|
Harchandpur
Harchandpur is a village and corresponding community development block in Raebareli district, Uttar Pradesh, India. It is located on the Baiti river, which is a tributary of the Sai, and it is northeast from the district headquarters on the road to Lucknow. Particularly since the coming of the railway in the 1800s, Harchandpur serves as one of the main commercial centres for the surrounding region; it is also a major exporter of local goods. As of 2011, its population is 4,348 people, in 833 households. Harchandpur is also a constituency of the Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly, under the district of Raebareli. The Pin Code of the town is 229303 and there are 47 Gram panchayats under Harchandpur. History Harchand was founded by Nabh Rai, a Kayastha who served as the diwan to the Bais raja Tilok Chand, and named after his son Har Chand, who was adopted in 1350 Samvat. His descendants are still major landowners in Harchandpur; one of them, Jai Narain Srivastava, was appoint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harchandpur Railway Station
Harchandpur is a village and corresponding community development block in Raebareli district, Uttar Pradesh, India. It is located on the Baiti river, which is a tributary of the Sai, and it is northeast from the district headquarters on the road to Lucknow. Particularly since the coming of the railway in the 1800s, Harchandpur serves as one of the main commercial centres for the surrounding region; it is also a major exporter of local goods. As of 2011, its population is 4,348 people, in 833 households. Harchandpur is also a constituency of the Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly, under the district of Raebareli. The Pin Code of the town is 229303 and there are 47 Gram panchayats under Harchandpur. History Harchand was founded by Nabh Rai, a Kayastha who served as the diwan to the Bais raja Tilok Chand, and named after his son Har Chand, who was adopted in 1350 Samvat. His descendants are still major landowners in Harchandpur; one of them, Jai Narain Srivastava, was appointed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harchandpur (Assembly Constituency)
Harchandpur is a constituency of the Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly covering the city of Harchandpur in the Rae Bareli district of Uttar Pradesh, India. Harchandpur is one of five assembly constituencies in the Lok Sabha constituency of Rae Bareli. Since 2008, this assembly constituency is numbered 179 amongst 403 constituencies. Election results 2022 Samajwadi Party candidate Rahul Rajpoot won in 2022 Uttar Pradesh Legislative Elections defeating BJP candidate Rakesh Singh by a margin of 14,489 votes. 2017 Indian National Congress candidate Rakesh Singh won in 2017 Uttar Pradesh Legislative Elections defeating BJP The Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP; ; ) is a political party in India, and one of the two major Indian political parties alongside the Indian National Congress. Since 2014, it has been the ruling political party in India under Narendra Modi ... candidate Kanchan Lodhi by a margin of 3,652 votes. 2012 References External links * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
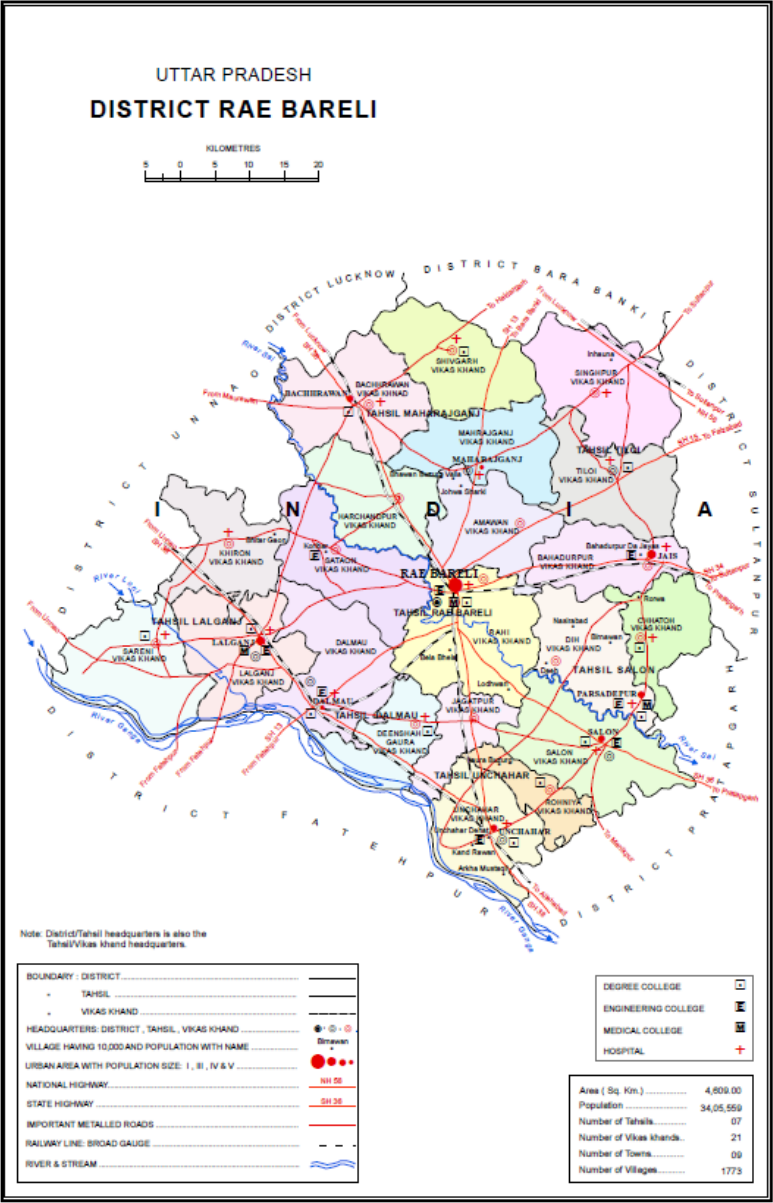
Raebareli District
Raebareli district is a district of Uttar Pradesh state in northern India. The city of Raebareli is the district headquarters. This district is a part of Lucknow Division in Uttar Pradesh state. The total area of Raebareli district is 3,371 Sq. km. As of 2011, its population is 3,405,559, which makes it the 27th largest in the state. It is a predominantly rural district, with 91% of the population living in rural areas. Geography Raebareli district is located in the southern part of Awadh, at the southern end of Lucknow Division. It is compact in shape — no part of the district is especially far from the city of Raebareli. In general, the terrain is flat or gently undulating, and the soil is especially fertile and well-suited to agriculture. The elevation ranges from 100 to 120 m above sea level. The prevailing slope is from higher in the northwest to lower in the southeast, and the rivers that traverse the district all flow in this direction. The main river of Raeba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States And Territories Of India
India is a federal union comprising 28 states and 8 union territories, with a total of 36 entities. The states and union territories are further subdivided into districts and smaller administrative divisions. History Pre-independence The Indian subcontinent has been ruled by many different ethnic groups throughout its history, each instituting their own policies of administrative division in the region. The British Raj mostly retained the administrative structure of the preceding Mughal Empire. India was divided into provinces (also called Presidencies), directly governed by the British, and princely states, which were nominally controlled by a local prince or raja loyal to the British Empire, which held ''de facto'' sovereignty ( suzerainty) over the princely states. 1947–1950 Between 1947 and 1950 the territories of the princely states were politically integrated into the Indian union. Most were merged into existing provinces; others were organised into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hasnapur
Hasnapur is a village in Nawabganj block of Unnao district, Uttar Pradesh, India. As of 2011, its population is 917, in 159 households, and it has a pre-primary school and no healthcare facilities. The 1961 census recorded Hasnapur as comprising 4 hamlets, with a total population of 296 (167 male and 129 female), in 60 households and 53 physical houses. The area of the village was given as 275 acre The acre is a unit of land area used in the imperial Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism. Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to: Places United States * Imperial, California * Imperial, Missouri * Imp ...s. References {{Unnao district Villages in Unnao district ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taluqdar
Taluqdars or Talukdar ( Hindustani: Devanagari: ; Perso-Arabic: , ; from ''taluq'' "estate/attachment" + '' dar'' "owner"), were aristocrats who formed the ruling class during the Delhi Sultanate, Bengal Sultanate, Mughal Empire and British Raj. They were owners of a vast amount of lands, consistently hereditary, and were responsible for collecting taxes. The Taluqdars played helpful roles in the progression of Indian architecture and Indian economy during the reign of Emperor Shah Jahan and Aurangzeb, particularly in Bengal Subah, the most economically developed province in South Asia.Om Prakash,Empire, Mughal, ''History of World Trade Since 1450'', edited by John J. McCusker, vol. 1, Macmillan Reference US, 2006, pp. 237–240, ''World History in Context''. Retrieved 3 August 2017 Being powerful peers, similar to those of Europe in the Middle Ages, after the decline of the Mughal state the Taluqdaris were to withstand the revenue collectors of the Colonial Powers while also br ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oilseed
Vegetable oils, or vegetable fats, are oils extracted from seeds or from other parts of fruits. Like animal fats, vegetable fats are ''mixtures'' of triglycerides. Soybean oil, grape seed oil, and cocoa butter are examples of seed oils, or fats from seeds. Olive oil, palm oil, and rice bran oil are examples of fats from other parts of fruits. In common usage, vegetable ''oil'' may refer exclusively to vegetable fats which are liquid at room temperature. Vegetable oils are usually edible. Uses In antiquity Oils extracted from plants have been used since ancient times and in many cultures. Archaeological evidence shows that olives were turned into olive oil by 6000 BCE and 4500 BCE in present-day Israel and Palestine. In addition to use as food, fats and oils (both vegetable and mineral) have long been used as fuel, typically in lamps which were a principal source of illumination in ancient times. Oils may have been used for lubrication, but there is no evidence for this. Vege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oudh And Rohilkhand Railway
Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway was an extensive railway network in the North India, mostly north of the Ganges, starting from Benares and subsequently up to Delhi. History The Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway was formed in 1872 with the assets of the Indian Branch Railway Company and the government guarantee. It had its headquarters at Lucknow. It built lines from Lucknow to Hardoi, Lucknow to Barabanki and Moradabad to Chandausi in 1872 and extended the last to Bareilly in 1873 It built a line from Varanasi to Lucknow in 1874, with an extension to Fyzabad known as Fyzabad Loop. The 4 miles long Broad gauge line from Burhwal to Bahramghat was opened on 1 April 1872 opened as part of the Bahramghat branch of the Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway the line got closed around 1943. The 17 miles long Burwhal-Barabanki metre gauge line was opened 1 April 1872 as part of the Bahramghat branch of the Oudh and Rohilkhand Railway. Upon conversion to mixed gauge, the metre gauge track formed part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
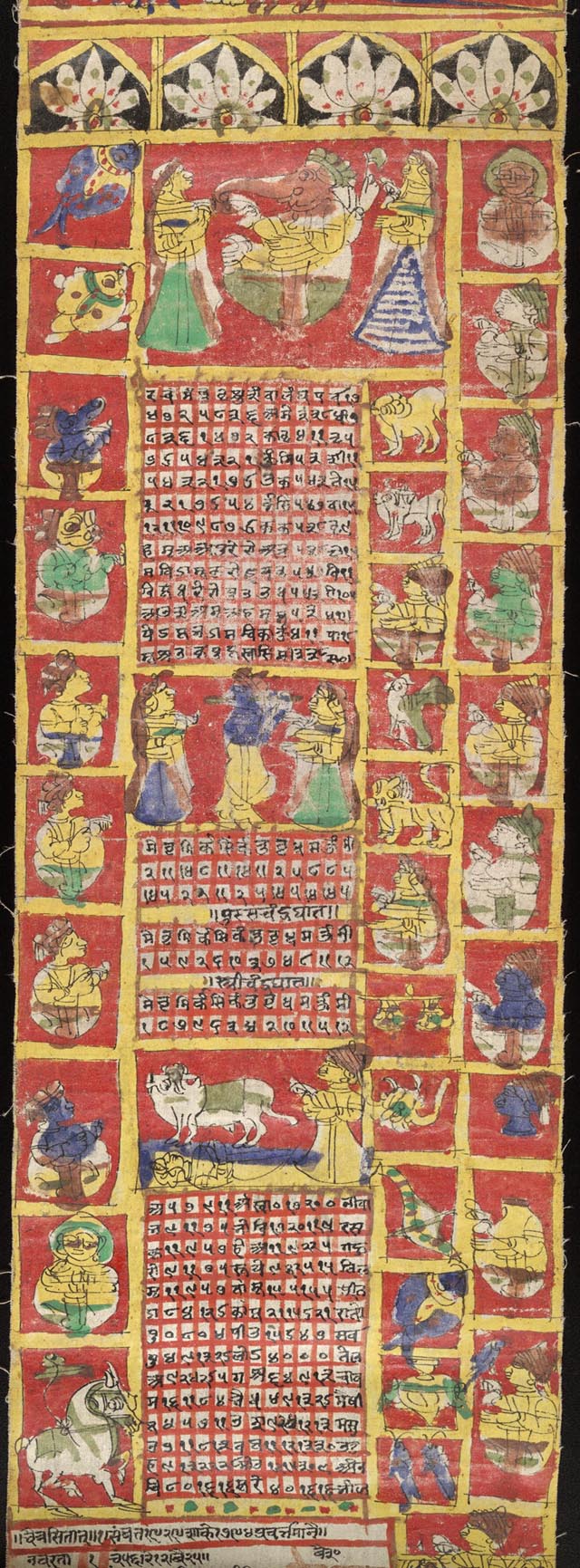
Samvat
The Hindu calendar, Panchanga () or Panjika is one of various lunisolar calendars that are traditionally used in the Indian subcontinent and Southeast Asia, with further regional variations for social and Hindu religious purposes. They adopt a similar underlying concept for timekeeping based on sidereal year for solar cycle and adjustment of lunar cycles in every three years, but differ in their relative emphasis to moon cycle or the sun cycle and the names of months and when they consider the New Year to start. Of the various regional calendars, the most studied and known Hindu calendars are the Shaka era, Shalivahana Shaka (Based on the Shalivahana, King Shalivahana, also the Indian national calendar) found in the Deccan Plateau, Deccan region of Southern India and the Vikram Samvat (Bikrami) found in Nepal and the North and Central regions of India – both of which emphasize the lunar cycle. Their new year starts in spring. In regions such as Tamil Nadu and Kerala, the solar c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bais (Rajput Clan)
The Bais () is a Rajput clan from India. History Their wealth caused Donald Butter, a visiting doctor who wrote ''Outlines of the Topography and Statistics of the Southern Districts of Oudh, and of the Cantonment of Sultanpur-Oudh'', to describe the Bais Rajput in the 1830s as the "best dressed and housed people of the southern Oudh". The Bais Rajputs were known for well-building. Famous Personalities Rana Beni Madho: Freedom fighter, leader of First war of independence or 1857 rebellion in Oudh. Major Dhyan Chand: Great hockey player and Olympian, India's highest sports award Major Dhyan Chand Khel Ratna is named after him. Tilok chand: The eponymous ancestor of the Bais of Baiswara. See also * Baiswara * Rajput clans Rajput (from Sanskrit ''raja-putra'' 'son of a king') is a large multi-component cluster of castes, kin bodies, and local groups, sharing social status and ideology of genealogical descent originating from the Indian subcontinent. The term Raj ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diwan (title)
''Dewan'' (also known as ''diwan'', sometimes spelled ''devan'' or ''divan'') designated a powerful government official, minister, or ruler. A ''dewan'' was the head of a state institution of the same name (see Divan). Diwans belonged to the elite families in the history of Mughal and post-Mughal India and held high posts within the government. Etymology The word is Persian in origin and was loaned into Arabic. The original meaning was "bundle (of written sheets)", hence "book", especially "book of accounts," and hence "office of accounts," "custom house," "council chamber". The meaning of the word, ''divan'' "long, cushioned seat" is due to such seats having been found along the walls in Middle Eastern council chambers. It is a common surname among Sikhs in Punjab. Council The word first appears under the Caliphate of Omar I (A.D. 634–644). As the Caliphate state became more complicated, the term was extended over all the government bureaus. The ''divan of the Sublime P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |