|
Harong Hurong
Harong Hurong ( bn, হারং হুরং) is the name of an ancient cave in the Sylhet region of Bangladesh. The word ''Harong Hurong'' are the two dialects of two ancient Sylheti word. In Sylheti language, the word 'harong' means narrow or alternative route, and 'hurang' means 'tunnel'. That is, the word 'harong hurong' refers to the alternative tunnel way. There is a legend that, in 1303, when the king of Gour Govinda heard the news of Shahjalal's arrival in the region, he along with his army fled through the tunnel and was missing forever. Etymology Hurong (হুরং) is the Sylheti dialectical form of the word ( bn, সুড়ঙ্গ, shurongo literally meaning tunnel), and the word Hurong is used to mean ( bn, সাঁকো, Sanko) the bamboo bridge in many areas of Sylhet and Sunamganj. So, if ''Hurong'' means a landscape or alternative route through a barrier, then Harong-Hurong describes an ''alternative tunnel route''. The tunnel is known by the people of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylhet District
Sylhet ( bn, সিলেট), located in north-east Bangladesh, is the divisional capital and one of the four districts in the Sylhet Division. History Sylhet district was established on 3 January 1782, and until 1878 it was part of Bengal Province under Dhaka Division. However, in that year, Sylhet was moved to the newly created Assam Province, and it remained as part of Assam up to 1947 (except during the administrative reorganisation of Bengal Province between 1905 and 1912). Sylhet district was divided into five subdivisions and the current Sylhet District was known as the North Sylhet subdivision. In 1947, Sylhet became a part of East Pakistan as a result of a referendum (except 3 thanas of Karimganj subdivision) as part of Chittagong Division. It was subdivided into four districts in 1983–84 with the current Sylhet District being known as North Sylhet. It became a part of Sylhet Division after its formation in 1995. Sylhet has played a vital role in the Bangladeshi econ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saturday
Saturday is the day of the week between Friday and Sunday. No later than the 2nd century, the Romans named Saturday ("Saturn's Day") for the planet Saturn, which controlled the first hour of that day, according to Vettius Valens. The day's name was introduced into West Germanic languages and is recorded in the Low German languages such as Middle Low German , ''saterdach'', Middle Dutch (Modern Dutch ) and Old English , ''Sæterndæġ'' or . Origins Between the 1st and 3rd centuries AD, the Roman Empire gradually replaced the eight-day Roman nundinal cycle with the seven-day week. The astrological order of the days was explained by Vettius Valens and Dio Cassius (and Chaucer gave the same explanation in his ''Treatise on the Astrolabe''). According to these authors, it was a principle of astrology that the heavenly bodies presided, in succession, over the hours of the day. The association of the weekdays with the respective deities is thus indirect, the days are named for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Sylhet
The Greater Sylhet region predominantly includes the Sylhet Division in Bangladesh, and Karimganj district in Assam, India. The history of the Sylhet region begins with the existence of expanded commercial centres in the area that is now Sylhet City. Historically known as ''Srihatta'' and ''Shilhatta'', it was ruled by the Buddhist and Hindu kingdoms of Harikela and Kamarupa before passing to the control of the Sena and Deva dynasties in the early medieval period. After the fall of these two Hindu principalities, the region became home to many more independent petty kingdoms such as Jaintia, Gour, Laur, and later Taraf, Pratapgarh, Jagannathpur, Chandrapur and Ita. After the Conquest of Sylhet in the 14th century, the region was absorbed into Shamsuddin Firoz Shah's independent principality based in Lakhnauti, Western Bengal. It was then successively ruled by the Muslim sultanates of Delhi and the Bengal Sultanate before collapsing into Muslim petty kingdoms, mostly ru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabiraj
Kabiraj ( bn, কবিরাজ, Kobiraj ; as, কবিৰাজ; or, କବିରାଜ; Magahi: कबिराज; ) is an occupational title found in persons of Eastern Indian subcontinent. In olden days people traditionally practising Ayurveda were generally called ''kabi''/''kobi'' in eastern India. Many of them were attached to royal courts to treat kings and the royal family. As such they were given the title of ''Kabirāj''/''Kobirāj'' ("King ''Kabi''", compare ''Rāj Vaidya'' used elsewhere). The descendants of such persons started using "Kabiraj" as a surname. This surname is often found in persons originating from Bangladesh and Indian States of West Bengal, Bihar, Assam and Orissa, which are in the same cultural region of the subcontinent and shares common linguistic origins. See also *Kaviraj, similar sounding title but etymologically different *Vaidhya Vaidya (Sanskrit: ), or vaid is a Sanskrit word meaning "traditional practitioner of Ayurveda", an indigen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supernatural
Supernatural refers to phenomena or entities that are beyond the laws of nature. The term is derived from Medieval Latin , from Latin (above, beyond, or outside of) + (nature) Though the corollary term "nature", has had multiple meanings since the ancient world, the term "supernatural" emerged in the Middle Ages and did not exist in the ancient world. The supernatural is featured in folklore and religious contexts, but can also feature as an explanation in more secular contexts, as in the cases of superstitions or belief in the paranormal. The term is attributed to non-physical entities, such as angels, demons, gods, and spirits. It also includes claimed abilities embodied in or provided by such beings, including magic, telekinesis, levitation, precognition, and extrasensory perception. The philosophy of naturalism contends that nothing exists beyond the natural world, and as such approaches supernatural claims with skepticism. Etymology and history of the concept Occurr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tantrika
Tantra (; sa, तन्त्र, lit=loom, weave, warp) are the esoteric traditions of Hinduism and Buddhism that developed on the Indian subcontinent from the middle of the 1st millennium CE onwards. The term ''tantra'', in the Indian traditions, also means any systematic broadly applicable "text, theory, system, method, instrument, technique or practice". A key feature of these traditions is the use of mantras, and thus they are commonly referred to as Mantramārga ("Path of Mantra") in Hinduism or Mantrayāna ("Mantra Vehicle") and Guhyamantra ("Secret Mantra") in Buddhism. Starting in the early centuries of the common era, newly revealed Tantras centering on Vishnu, Shiva or Shakti emerged. There are tantric lineages in all main forms of modern Hinduism, such as the Shaiva Siddhanta tradition, the Shakta sect of Sri-Vidya, the Kaula, and Kashmir Shaivism. In Buddhism, the Vajrayana traditions are known for tantric ideas and practices, which are based on Indian Buddh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian People
Indians or Indian people are the Indian nationality law, citizens and nationals of India. In 2022, the population of India stood at over 1.4 billion people, making it the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, second-most populous country, containing 17.7 percent of the global population. In addition to the Indian population, the Non-resident Indian and Overseas Citizen of India, Indian overseas diaspora also boasts large numbers, particularly in the Arab states of the Persian Gulf and the Western world. While the demonym "Indian" applies to people originating from the present-day Republic of India, it was also formerly used as the identifying term for people originating from Pakistan and Bangladesh during British Raj, British colonial era until 1947. Particularly in North America, the terms "Asian Indian" and "East Indian" are sometimes used to differentiate Indians from the indigenous peoples of the Americas; although the Native American name controversy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jaintiapur Upazila
Jaintiapur ( bn, জৈন্তাপুর, translit=Jointapur) is an upazila of Sylhet District in the Division of Sylhet, Bangladesh. History Pan, Pani Nari- Ei tiney Jaintapuri- Betel, water and women, these three make Jaintapuri. That's the first line of a rhyme that has become something of a catchphrase among Sylhetis to describe Jaintiapur, a historically rich upazila of Sylhet. A long time ago, the present plain land was probably under water and part of a huge water body, which might have separated Jaintiapur from Sylhet, historians say. Because of this geophysical condition, the region remained independent for a long time and was known as the Jaintia Kingdom. Jaintia (Sutnga kingdom) was a hill kingdom of ancient Meghalaya. In the sixteenth century, most of the greater Sylhet region was under the jurisdiction of Jaintia king who ruled from the capital Jaintiapur. The inhabiting Khasi people (ethnic group) had a matriarchal society and its own language. Sometime around 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myth
Myth is a folklore genre consisting of Narrative, narratives that play a fundamental role in a society, such as foundational tales or Origin myth, origin myths. Since "myth" is widely used to imply that a story is not Objectivity (philosophy), objectively true, the identification of a narrative as a myth can be highly controversial. Many adherents of religions view their own religions' stories as truth and so object to their characterization as myth, the way they see the stories of other religions. As such, some scholars label all religious narratives "myths" for practical reasons, such as to avoid depreciating any one tradition because cultures interpret each other differently relative to one another. Other scholars avoid using the term "myth" altogether and instead use different terms like "sacred history", "holy story", or simply "history" to avoid placing pejorative overtones on any sacred narrative. Myths are often endorsed by secular and religious authorities and are close ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, ranging from traditional building styles common to the group. Folklore also includes customary lore, taking actions for folk beliefs, the forms and rituals of celebrations such as Christmas and weddings, folk dances and initiation rites. Each one of these, either singly or in combination, is considered a folklore artifact or traditional cultural expression. Just as essential as the form, folklore also encompasses the transmission of these artifacts from one region to another or from one generation to the next. Folklore is not something one can typically gain in a formal school curriculum or study in the fine arts. Instead, these traditions are passed along informally from one individual to another either through verbal instruction or demonstr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kaler Kantho
''Kaler Kantho'' ( bn, কালের কণ্ঠ, translit=Daily Voice of Time) is one of the most popular Bengali newspapers in Bangladesh. It is an enterprise of East-West Media Group, a sister concern of Bangladesh's leading business conglomerate Bashundhara Group. The same group owns ''Bangladesh Pratidin'', ''Daily Sun'', News24, Radio Capital and '' Banglanews24''. Abed Khan was the founder editor of ''Kaler Kantho''. The daily was first published on 10 January 2010. After a short span of time Khan resigned as editor (June 2011). After Abed Khan's resignation Imdadul Haq Milan, a popular novelist from Bangladesh became the editor. Shahed Mohammad Ali, former senior news editor of Prothom Alo became the acting editor on 3rd October 2021 after Imdadul Haq Milan had become the director and brand ambassador of East West Media Group. There are many feature and daily pages in ''Kaler Kantho'', including - Tech Bisshow (IT feature page), Tech Pratidin, Campus, Poralekha (Edu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcontinent
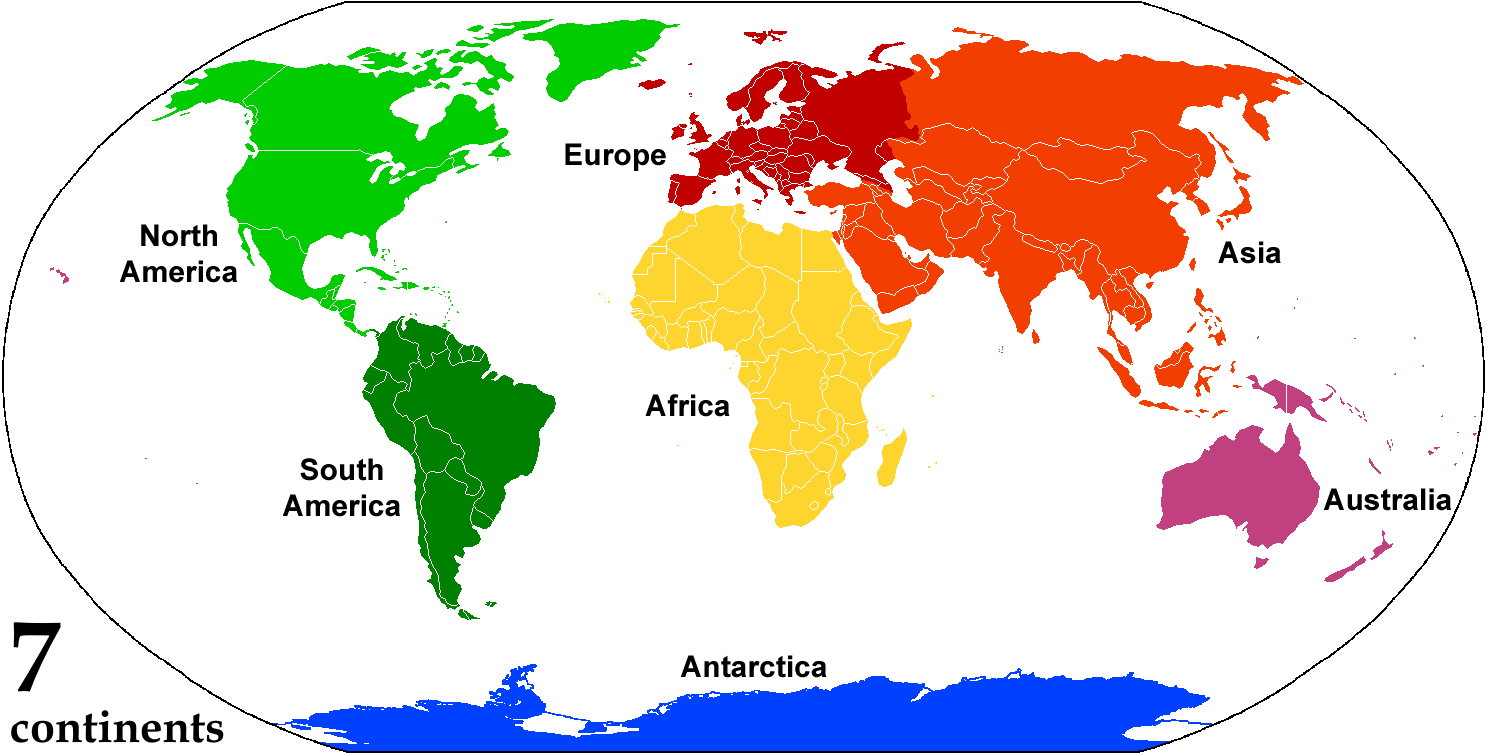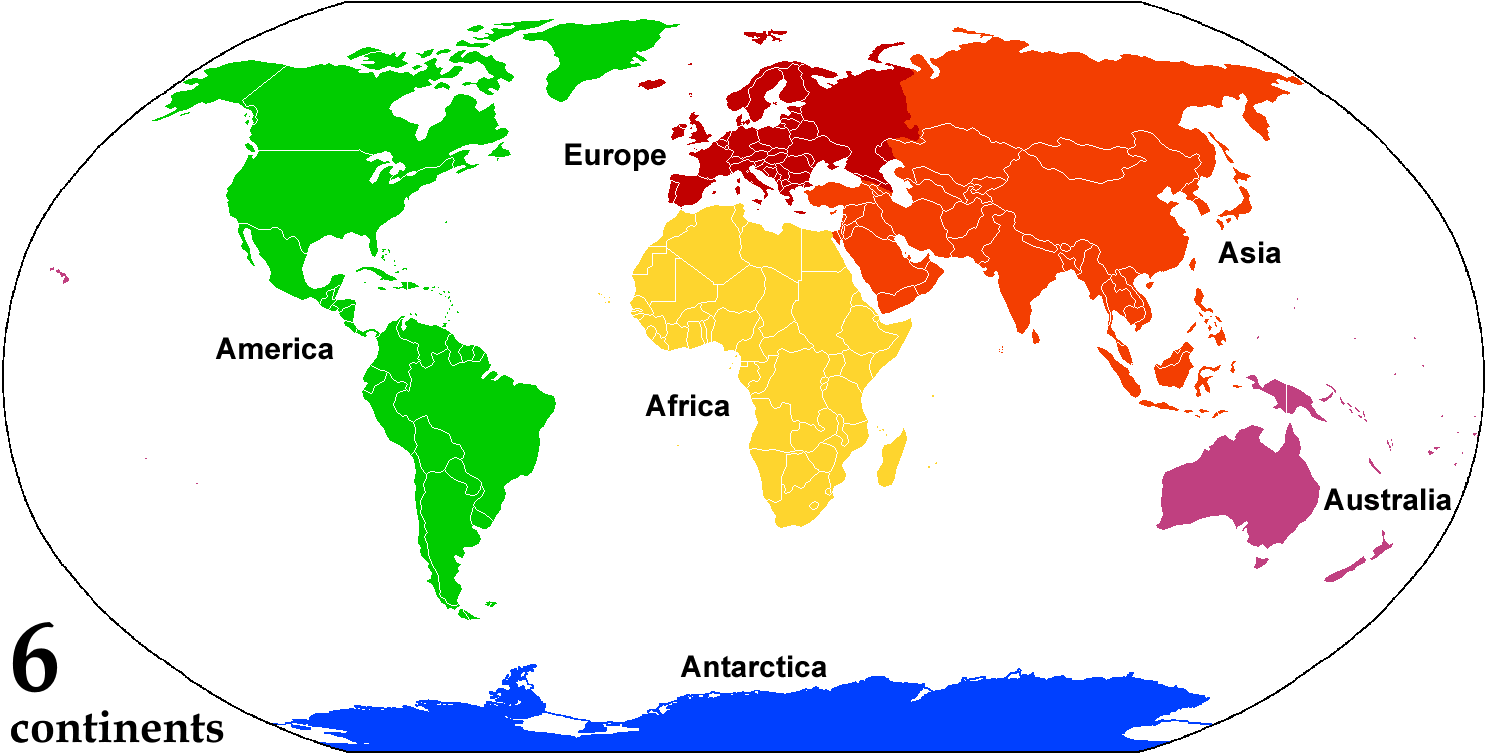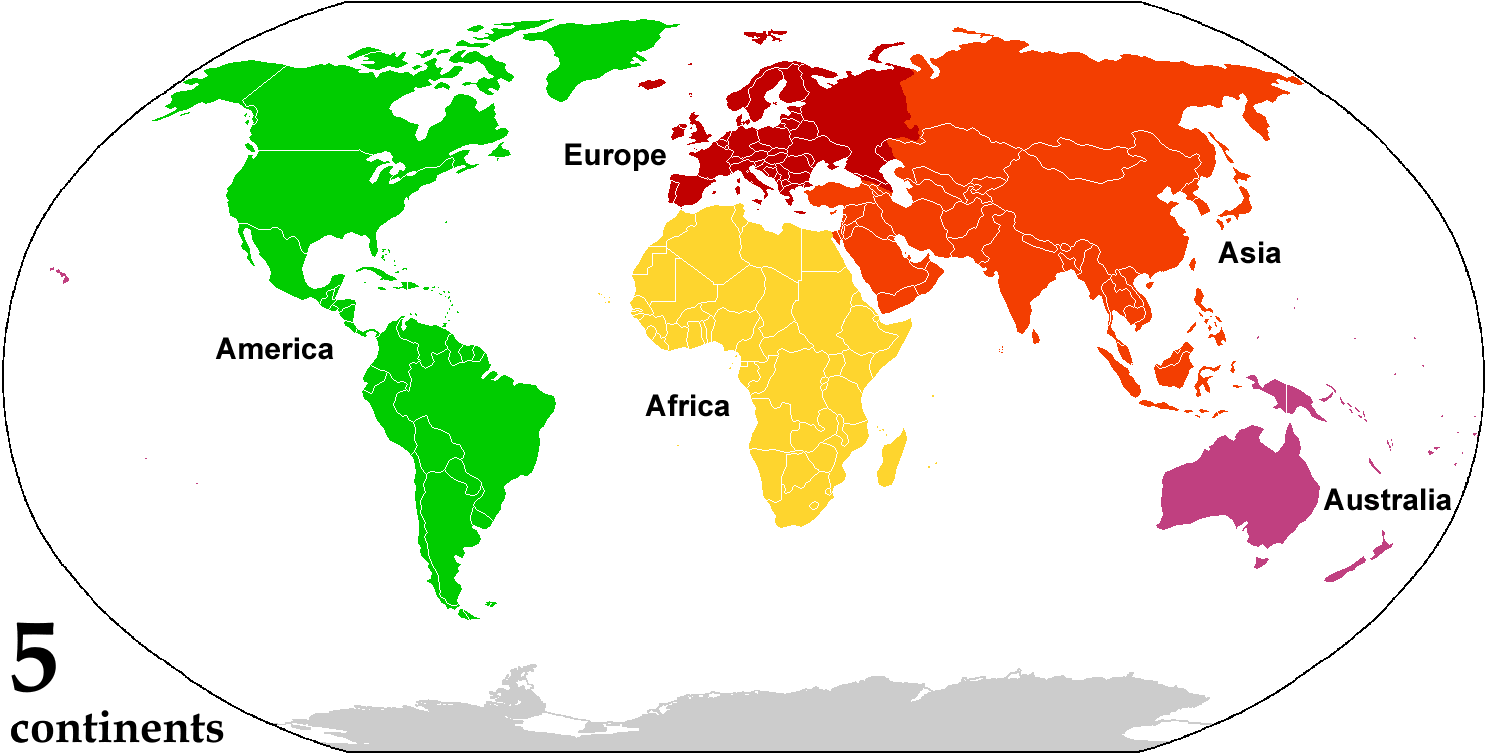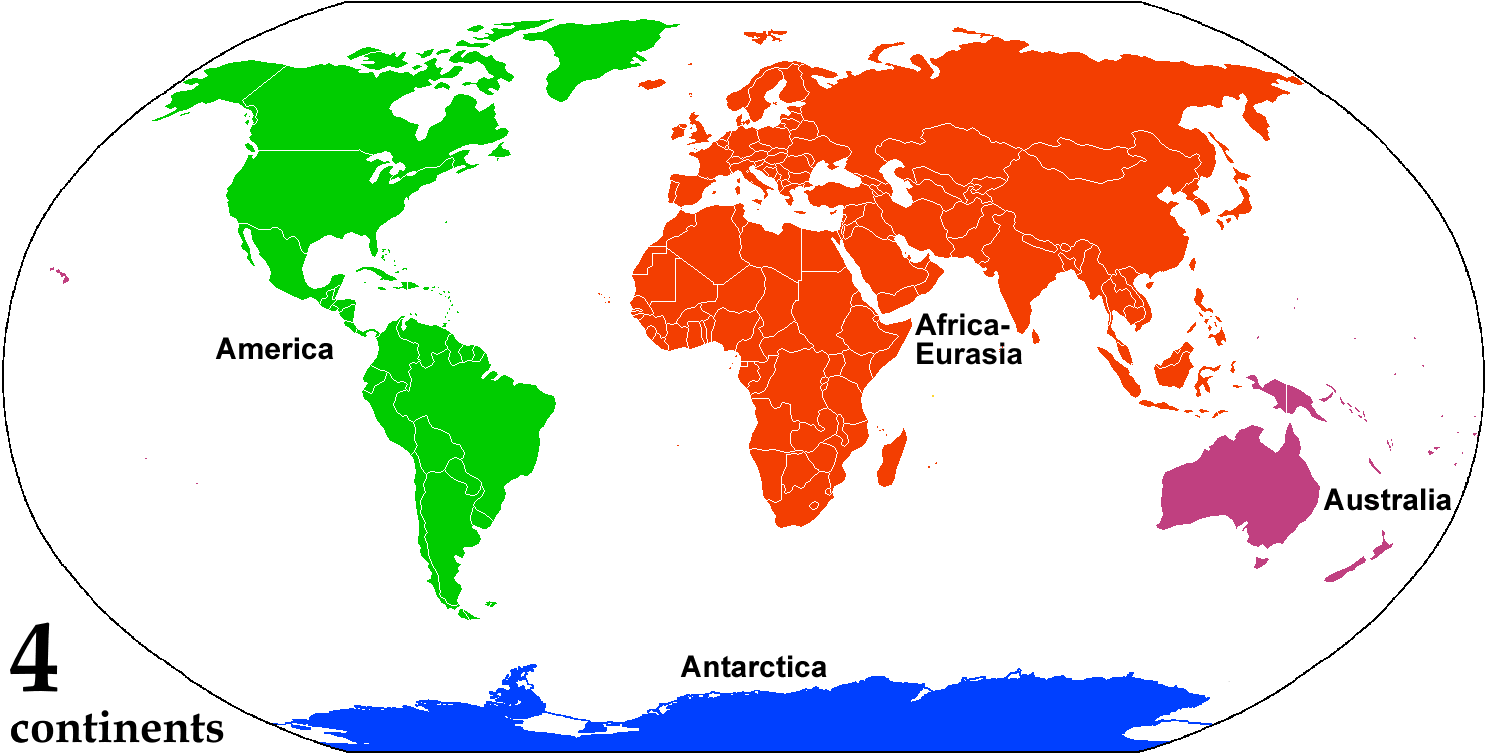
A continent is any of several large landmasses. Generally identified by convention rather than any strict criteria, up to seven geographical regions are commonly regarded as continents. Ordered from largest in area to smallest, these seven regions are: Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia. "Most people recognize seven continents—Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia, from largest to smallest—although sometimes Asia and Europe are considered a single continent, Eurasia." Variations with fewer continents may merge some of these, for example America, Eurasia, or Afro-Eurasia are sometimes treated as single continents, which can bring the total number as low as four. Zealandia, a largely submerged mass of continental crust, has also been described as a continent. Oceanic islands are frequently grouped with a nearby continent to divide all the world's land into geographical regions. Under this sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |