|
Hanseatic Legion
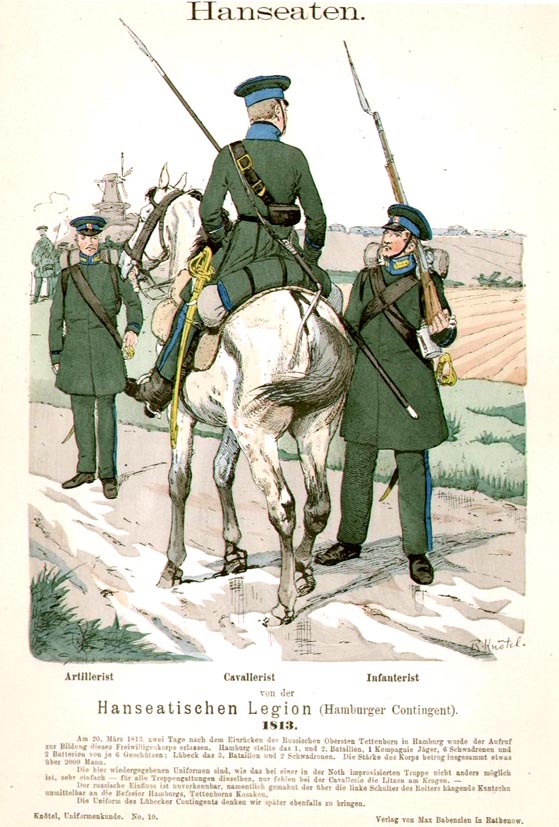
The Hanseatic Legion was a military unit, first formed of a group of citizens from Hamburg. They had met in 1813 on the instigation of General Friedrich Karl von Tettenborn, in order to fight in the War of the Sixth Coalition. This association of volunteers was joined immediately by volunteers from Hamburg's Hanseatic sister cities Bremen and Lübeck. The Legion should not be confused with the '' Hamburger Bürgermilitär'' (Hamburg Citizen Militia). During their time of coexistence, the militia restricted itself to ejecting the French garrisons stationed in Hamburg and the other two Hanseatic cities, whereas the ''Legion'' also participated in the rest of the campaign. History The Legion defended the Hanseatic cities against Davout's and Vandamme's troops until Tettenborn completed the raising of their sieges in the night of 29/30 May 1813. The Legion and the Hanseatischen Bürgergarden went with Count Tettenborn and in Mecklenburg joined the Allied northern army, later ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominique Vandamme
General Dominique-Joseph René Vandamme, Count of Unseburg (5 November 1770, Cassel, Nord15 July 1830) was a French military officer, who fought in the Napoleonic Wars. He was a dedicated career soldier with a reputation as an excellent division and corps commander. However he had a nasty disposition that alienated his colleagues, and would publicly criticize Napoleon, who never appointed him marshal. Biography Vandamme enlisted in the army in 1786 and rapidly rose through the ranks. At the outbreak of the French Revolutionary Wars in 1793 he was a Brigadier General. He served in this rank in the campaigns of 1794 in the Low Countries, 1795 on the Rhine and 1796 in Germany. He was court-martialled for looting and suspended. Reinstated, he fought at the First Battle of Stockach on 25 March 1799, but disagreement with General Jean Moreau led to his being sent to occupation duties in Holland. At the Battle of Austerlitz in 1805 he led his division, alongside Gen. St. Hilaire's, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Of Hamburg
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Lübeck
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, discovery, collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts, art and material artifacts, and ecological markers. History is not complete and still has debatable mysteries. History is also an academic discipline which uses narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians often debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians also debate the nature of history as an end in itself, as well as its usefulness to give perspective on the problems of the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th Century In Hamburg
19 (nineteen) is the natural number following 18 and preceding 20. It is a prime number. Mathematics 19 is the eighth prime number, and forms a sexy prime with 13, a twin prime with 17, and a cousin prime with 23. It is the third full reptend prime, the fifth central trinomial coefficient, and the seventh Mersenne prime exponent. It is also the second Keith number, and more specifically the first Keith prime. * 19 is the maximum number of fourth powers needed to sum up to any natural number, and in the context of Waring's problem, 19 is the fourth value of g(k). * The sum of the squares of the first 19 primes is divisible by 19. *19 is the sixth Heegner number. 67 and 163, respectively the 19th and 38th prime numbers, are the two largest Heegner numbers, of nine total. * 19 is the third centered triangular number as well as the third centered hexagonal number. : The 19th triangular number is 190, equivalently the sum of the first 19 non-zero integers, that is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Bremen (city)
For most of its 1,200 year history, Bremen was an independent city within the confederal jurisdiction of Germany's Holy Roman Empire. In the late Middle Ages, its governing merchant guilds were at the centre of the Hanseatic League that sought to monopolise North Sea and Baltic trade. To enlarge and confirm its independence, the city had to contend until the Reformation with the Prince-Archbishop of Bremen, and after the Thirty Years War with the Swedes, masters of the surrounding, former episcopal, duchies. In the late nineteenth century Bremen was drawn by Prussia into the German Empire. With new sea wharves and anchorage at Bremerhaven, it became Germany's principal port of emigration to the Americas, and an entrepôt for her late developing colonial trade. The Norddeutscher Lloyd (NDL), founded in Bremen in 1857, developed as one of the world's leading shipping companies. In the twentieth century, Bremen, a broadly liberal and social-democratic city, lost its autonomy under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Military Units And Formations Of The Napoleonic Wars
German(s) may refer to: * Germany (of or related to) **Germania (historical use) * Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language ** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law **Germanic peoples (Roman times) * German language **any of the Germanic languages * German cuisine, traditional foods of Germany People * German (given name) * German (surname) * Germán, a Spanish name Places * German (parish), Isle of Man * German, Albania, or Gërmej * German, Bulgaria * German, Iran * German, North Macedonia * German, New York, U.S. * Agios Germanos, Greece Other uses * German (mythology), a South Slavic mythological being * Germans (band), a Canadian rock band * "German" (song), a 2019 song by No Money Enterprise * ''The German'', a 2008 short film * "The Germans", an episode of ''Fawlty Towers'' * ''The German'', a nickname for Congolese rebel André Kisase Ngandu See also * Germanic (other) * Germa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanseatic Cities
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=German language, Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the late 12th century, the League ultimately encompassed nearly 200 settlements across seven modern-day countries; at its height between the 13th and 15th centuries, it stretched from the Netherlands in the west to Russia in the east, and from Estonia in the north to Kraków, Poland in the south. The League originated from various loose associations of German traders and towns formed to advance mutual commercial interests, such as protection against piracy and banditry. These arrangements gradually coalesced into the Hanseatic League, whose traders enjoyed Duty-free trade, duty-free treatment, protection, and diplomatic privileges in affiliated communitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
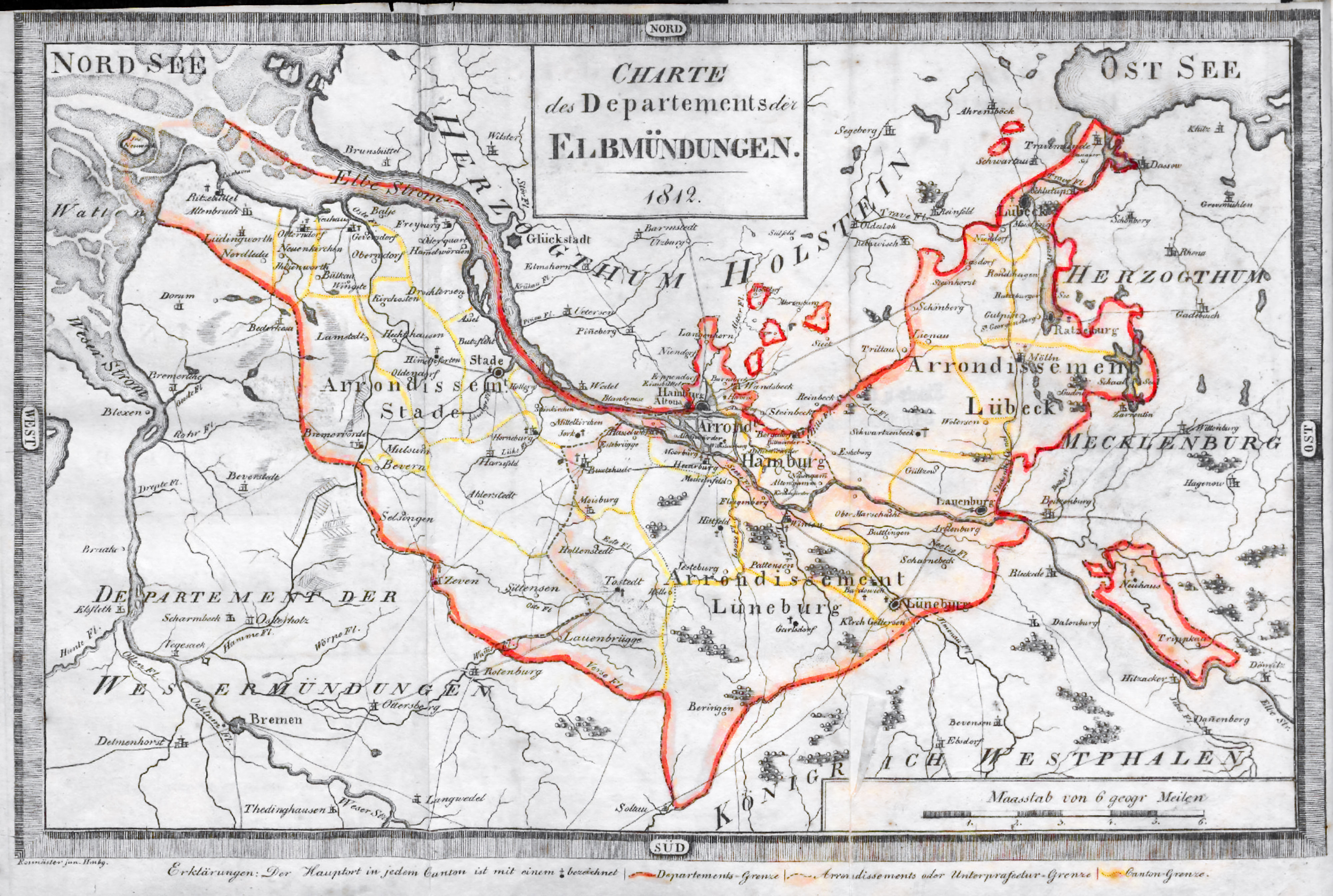
Bouches-de-l'Elbe
Bouches-de-l'Elbe (; "Mouths of the Elbe", ) was a departments of France, department of the First French Empire in present-day Germany that survived for three years. It was named after the mouth of the river Elbe. It was formed in 1811, when the region, originally belonging partially to Bremen-Verden (which in 1807 had been intermittently incorporated into the Kingdom of Westphalia), to Hamburg, Free City of Lübeck, Lübeck and Saxe-Lauenburg, was annexed by France. Its territory is part of the present-day German states of Lower Saxony, Schleswig-Holstein and Hamburg. Its capital was Hamburg. The department was subdivided into four arrondissements and the following canton (subnational entity), cantons (situation in 1812, French translated names where applicable):Almanach Impérial an bissextil MDCCCXII p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Schleswig
The Duchy of Schleswig ( da, Hertugdømmet Slesvig; german: Herzogtum Schleswig; nds, Hartogdom Sleswig; frr, Härtochduum Slaswik) was a duchy in Southern Jutland () covering the area between about 60 km (35 miles) north and 70 km (45 mi) south of the current border between Germany and Denmark. The territory has been divided between the two countries since 1920, with Northern Schleswig in Denmark and Southern Schleswig in Germany. The region is also called Sleswick in English. Unlike Holstein and Lauenburg, Schleswig was never a part of the German Confederation. Schleswig was instead a fief of Denmark, and its inhabitants spoke Danish, German, and North Frisian. Both Danish and German National Liberals wanted Schleswig to be part of a Danish or German national state in the 19th century. A German uprising in March 1848 caused the First Schleswig War which ended in 1852. The Second Schleswig War (1864) ended with the three duchies being governed jointly by Austria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label=Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schwerin, Neubrandenburg, Wismar and Güstrow. The name Mecklenburg derives from a castle named '' Mikilenburg'' (Old Saxon for "big castle", hence its translation into New Latin and Greek as ), located between the cities of Schwerin and Wismar. In Slavic languages it was known as ''Veligrad'', which also means "big castle". It was the ancestral seat of the House of Mecklenburg; for a time the area was divided into Mecklenburg-Schwerin and Mecklenburg-Strelitz among the same dynasty. Linguistically Mecklenburgers retain and use many features of Low German vocabulary or phonology. The adjective for the region is ''Mecklenburgian'' or ''Mecklenburgish'' (german: mecklenburgisch, link=no); inhabitants are called Mecklenburgians or Mecklenburgers ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Nicolas Davout
Louis-Nicolas d'Avout (10 May 1770 – 1 June 1823), better known as Davout, 1st Duke of Auerstaedt, 1st Prince of Eckmühl, was a French military commander and Marshal of the Empire who served during both the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. His talent for war, along with his reputation as a stern disciplinarian, earned him the nickname "The Iron Marshal" (''Le Maréchal de fer''). He is ranked along with Marshals Louis-Alexandre Berthier and Jean Lannes as one of Napoleon's finest commanders. His loyalty and obedience to Napoleon were absolute. During his lifetime, Davout's name was commonly spelled Davoust - this spelling appears on the Arc de Triomphe and in much of the correspondence between Napoleon and his generals. Biography Davout was born in the small village Annoux (Yonne) as the eldest son of Jean-François d'Avout (1739–1779), a calvalry officer and his wife (married in 1768) Françoise-Adélaïde Minard de Velars (1741–1810). He was of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)