|
Harpagoside
Harpagoside is a natural product found in the plant '' Harpagophytum procumbens'', also known as devil's claw. It is the active chemical constituent responsible for the medicinal properties of the plant, which have been used for centuries by the Khoisan people of southern Africa to treat diverse health disorders, including fever, diabetes, hypertension, and various blood related diseases. Biosynthesis Harpagoside is characterized as an iridoid glycoside, which is a product of the mevalonate pathway present in the metabolism of eukaryotes, archaea and some bacteria. The iridane skeleton found in iridoids is monoterpenoid in origin and contains a cyclopentane ring fused to a six-membered oxygen heterocycle. The iridoid system arises from geraniol, which itself is synthesized from geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) by geraniol diphosphate synthase (E1). A p450 type enzyme, geraniol 8-hydroxylase (E2), then hydroxylates geraniol at the 8 position to form 8-hydroxygeraniol. The diol then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harpagophytum Procumbens
''Harpagophytum'' ( ), also called grapple plant, wood spider, and most commonly devil's claw, is a genus of plants in the sesame family, native to southern Africa. Plants of the genus owe their common name "devil's claw" to the peculiar appearance of their hooked fruit. Several species of North American plants in the genus ''Proboscidea'' and certain species of ''Pisonia'', however, are also known by this name. Devil's claw's tuberous roots are used in folk medicine to reduce pain. Range ''Harpagophytum procumbens'' is mainly found in the eastern and south eastern parts of Namibia, Southern Botswana, and the Kalahari region of the Northern Cape, South Africa. '' H. zeyheri'' is found in the northern parts of Namibia (Ovamboland) and southern Angola. Etymology The generic name, ''Harpagophytum'', is derived from the Greek words ''harpago'' meaning "hook" and ''phyton'' meaning "plant".Ib Friis and Olof Ryding (Editors) Folk medicine and research The ethnobotanical use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Product
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synthesis (both semisynthesis and total synthesis) and have played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry by providing challenging synthetic targets. The term natural product has also been extended for commercial purposes to refer to cosmetics, dietary supplements, and foods produced from natural sources without added artificial ingredients. Within the field of organic chemistry, the definition of natural products is usually restricted to organic compounds isolated from natural sources that are produced by the pathways of primary or secondary metabolism. Within the field of medicinal chemistry, the definition is often further restricted to secondary metabolites. Secondary metabolites (or specialized metabolites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khoisan
Khoisan , or (), according to the contemporary Khoekhoegowab orthography, is a catch-all term for those indigenous peoples of Southern Africa who do not speak one of the Bantu languages, combining the (formerly "Khoikhoi") and the or ( in the Nǁng language). The San were formerly called Bushmen, (from Afrikaans ''Boesmans'' from nl, Boschjesmens); and the were formerly known as " Hottentots", speculated to be a Dutch onomatopoeic term referring to the click consonants prevalent in the Khoekhoe languages. However there is no evidence of this etymology."A very large number of different etymologies for the name have been suggested ... The most frequently repeated suggestion ... is that the word was a spec. use of a formally identical Dutch word meaning ‘stammerer, stutterer’, which came to be applied to the Khoekhoe and San people on account of the clicks characteristic of their languages. However, evidence for the earlier general use appears to be lacking. Another fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iridoid Glycoside
In chemistry, a glycoside is a molecule in which a sugar is bound to another functional group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides play numerous important roles in living organisms. Many plants store chemicals in the form of inactive glycosides. These can be activated by enzyme hydrolysis, which causes the sugar part to be broken off, making the chemical available for use. Many such plant glycosides are used as medications. Several species of ''Heliconius'' butterfly are capable of incorporating these plant compounds as a form of chemical defense against predators. In animals and humans, poisons are often bound to sugar molecules as part of their elimination from the body. In formal terms, a glycoside is any molecule in which a sugar group is bonded through its anomeric carbon to another group via a glycosidic bond. Glycosides can be linked by an O- (an ''O-glycoside''), N- (a ''glycosylamine''), S-(a ''thioglycoside''), or C- (a ''C-glycoside'') glycosidic bond. According to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mevalonate Pathway
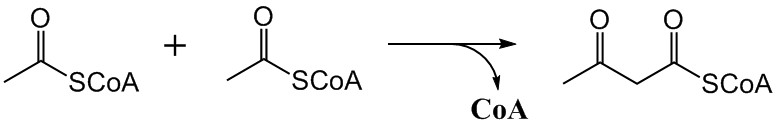
The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), which are used to make isoprenoids, a diverse class of over 30,000 biomolecules such as cholesterol, vitamin K, coenzyme Q10, and all steroid hormones. The mevalonate pathway begins with acetyl-CoA and ends with the production of IPP and DMAPP. It is best known as the target of statins, a class of cholesterol lowering drugs. Statins inhibit HMG-CoA reductase within the mevalonate pathway. Upper mevalonate pathway The mevalonate pathway of eukaryotes, archaea, and eubacteria all begin the same way. The sole carbon feed stock of the pathway is acetyl-CoA. The first step condenses two acetyl-CoA molecules to yield acetoacetyl-CoA. This is followed by a second condensation to for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geraniol 8-hydroxylase
Geraniol 8-hydroxylase (, Formerly , ''CYP76B6'', ''G10H'', ''CrG10H'', ''SmG10H'') is an enzyme with systematic name ''geraniol,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (8-hydroxylating)''. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction : geraniol + NADPH + H+ + O2 \rightleftharpoons (6E)-8-hydroxygeraniol + NADP+ + H2O Geraniol 8-hydroxylase is a cytochrome P450 and therefore requires a partner cytochrome P450 reductase Cytochrome P450 reductase (; also known as NADPH:ferrihemoprotein oxidoreductase, NADPH:hemoprotein oxidoreductase, NADPH:P450 oxidoreductase, P450 reductase, POR, CPR, CYPOR) is a membrane-bound enzyme required for electron transfer from NADP ... for functional expression. References External links * {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no EC 1.14.14 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iridodial
Iridodial is an iridoid Iridoids are a type of monoterpenoids in the general form of cyclopentanopyran, found in a wide variety of plants and some animals. They are biosynthetically derived from 8-oxogeranial. Iridoids are typically found in plants as glycosides, mos .... It is produced from 8-oxogeranial by the enzyme iridoid synthase (IS). Iridodial is one of the substrates for the enzyme iridoid oxidase (IO) which produces 7-deoxyloganetic acid. Although it may not be known at this time whether the compound proper iridodial is actually present in natural plant species or not, the use of analogous ion iridodial cation is mentioned in several papers on iridoid biosyntheses in plant species. References {{Reflist Iridoids Aldehydes Cyclopentanes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secologanin
Secologanin is a secoiridoid monoterpene synthesized from geranyl pyrophosphate in the mevalonate pathway. Secologanin then proceeds with dopamine or tryptamine to form ipecac and terpene indole alkaloids, respectively. Biosynthesis Secologanin biosynthesis begins from geranyl pyrophosphate (GPP) taken from the mevalonate pathway used to make terpenoids. Recent efforts have characterized the entire secologanin biosynthetic pathway. Secologanin is formed from loganin through the action of the enzyme secologanin synthase In enzymology, a secologanin synthase (, was wrongly classified as in the past) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :loganin + NADPH + H+ + O2 \rightleftharpoons secologanin + NADP+ + 2 H2O The 4 substrates of this enzyme are lo .... Secologanin is then able to proceed onto produce ipecac and terpene indole alkaloids. References {{Reflist Glucosides Methyl esters Aldehydes Vinyl compounds ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Products- Harpagoside
Nature, in the broadest sense, is the physical world or universe. "Nature" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large, if not the only, part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena. The word ''nature'' is borrowed from the Old French ''nature'' and is derived from the Latin word ''natura'', or "essential qualities, innate disposition", and in ancient times, literally meant " birth". In ancient philosophy, ''natura'' is mostly used as the Latin translation of the Greek word '' physis'' (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics of plants, animals, and other features of the world to develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.jpg)