|
Harriet A. Glazebrook
Harriet Ann Glazebrook (1847 – December 16, 1937) was an English Temperance movement advocate, author and editor, and the Mayoress of Cardiff (1896–7). Biography Harriet Ann Glazebrook was the second of six children born to Reverend Benjamin Glazebrook and Betty (nee Eckersley) in Glossop, Derbyshire, England in 1847. Her siblings were Sarah, Alice, Florence, Hanna, and Benjamin, Jr. Harriet's calling as a temperance advocate began in her youth, when she became a ''Band of Hope'' pledge, and continued throughout her life. The Glazebrooks were avid supporters of the Temperance movement. Her father was himself an early reformer. "Alice Lea (a.k.a.) the Lips that touch liquor shall never touch mine" was considered to be her first work, as well as her most well-known poem, on the subject of Temperance, published in 1867. The last verse of the poem, however, was not her original script. It is an adaptation of the last verse from a poem written by George W. Young, as a broadside ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperance Movement
The temperance movement is a social movement promoting temperance or complete abstinence from consumption of alcoholic beverages. Participants in the movement typically criticize alcohol intoxication or promote teetotalism, and its leaders emphasize alcohol's negative effects on people's health, personalities and family lives. Typically the movement promotes alcohol education and it also demands the passage of new laws against the sale of alcohol, either regulations on the availability of alcohol, or the complete prohibition of it. During the 19th and early 20th centuries, the temperance movement became prominent in many countries, particularly in English-speaking, Scandinavian, and majority Protestant ones, and it eventually led to national prohibitions in Canada (1918 to 1920), Norway (spirits only from 1919 to 1926), Finland (1919 to 1932), and the United States (1920 to 1933), as well as provincial prohibition in India (1948 to present). A number of temperance organiza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossop, Derbyshire
Glossop is a market town in the Borough of High Peak, Derbyshire, England. It is located east of Manchester, north-west of Sheffield and north of the county town, Matlock. Glossop lies near Derbyshire's borders with Cheshire, Greater Manchester, South Yorkshire and West Yorkshire. It is between above sea level and is bounded by the Peak District National Park to the south, east and north. Historically, the name ''Glossop'' refers to the small hamlet that gave its name to an ancient parish recorded in the Domesday Book of 1086 and then the manor given by William I of England to William Peverel. A municipal borough was created in 1866, which encompassed less than half of the manor's territory.The Ancient Parish of Glossop Retrieved 18 June 2008 The area now known as Glossop approximates to the villages that us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Of Hope
Hope UK is a United Kingdom Christian charity based in London, England which educates children and young people about drug and alcohol abuse. Local meetings started in 1847 and a formal organisation was established in 1855 with the name The United Kingdom Band of Hope Union. Band of Hope The Band of Hope was first proposed by Rev. Jabez Tunnicliff, who was a Baptist minister in Leeds, following the death in June 1847 of a young man whose life was cut short by alcohol.H Marles, ''The Life and Labours of Rev Jabez Tunnicliff'', 1865, pp. 213–210. While working in Leeds, Tunnicliff had become an advocate for total abstinence from alcohol. In the autumn of 1847, with the help of other temperance workers including Anne Jane Carlile, the Band of Hope was founded. Its objective was to teach children the importance and principles of sobriety and teetotalism. In 1855, a national organisation was formed amidst an explosion of Band of Hope work. Meetings were held in churches througho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
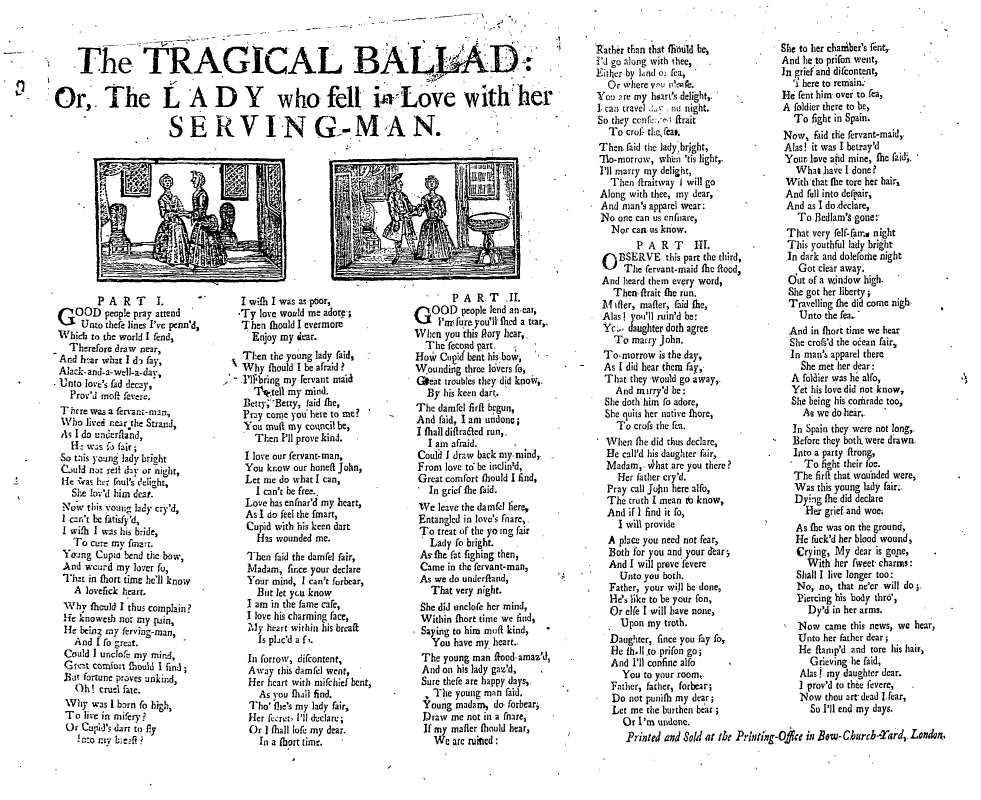
Broadside Ballad
A broadside (also known as a broadsheet) is a single sheet of inexpensive paper printed on one side, often with a ballad, rhyme, news and sometimes with woodcut illustrations. They were one of the most common forms of printed material between the sixteenth and nineteenth centuries, particularly in Britain, Ireland and North America because they are easy to produce and are often associated with one of the most important forms of traditional music from these countries, the ballad. Development of broadsides Ballads developed out of minstrelsy from the fourteenth and fifteenth century. These were narrative poems that had combined with French courtly romances and Germanic legends that were popular at the King’s court, as well as in the halls of lords of the realm. By the seventeenth century, minstrelsy had evolved into ballads whose authors wrote on a variety of topics. The authors could then have their ballads printed and distributed. Printers used a single piece of paper known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond Jubilee Of Queen Victoria
The Diamond Jubilee of Queen Victoria was officially celebrated on 22 June 1897 to mark the occasion of the 60th anniversary of Queen Victoria's accession on 20 June 1837. Queen Victoria was the first British monarch ever to celebrate a Diamond Jubilee. Background Queen Victoria surpassed her grandfather King George III as the longest-reigning British monarch on 23 September 1896, an event that she marked privately at Balmoral Castle. She wrote in her journal, "People wished to make all sorts of demonstrations, which I asked them not to do until I had completed the sixty years next June." The Diamond Jubilee was therefore an opportunity to celebrate Victoria's status as longest-reigning monarch, in addition to marking 60 years on the throne. On 20 June 1897, the sixtieth anniversary of her accession, Victoria wrote in her journal: The sixtieth anniversary of her accession was celebrated on 20 June 1897 with a thanksgiving service at St George's Chapel, Windsor Castle. Cele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |