|
Hardieopteridae
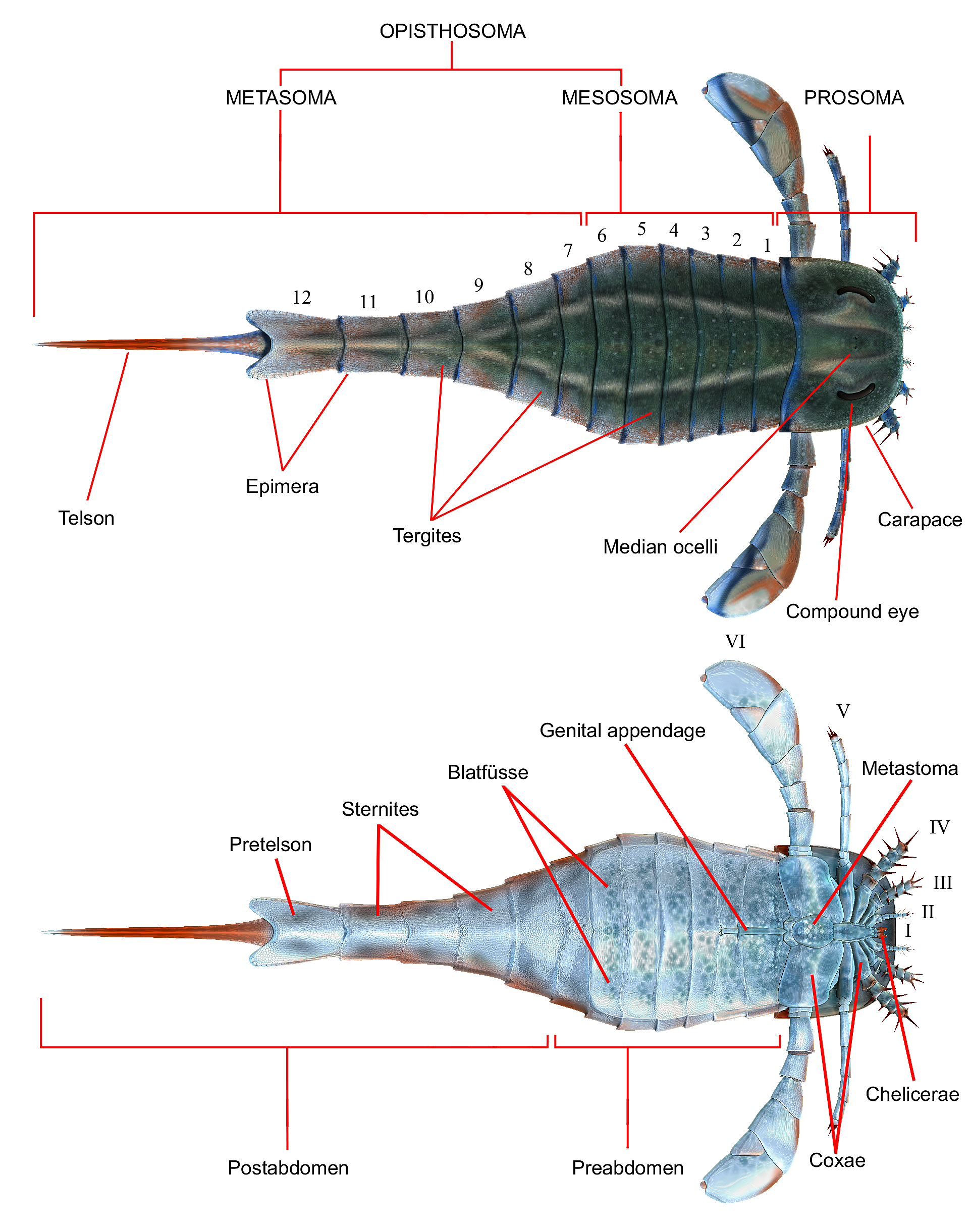
The Hardieopteridae are a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is one of two families contained in the superfamily Kokomopteroidea (along with Kokomopteridae), which in turn is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina. Hardieopterids have been recovered from deposits of Early Silurian to Late Devonian age in the United States and the United Kingdom. Hardieopterids are defined as kokomopteroids with lateral pleurae on their metastoma and pretelson, large lunate scales on the posterior margin of the carapace and a clavate telson. The opisthosoma shows both a second and fourth order differentiation into a mesosoma and metasoma. Appendages II-IV are unknown, though appendage V is spiniferous and VI is non-spiniferous as in the genus '' Hardieopterus''. The Hardieopteridae display some adaptations towards sweep-feeding, such as a broadening of the metastoma and the spines of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokomopteroidea
Kokomopteroidea is an extinct superfamily of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". It is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina. Kokomopteroids have been recovered from deposits of Early Silurian to Late Devonian age in the United States and the United Kingdom. Description Kokomopteroids are stylonurines with a spiniferous appendage V and a posterior notch on the metastoma. The superfamily forms two distinct clades; the Kokomopteridae (including the genera '' Kokomopterus'' and '' Lamontopterus'') and the Hardieopteridae (including the genera '' Hardieopterus'', '' Tarsopterella'' and '' Hallipterus''). The Kokomopteroidea retains primitive ''Hughmilleria''-type prosomal appendages for unsuitable raking through the bottom sediments of marine environments. As such, the members of the superfamily were likely scavengers. The Hardieopteridae display some sweep-feeding characteristics similarl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stylonurina
Stylonurina is one of two suborders of eurypterids, a group of extinct arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". Members of the suborder are collectively and informally known as "stylonurine eurypterids" or "stylonurines". They are known from deposits primarily in Europe and North America, but also in Siberia. Compared to the other suborder, Eurypterina, the stylonurines were comparatively rare and retained their posterior prosomal appendages for walking. Despite their rarity, the stylonurines have the longest temporal range of the two suborders. The suborder contains some of the oldest known eurypterids, such as ''Brachyopterus'', from the Middle Ordovician as well as the youngest known eurypterids, from the Late Permian. They remained rare throughout the Ordovician and Silurian, though the radiation of the mycteropoids (a group of large sweep-feeding forms) in the Late Devonian and Carboniferous is the last major radiation of the eurypterids before their extinction in the Pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hallipterus
''Hallipterus'' is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid classified as part of the family Hardieopteridae. Description ''Hallipterus'' was a gigantic Hardieopterid eurypterid. Though some previous estimates have placed its size at over 1.5 meters in length, these were likely excessive. Still, assigned specimens suggest a size of over 1 meter long. The carapace was subelliptical, greater in length than in width, with a prominent and unornamented marginal rim. The eyes were very small, close to each other and separated by a prominent median ridge with large ocelli at the posterior extremity. The chelicerae were simple and elongated. The first walking legs possessed flat and movable spines. The rest of the legs and the opisthosoma remain unknown. Species ''Hallipterus'' contains one valid species, ''H. excelsior'', from the Devonian of New York.Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2015. A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives. In World Spider Catalog. Natural Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurypterid
Eurypterids, often informally called sea scorpions, are a group of extinct arthropods that form the Order (biology), order Eurypterida. The earliest known eurypterids date to the Darriwilian stage of the Ordovician period 467.3 Myr, million years ago. The group is likely to have appeared first either during the Early Ordovician or Late Cambrian period. With approximately 250 species, the Eurypterida is the most diverse Paleozoic Chelicerata, chelicerate order. Following their appearance during the Ordovician, eurypterids became major components of marine faunas during the Silurian, from which the majority of eurypterid species have been described. The Silurian genus ''Eurypterus'' accounts for more than 90% of all known eurypterid specimens. Though the group continued to diversify during the subsequent Devonian period, the eurypterids were heavily affected by the Late Devonian extinction event. They declined in numbers and diversity until becoming extinct during the Permian–Tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardieopterus
''Hardieopterus'' is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid classified within the family Hardieopteridae. The genus contains four species, all Silurian in age; ''H. lanarkensis'' and ''H. macrophthalmus'' from Scotland, ''H. megalops'' from England and ''H. myops'' from the United States.Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2015. A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives. In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch, version 16.0 http://www.wsc.nmbe.ch/resources/fossils/Fossils16.0.pdf (PDF). See also * List of eurypterids This list of eurypterid genera is a comprehensive listing of all genera that have ever been included in the order Eurypterida, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now conside ... References Stylonurina Silurian arthropods of Europe Fossils of Great Britain Silurian arthropods of North America Silurian eurypterids Eurypterids of Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tarsopterella
''Tarsopterella'' is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid classified within the family Hardieopteridae. It contains only one species, ''T. scotica'' from the Lower Devonian of Scotland Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ....Dunlop, J. A., Penney, D. & Jekel, D. 2015. A summary list of fossil spiders and their relatives. In World Spider Catalog. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch, version 16.0 http://www.wsc.nmbe.ch/resources/fossils/Fossils16.0.pdf (PDF). Description ''Tarsopterella'' is distinguished by its prosoma (head), which is subrectangular and slightly concave in front, with small compound eyes. Its abdomen has pronounced lateral epimera (marginal spines similar to those of horseshoe crabs). ''Tarsopterella'' dates from the Lower Devonia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kokomopteridae
The Kokomopteridae are a family of eurypterids, an extinct group of chelicerate arthropods commonly known as "sea scorpions". The family is one of two families contained in the superfamily Kokomopteroidea (along with Hardieopteridae), which in turn is one of four superfamilies classified as part of the suborder Stylonurina. Kokomopterids are defined as kokomopteroids with an undifferentiated opisthosoma with a marginal rim. Appendages II-V are spiniferous as in '' Lamontopterus'' and VI is non-spiniferous as in ''Kokomopterus''. The Kokomopteridae retains primitive ''Hughmilleria''-type prosomal appendages II-IV, unsuited to the sweep-feeding lifestyle used by some of the superfamilies of the Stylonurina (Stylonuroidea and Hibbertopteroidea), and were as such likely mainly scavengers. Genera Family Kokomopteridae Kjellesvig-Waering, 1966 * ''Kokomopterus ''Kokomopterus'' is a genus of prehistoric eurypterid. The genus contains a single species, ''Kokomopterus longicaudat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Arthropod Families
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benthic Zone
The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths." Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms (e.g., bacteria and fungi) as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud. Description Oceans The benthic region of the ocean begins at the shore line (intertida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Systematic Palaeontology
The ''Journal of Systematic Palaeontolog'y'' (Print: , online: ) is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of palaeontology published by Taylor & Francis on behalf of the British Natural History Museum. , the editor-in-chief is Paul D. Taylor. The journal covers papers on new or poorly known faunas and floras and new approaches to systematics. It was established in 2003. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2014 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 3.727, ranking it second out of 49 journals in the category 'Paleontology'. References External links * Paleontology journals Taylor & Francis academic journals Quarterly journals Publications established in 2003 English-language journals {{paleo-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |