|
Harry Jones (British Army Officer)
General Sir Henry David Jones DCL (14 March 1791 – 4 August 1866) was a British Army officer who became Governor of the Royal Military College, Sandhurst. Life He was the fifth son of John Jones by his wife, Mary, daughter of John Roberts, Esq., of Landguard Fort, an officer 29th Foot, and was brother of Major-General Sir John Thomas Jones, Bart., KCB, and uncle of Sir Willoughby Jones, Bart., of Cranmer Hall, Fakenham, Norfolk. Educated at the Royal Military Academy, Woolwich, Jones was commissioned into the Royal Engineers in September 1808. In 1809 he was involved in the attack on the fortress at Flushing during the Walcheren Campaign. He then took part in the defence of Cadiz in 1809, the Siege of Badajoz in 1812, the Battle of Vitoria in 1813 and the Battle of Nivelle in 1813. He was wounded while leading the forlorn hope during the first assault at the Siege of San Sebastián in September 1813. In February, 1815, he joined the army under General John Lambert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
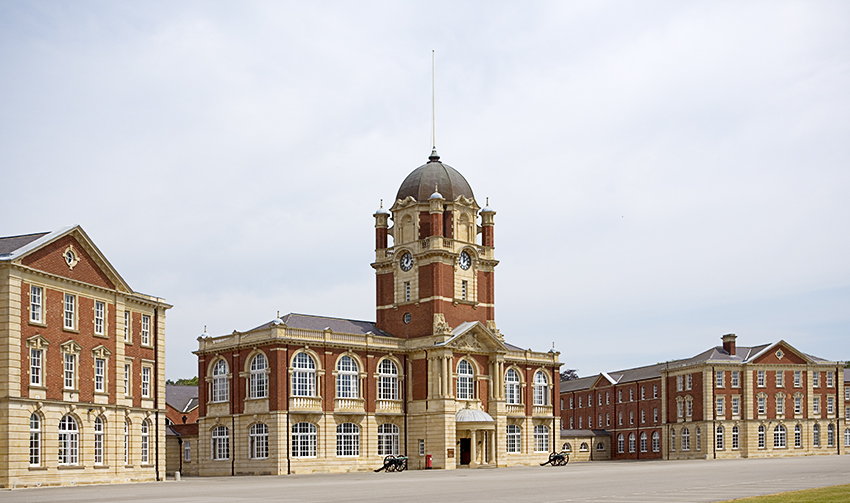
Sandhurst, Berkshire
Sandhurst is a town and civil parish in the Bracknell Forest borough in Berkshire, England. It is in the south eastern corner of Berkshire, and is situated west-southwest of central London, north west of Camberley and south of Bracknell. Sandhurst is known worldwide as the location of the Royal Military Academy Sandhurst (often referred to simply as "Sandhurst", "The Academy" or "The RMA"). Despite its close proximity to Camberley, Sandhurst is also home to a large and well-known out-of-town mercantile development. The site is named "The Meadows" and has a Tesco Extra hypermarket and a Marks & Spencer, two of the largest in the country. A large Next clothing and homeware store is open on the site of the old Homebase. Geography Sandhurst is in South East England near the junction of Berkshire, Hampshire and Surrey. The town has four main districts, from west to east: Little Sandhurst, Sandhurst (central) and College Town, with Owlsmoor to the northeast. North of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fakenham
Fakenham is a market town and civil parish in Norfolk, England. It is situated on the River Wensum, about north west of Norwich. The town is the junction of several local roads, including the A148 from King's Lynn to Cromer, the A1067 to Norwich and the A1065 to Swaffham. The civil parish has an area of and in the 2001 census had a population of 7,357 in 3,292 households, the population increasing to 7,617 at the 2011 census. For the purposes of local government, the parish falls within the district of North Norfolk.Office for National Statistics & Norfolk County Council (2001). Census population and household counts for unparished urban areas and all parishes'. Retrieved 2 December 2005. Fakenham has been a market town since 1250, particularly known for its corn, barley and wheat trading, and in the 19th century it became noted for its printing. Fakenham Racecourse is a thoroughbred horse racing venue to the south of Fakenham. The town has a long name of Fakenham Lancaster ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dauphin Island, Alabama
Dauphin Island is an island town in Mobile County, Alabama, United States, on a barrier island of the same name, in the Gulf of Mexico. It incorporated in 1988. The population was 1,778 at the 2020 census, up from 1,238 at the 2010 census. The town is part of the Mobile metropolitan area. The island (originally named Massacre Island) was renamed for Louis XIV of France's great-grandson and heir, the dauphin, the future Louis XV of France. The name of the island is often mistaken as Dolphin Island; the word ''dauphin'' is French for dolphin, but historically, the term was used as the title of the heir apparent to the French monarch. The island is one of the Mississippi–Alabama barrier islands, with the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and the Mississippi Sound and Mobile Bay to the north. The island's eastern end helps define the mouth of Mobile Bay. The eastern, wider portion of the island is shaded by thick stands of pine trees and saw palmettos, but the narrow, western part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Lambert (British Army Officer)
General Sir John Lambert (28 April 1772 – 14 September 1847) was a British Army officer who served in the French Revolutionary Wars, the Napoleonic Wars and the War of 1812. He is best known for his consummate actions whilst commanding the tenth brigade during the Battle of Waterloo, which kept open the vital line of communication between Hougoumont farmhouse and the rest of the Allied army. Life Lambert entered the British Army on 27 January 1791, as an ensign in the 1st Foot Guards. He was promoted to lieutenant and captain on 9 October 1793. He served at the sieges of Valenciennes and Dunkirk, and was in the Battle of Lincelles in 1793. He was adjutant of the third battalion in the campaign of 1794, served with it during the Irish Rebellion of 1798, and in the expedition to Holland in 1799. He was promoted captain and lieutenant-colonel on 14 May 1801. He served in Portugal and Spain in 1808, and was present at Corunna, and he commanded the light companies of the guard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of San Sebastián
In the siege of San Sebastián (7 July – 8 September 1813), part of the Peninsular War, Allied forces under the command of Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington failed to capture the city in a siege. However in a second siege the Allied forces under Thomas Graham captured the city of San Sebastián in northern Basque Country from its French garrison under Louis Emmanuel Rey. During the final assault, the British and Portuguese troops rampaged through the town and razed it to the ground. Situation After winning the decisive Battle of Vitoria on 21 June 1813, Wellington's army advanced into the western Pyrenees to take the mountain passes and to face Marshal Soult's who had retreated back to France to try to reorganise his army. To clear his rear area, and to evict the last French forces from Spain, Wellington needed to take Pamplona and San Sebastián. Lacking resources to attack both simultaneously, Pamplona was blockaded and San Sebastián was put under siege. The b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forlorn Hope
A forlorn hope is a band of soldiers or other combatants chosen to take the vanguard in a military operation, such as a suicidal assault through the kill zone of a defended position, or the first men to climb a scaling ladder against a defended fortification, where the risk of casualties is high. Such a band is also known as the (). Etymology The term comes from the Dutch , literally 'lost heap'. The term was used in military contexts to denote a troop formation. The Dutch word (in its sense of 'heap' in English) is not cognate with English 'hope': this is an example of folk etymology. The translation of as "forlorn hope" is "a quaint misunderstanding" using the nearest-sounding English words. This folk etymology has been strengthened by the fact that in Dutch, the word is a homograph meaning "hope" as well as "heap", although the two senses have different etymologies. History In the German mercenary armies of the , these troops were called the , which has the same meani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Nivelle
The Battle of Nivelle (10 November 1813) took place in front of the river Nivelle near the end of the Peninsular War (1808–1814). After the Allied siege of San Sebastian, Wellington's 80,000 British, Portuguese and Spanish troops (20,000 of the Spaniards were untried in battle) were in hot pursuit of Marshal Soult who had 60,000 men to place in a 20-mile perimeter. After the Light Division, the main British army was ordered to attack and the 3rd Division split Soult's army in two. By two o'clock, Soult was in retreat and the British in a strong offensive position. Soult had lost another battle on French soil and had lost 4,500 men to Wellington's 5,500. Background In the Siege of San Sebastian, the Anglo-Portuguese stormed and captured the port at the beginning of September 1813. In the Battle of San Marcial on 31 August, Soult failed to break through the Spanish defences in his final attempt to relieve the siege. The French army then fell back to defend the Bidassoa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Vitoria
At the Battle of Vitoria (21 June 1813) a British, Portuguese and Spanish army under the Marquess of Wellington broke the French army under King Joseph Bonaparte and Marshal Jean-Baptiste Jourdan near Vitoria in Spain, eventually leading to victory in the Peninsular War. Background In July 1812, after the Battle of Salamanca, the French had evacuated Madrid, which Wellington's army entered on 12 August 1812. Deploying three divisions to guard its southern approaches, Wellington marched north with the rest of his army to lay siege to the fortress of Burgos, away, but he had miscalculated the enemy's strength, and on 21 October he had to abandon the Siege of Burgos and retreat. By 31 October he had abandoned Madrid too and retreated first to Salamanca then to Ciudad Rodrigo, near the Portuguese frontier, to avoid encirclement by French armies from the north-east and south-east. Wellington spent the winter reorganizing and reinforcing his forces to attack King Joseph in Madr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
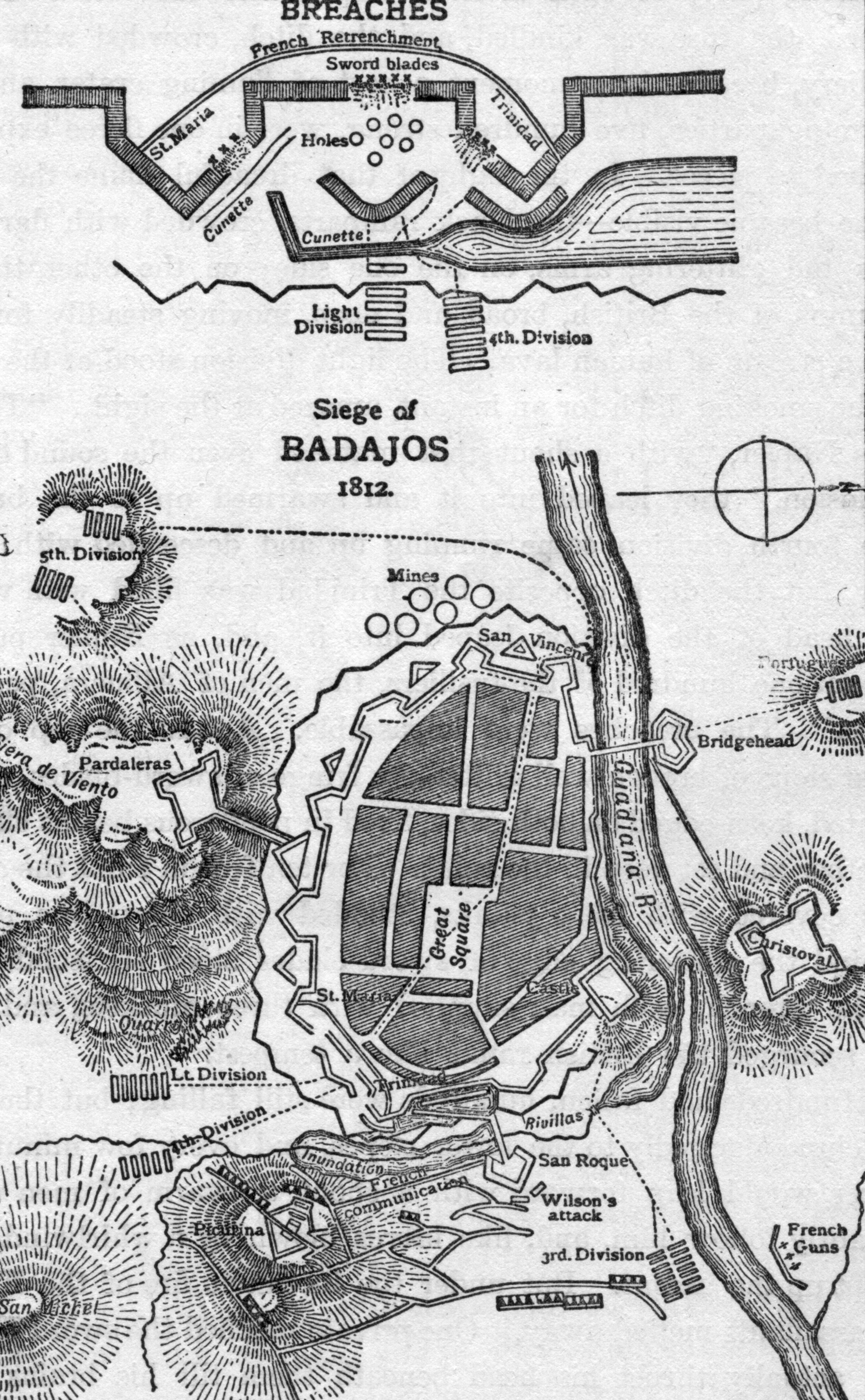
Siege Of Badajoz (1812)
In the siege of Badajoz (16 March – 6 April 1812), also called the third siege of Badajoz, an Anglo-Portuguese Army under the Earl of Wellington (later the Duke of Wellington) besieged Badajoz, Spain, and forced the surrender of the French garrison. The siege was one of the bloodiest in the Napoleonic Wars and was considered a costly victory by the British, with some 4,800 Allied soldiers killed or wounded in a few short hours of intense fighting during the storming of the breaches as the siege drew to an end. Enraged at the huge number of casualties they suffered in seizing the city, the troops broke into houses and stores consuming vast quantities of alcohol with many of them then going on a rampage, threatening their officers and ignoring their commands to desist, and even killing several. It took three days before the men were brought back into order. When order was restored, an estimated 200-300 civilians had been killed or injured. Background The allied campaign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
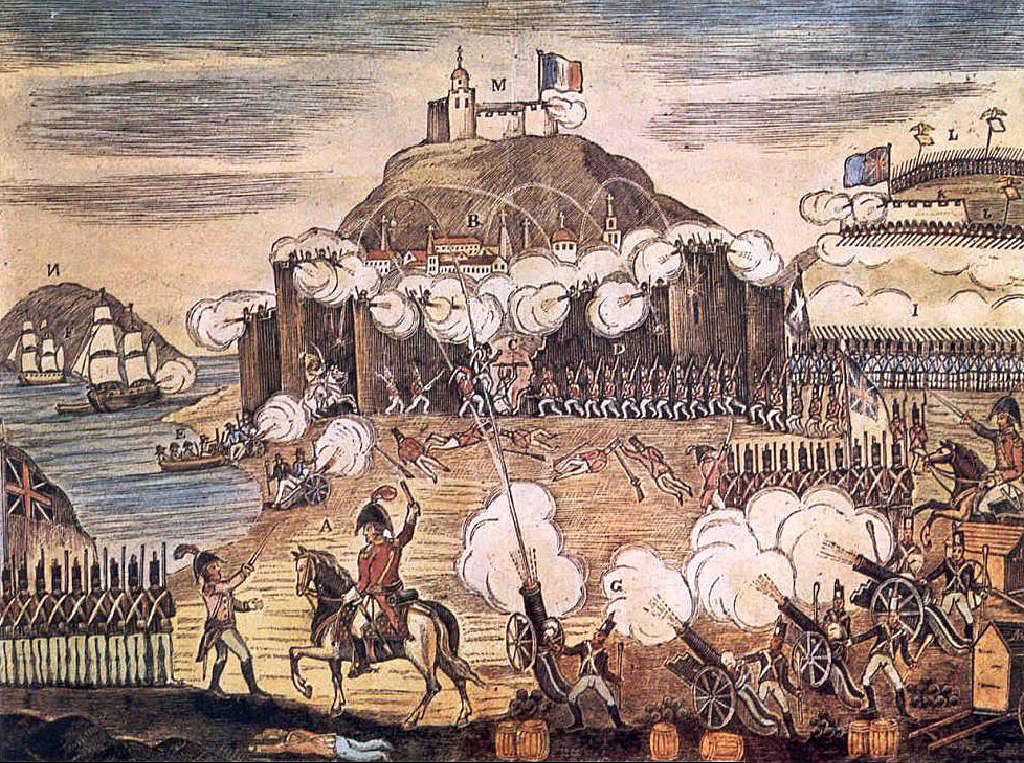
Walcheren Campaign
The Walcheren Campaign ( ) was an unsuccessful British expedition to the Netherlands in 1809 intended to open another front in the Austrian Empire's struggle with France during the War of the Fifth Coalition. Sir John Pitt, 2nd Earl of Chatham, was the commander of the expedition, with the missions of capturing Flushing and Antwerp in the Netherlands and enabling navigation of the Scheldt River. Some 39,000 soldiers, 15,000 horses together with field artillery and two siege trains crossed the North Sea and landed at Walcheren on 30July. This was the largest British expedition of that year, larger than the army serving in the Peninsular War in Portugal. Nevertheless, it failed to achieve any of its goals. The Walcheren Campaign involved little fighting, but heavy losses from the sickness popularly dubbed "Walcheren Fever". Although more than 4,000 British troops died during the expedition, only 106 died in combat; the survivors withdrew on 9December. Background In July 1809, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vlissingen, Netherlands
Vlissingen (; zea, label=Zeelandic, Vlissienge), historically known in English as Flushing, is a municipality and a city in the southwestern Netherlands on the former island of Walcheren. With its strategic location between the Scheldt river and the North Sea, Vlissingen has been an important harbour for centuries. It was granted city rights in 1315. In the 17th century Vlissingen was a main harbour for ships of the Dutch East India Company (VOC). It is also known as the birthplace of Admiral Michiel de Ruyter. Vlissingen is mainly noted for the yards on the Scheldt where most of the ships of the Royal Netherlands Navy (''Koninklijke Marine'') are built. Geography The municipality of Vlissingen consists of the following places: * City: Vlissingen * Villages: Oost-Souburg, Ritthem, and West-Souburg * Hamlet: Groot-Abeele History The fishermen's hamlet that came into existence at the estuary of the Schelde around AD 620 has grown over its 1,400-year history into the third ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |