|
Harald Von Boehmer
Harald von Boehmer (30 November 1942 – 24 June 2018) was a German- Swiss immunologist best known for his work on T lymphocytes. Career The youngest of Hasso von Boehmer's three children, von Boehmer obtained an M.D. from the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (1968) and a Ph.D. from Melbourne University, Australia (1974). He was a member of the Basel Institute for Immunology in Switzerland (1973–1996), director of Unité INSERM 373 at the René Descartes University in Paris, France and is Professor of Pathology at Harvard Medical School and the Faculty of Arts and Sciences of Harvard University, Cambridge and Chief of the Laboratory for Lymphocyte Biology at the Dana Farber Cancer Institute in Boston. He was an adjunct professor at the University of Florida. Von Boehmer studied the role of T lymphocytes in the immune system. In particular he addressed the contribution of the T cell receptor (TCR) to recognition by T cells of peptide- MHC complexes by transfer of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard Medical School
Harvard Medical School (HMS) is the graduate medical school of Harvard University and is located in the Longwood Medical Area of Boston, Massachusetts. Founded in 1782, HMS is one of the oldest medical schools in the United States and is consistently ranked first for research among medical schools by '' U.S. News & World Report''. Unlike most other leading medical schools, HMS does not operate in conjunction with a single hospital but is directly affiliated with several teaching hospitals in the Boston area. Affiliated teaching hospitals and research institutes include Dana–Farber Cancer Institute, Massachusetts General Hospital, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston Children's Hospital, McLean Hospital, Cambridge Health Alliance, The Baker Center for Children and Families, and Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital. History Harvard Medical School was founded on September 19, 1782, after President Joseph Willard presented a report with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academia Europaea
The Academia Europaea is a pan-European Academy of Humanities, Letters, Law, and Sciences. The Academia was founded in 1988 as a functioning Europe-wide Academy that encompasses all fields of scholarly inquiry. It acts as co-ordinator of European interests in national research agencies. History The concept of a 'European Academy of Sciences' was raised at a meeting in Paris of the European Ministers of Science in 1985. The initiative was taken by the Royal Society (United Kingdom) which resulted in a meeting in London in June 1986 of Arnold Burgen (United Kingdom), Hubert Curien (France), Umberto Colombo (Italy), David Magnusson (Sweden), Eugen Seibold (Germany) and Ruurd van Lieshout (the Netherlands) – who agreed to the need for a new body. The two key purposes of Academia Europaea are: * express ideas and opinions of individual scientists from Europe * act as co-ordinator of European interests in national research agencies It does not aim to replace existing national a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Genève ) frp, Genèva ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the List of cities in Switzerland, second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Zürich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situated in the south west of the country, where the Rhône exits Lake Geneva, it is the capital of the Canton of Geneva, Republic and Canton of Geneva. The city of Geneva () had a population 201,818 in 2019 (Jan. estimate) within its small municipal territory of , but the Canton of Geneva (the city and its closest Swiss suburbs and exurbs) had a population of 499,480 (Jan. 2019 estimate) over , and together with the suburbs and exurbs located in the canton of Vaud and in the French Departments of France, departments of Ain and Haute-Savoie the cross-border Geneva metropolitan area as officially defined by Eurostat, which extends over ,As of 2020, the Eurostat-defined Functional Urban Area of Geneva was made up of 9 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gottfried Schatz
Gottfried Schatz (18 August 1936 – 1 October 2015) was a Swiss-Austrian biochemist. Life and career Schatz was born in Strem. Upon obtaining his PhD in chemistry and biochemistry at the University of Graz (Austria), he did postdoctoral work at the University of Vienna and at "The Public Health Institute" of the City of New York. In 1968, he emigrated to the US in order to assume a professorship Cornell University in Ithaca, New York. Six years later, he returned to Europe in order to join the newly created Biozentrum at the University of Basel, which he chaired from 1983 to 1985, From 1984 to 1989 he was Secretary General of the European Molecular Biology Organization (EMBO). After his retirement in 2000, he presided the ''Swiss Science and Technology Council'' (SSTC) until 2003. He is the author of more than 200 professional publications as well as of two books of essays on the broader implications of science. His scientific autobiography ''Interplanetary travels'' was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicole Le Douarin
Nicole Marthe Le Douarin (born 20 August 1930) is a developmental biologist known for her studies of chimeras, which have led to critical insights regarding higher animal nervous and immune systems. Le Douarin invented an embryo manipulation technology to produce chimeric embryos, from chicken and quails. Her research has shed light on the development of higher animal nervous and immune systems. She showed that precursor cells within the neural crest were multipotent. Her technique has also permitted her to shed light on the development of the blood and immune systems. Her work on antero-posterior patterning of the vertebrate digestive tract laid the grounds for future work, leading to a better understanding of antero-posterior patterning in the digestive tract. Early years and education Le Douarin was born on 20 August 1930 in Lorient, France. She was an only child, raised by both parents in the town of Lorient, where her mother worked as a schoolteacher and her father as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
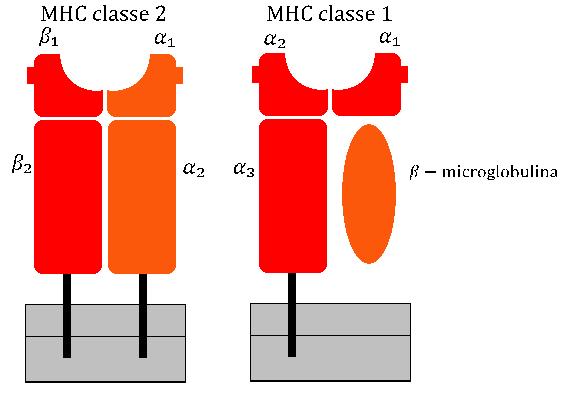
MHC Class II
MHC Class II molecules are a class of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules normally found only on professional antigen-presenting cells such as dendritic cells, mononuclear phagocytes, some endothelial cells, thymic epithelial cells, and B cells. These cells are important in initiating immune responses. The antigens presented by class II peptides are derived from extracellular proteins (not cytosolic as in MHC class I). Loading of a MHC class II molecule occurs by phagocytosis; extracellular proteins are endocytosed, digested in lysosomes, and the resulting epitopic peptide fragments are loaded onto MHC class II molecules prior to their migration to the cell surface. In humans, the MHC class II protein complex is encoded by the human leukocyte antigen gene complex (HLA). HLAs corresponding to MHC class II are HLA-DP, HLA-DM, HLA-DOA, HLA-DOB, HLA-DQ, and HLA-DR. Mutations in the HLA gene complex can lead to bare lymphocyte syndrome (BLS), which is a type of MHC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MHC Class I
MHC class I molecules are one of two primary classes of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules (the other being MHC class II) and are found on the cell surface of all nucleated cells in the bodies of vertebrates. They also occur on platelets, but not on red blood cells. Their function is to display peptide fragments of proteins from within the cell to cytotoxic T cells; this will trigger an immediate response from the immune system against a particular non-self antigen displayed with the help of an MHC class I protein. Because MHC class I molecules present peptides derived from cytosolic proteins, the pathway of MHC class I presentation is often called ''cytosolic'' or ''endogenous pathway''. In humans, the HLAs corresponding to MHC class I are HLA-A, HLA-B, and HLA-C. Function Class I MHC molecules bind peptides generated mainly from degradation of cytosolic proteins by the proteasome. The MHC I:peptide complex is then inserted via endoplasmic reticulum into the ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. The thymus is located in the upper front part of the chest, in the anterior superior mediastinum, behind the sternum, and in front of the heart. It is made up of two lobes, each consisting of a central medulla and an outer cortex, surrounded by a capsule. The thymus is made up of immature T cells called thymocytes, as well as lining cells called epithelial cells which help the thymocytes develop. T cells that successfully develop react appropriately with MHC immune receptors of the body (called ''positive selection'') and not against proteins of the body (called ''negative selection''). The thymus is largest and most active during the neonatal and pre-adolescent periods. By the early teens, the thymus begins to decrease in size and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major Histocompatibility Complex
The major histocompatibility complex (MHC) is a large locus on vertebrate DNA containing a set of closely linked polymorphic genes that code for cell surface proteins essential for the adaptive immune system. These cell surface proteins are called MHC molecules. This locus got its name because it was discovered via the study of transplanted tissue compatibility. Later studies revealed that tissue rejection due to incompatibility is only a facet of the full function of MHC molecules: binding an antigen derived from self-proteins, or from pathogens, and bringing the antigen presentation to the cell surface for recognition by the appropriate T-cells. MHC molecules mediate the interactions of leukocytes, also called white blood cells (WBCs), with other leukocytes or with body cells. The MHC determines donor compatibility for organ transplant, as well as one's susceptibility to autoimmune diseases. In a cell, protein molecules of the host's own phenotype or of other biologic entities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell Receptor
The T-cell receptor (TCR) is a protein complex found on the surface of T cells, or T lymphocytes, that is responsible for recognizing fragments of antigen as peptides bound to major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules. The binding between TCR and antigen peptides is of relatively low affinity and is degenerate: that is, many TCRs recognize the same antigen peptide and many antigen peptides are recognized by the same TCR. The TCR is composed of two different protein chains (that is, it is a heterodimer). In humans, in 95% of T cells the TCR consists of an alpha (α) chain and a beta (β) chain (encoded by '' TRA'' and ''TRB'', respectively), whereas in 5% of T cells the TCR consists of gamma and delta (γ/δ) chains (encoded by '' TRG'' and '' TRD'', respectively). This ratio changes during ontogeny and in diseased states (such as leukemia). It also differs between species. Orthologues of the 4 loci have been mapped in various species. Each locus can produce a vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida, traces its origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its Gainesville campus since September 1906. After the Florida state legislature's creation of performance standards in 2013, the Florida Board of Governors designated the University of Florida as a "preeminent university". For 2022, '' U.S. News & World Report'' ranked Florida as the fifth (tied) best public university and 28th (tied) best university in the United States. The University of Florida is the only member of the Association of American Universities in Florida and is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". The university is accredited by the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools (SACS). It is the third largest Florida university by student population,Nathan Crabbe, UF is no longer la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_p174_GAINESVILLE%2C_EAST_FLORIDA_SEMINARY.jpg)