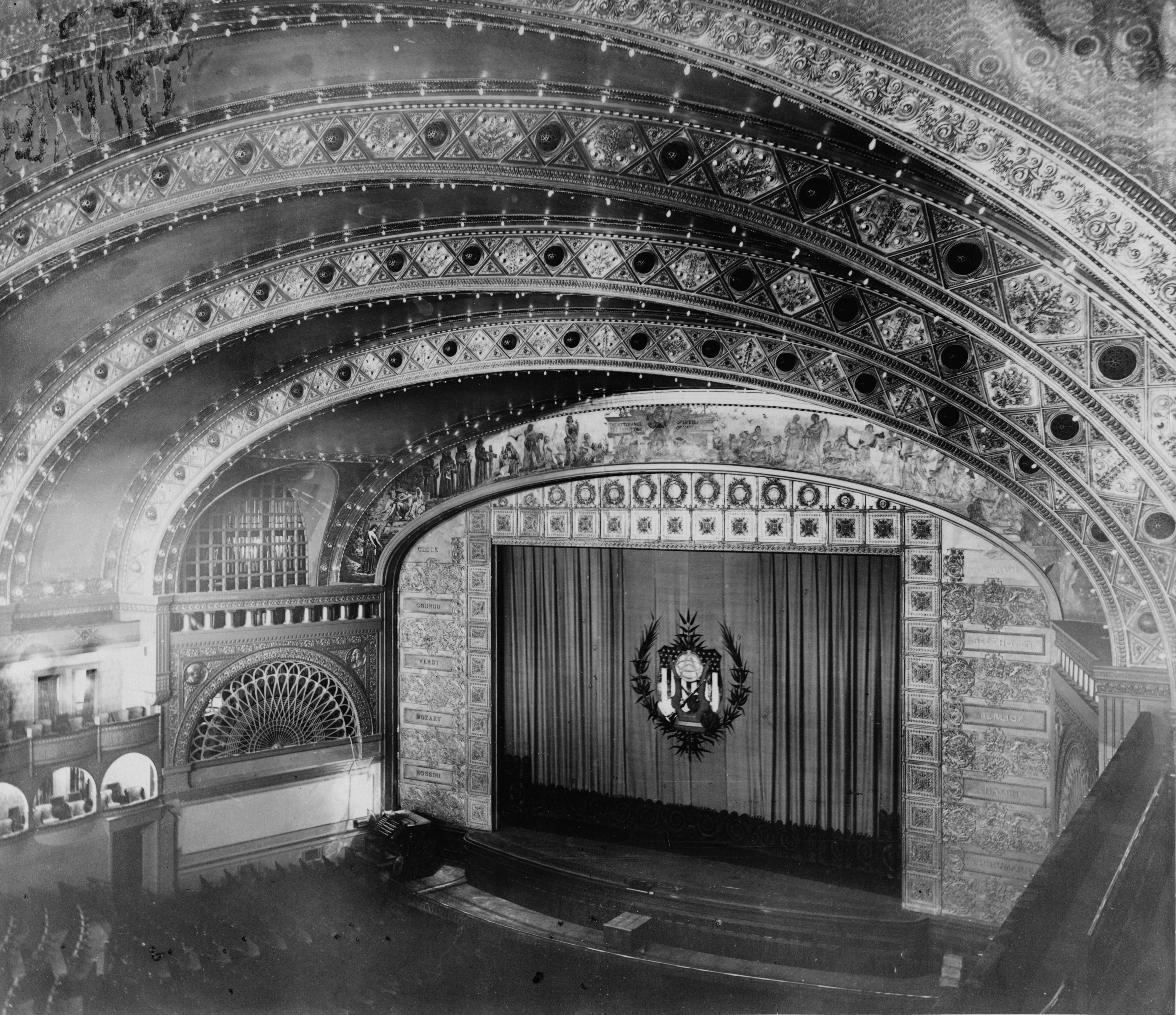
Proscenium
A proscenium ( grc-gre, προσκήνιον, ) is the metaphorical vertical plane of space in a theatre, usually surrounded on the top and sides by a physical proscenium arch (whether or not truly "arched") and on the bottom by the stage floor itself, which serves as the frame into which the audience observes from a more or less unified angle the events taking place upon the stage during a theatrical performance. The concept of the fourth wall of the theatre stage space that faces the audience is essentially the same. It can be considered as a social construct which divides the actors and their stage-world from the audience which has come to witness it. But since the curtain usually comes down just behind the proscenium arch, it has a physical reality when the curtain is down, hiding the stage from view. The same plane also includes the drop, in traditional theatres of modern times, from the stage level to the "stalls" level of the audience, which was the original meaning of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the United States and Europe during the 1920s and 1930s. Through styling and design of the exterior and interior of anything from large structures to small objects, including how people look (clothing, fashion and jewelry), Art Deco has influenced bridges, buildings (from skyscrapers to cinemas), ships, ocean liners, trains, cars, trucks, buses, furniture, and everyday objects like radios and vacuum cleaners. It got its name after the 1925 Exposition internationale des arts décoratifs et industriels modernes (International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts) held in Paris. Art Deco combined modern styles with fine craftsmanship and rich materials. During its heyday, it represented luxury, glamour, exuberance, and faith in socia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village Lock-up
A village lock-up is a historic building once used for the temporary detention of people in England and Wales, mostly where official prisons or criminal courts were beyond easy walking distance. Lockups were often used for the confinement of drunks, who were usually released the next day, or to hold people being brought before the local magistrate. The archetypal form comprises a small room with a single door and a narrow slit window, grating or holes. Most lock-ups feature a tiled or stone-built dome or spire as a roof and are built from brick, stone and/or timber. Such a room was built in many shapes; many are round, which gives rise to a sub-description: the punishment or village round-house. Village lock-ups, though usually freestanding, were often attached to walls, tall pillar/tower village crosses or incorporated into other buildings. Varying in architectural strength and ornamentation, they were all built to perform the same function. Nicknames and forms They have acqui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
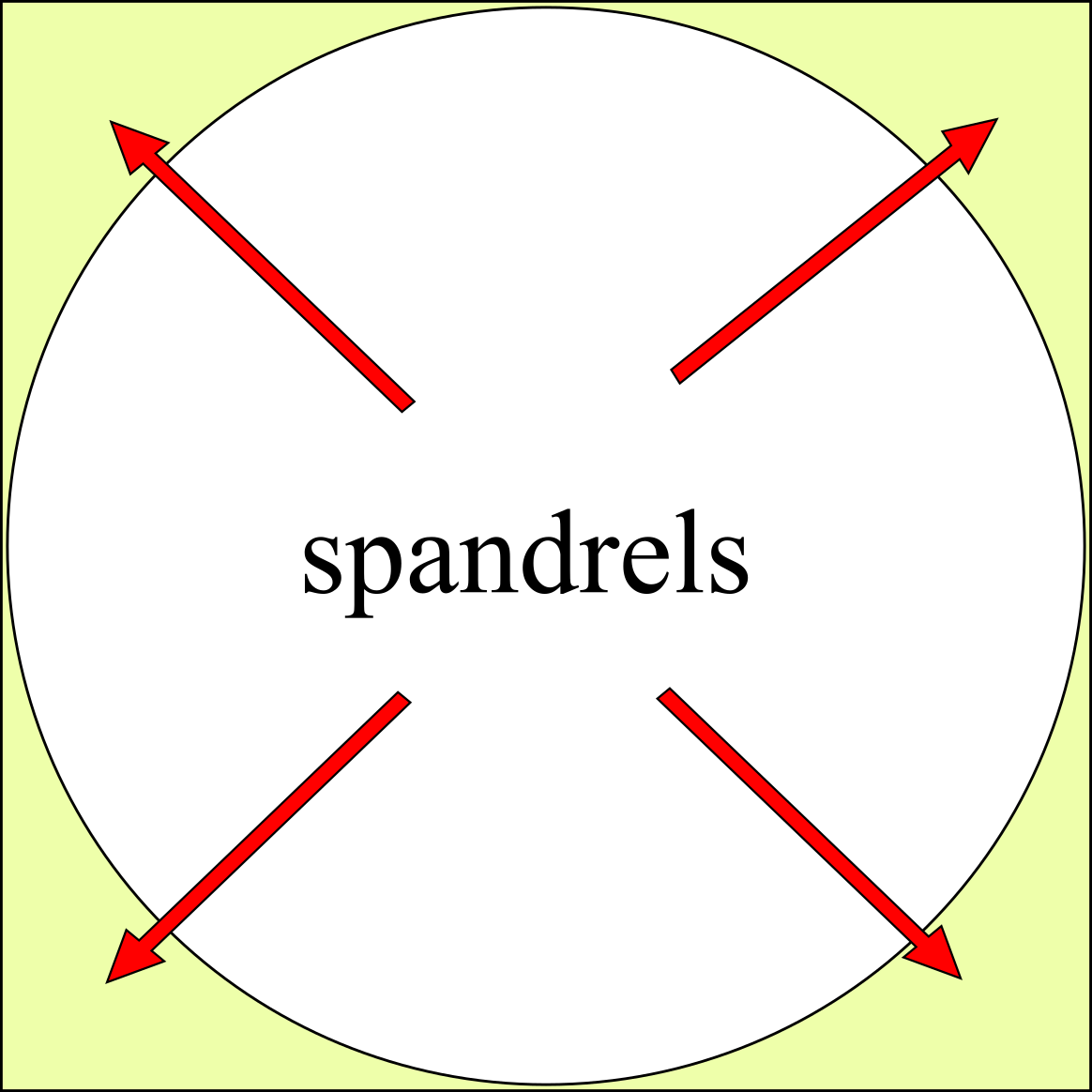
Spandrel
A spandrel is a roughly triangular space, usually found in pairs, between the top of an arch and a rectangular frame; between the tops of two adjacent arches or one of the four spaces between a circle within a square. They are frequently filled with decorative elements. Meaning There are four or five accepted and cognate meanings of the term ''spandrel'' in architectural and art history, mostly relating to the space between a curved figure and a rectangular boundary – such as the space between the curve of an arch and a rectilinear bounding moulding, or the wallspace bounded by adjacent arches in an arcade and the stringcourse or moulding above them, or the space between the central medallion of a carpet and its rectangular corners, or the space between the circular face of a clock and the corners of the square revealed by its hood. Also included is the space under a flight of stairs, if it is not occupied by another flight of stairs. In a building with more than one floor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_interior.jpg)