|
Hans Von Schack
Hans Schack (28 October 1608 – 27 February 1676) was a member of the north German noble family Schack, who after many years in French service, entered the Danish service, made major contributions during the war with Sweden, and loyally supported Frederick III when he overthrew the Danish constitution. He became a Danish field-marshal, commander-in-chief of the Danish army, member of the Board of State, and of the Danish Privy Council, and made a Danish count. Early career As a young man, Schack began his military career by serving in the Danish army during the early years of the Thirty Years' War. He entered Swedish service in 1630, and thence in French in 1635, becoming colonel of cavalry 1642, and later ''maréchal de camp''. In 1651 Schack retired from the French service to his estates in Saxe-Lauenburg, where he remained until 1656, when he became military commandant of Hamburg. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Langballig
Langballig ( da, Langballe) is a municipality in the district of Schleswig-Flensburg, in Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. It is situated near the Baltic Sea The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and ..., approx. 13 km east of Flensburg. Langballig is the seat of the '' Amt'' ("collective municipality") Langballig. References Schleswig-Flensburg {{SchleswigFlensburg-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Danish Privy Council
The Council of State (, , ) is the privy council of the Kingdom of Denmark. The body of advisors to the Danish monarch, the council is a formal institution, with largely ceremonial functions. Chaired by the monarch, the council comprises all cabinet ministers and the crown prince or hereditary princess when coming of age. When unavailable, the monarch is represented by the regent or Lord Protector (). In its beginnings, the council was a place of debate amongst the ministers over government policy. However, since the formation of real political parties at the beginning of the 20th century, these debates were moved from the council to informal ministerial meetings where government policy could be coordinated – usually held every Wednesday. As a result, the primary function of the council today is to grant royal assent, which is done by the counter-signatures of the monarch and a minister. Before granting the assent, a relevant minister explains the general aim of the bill brough ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
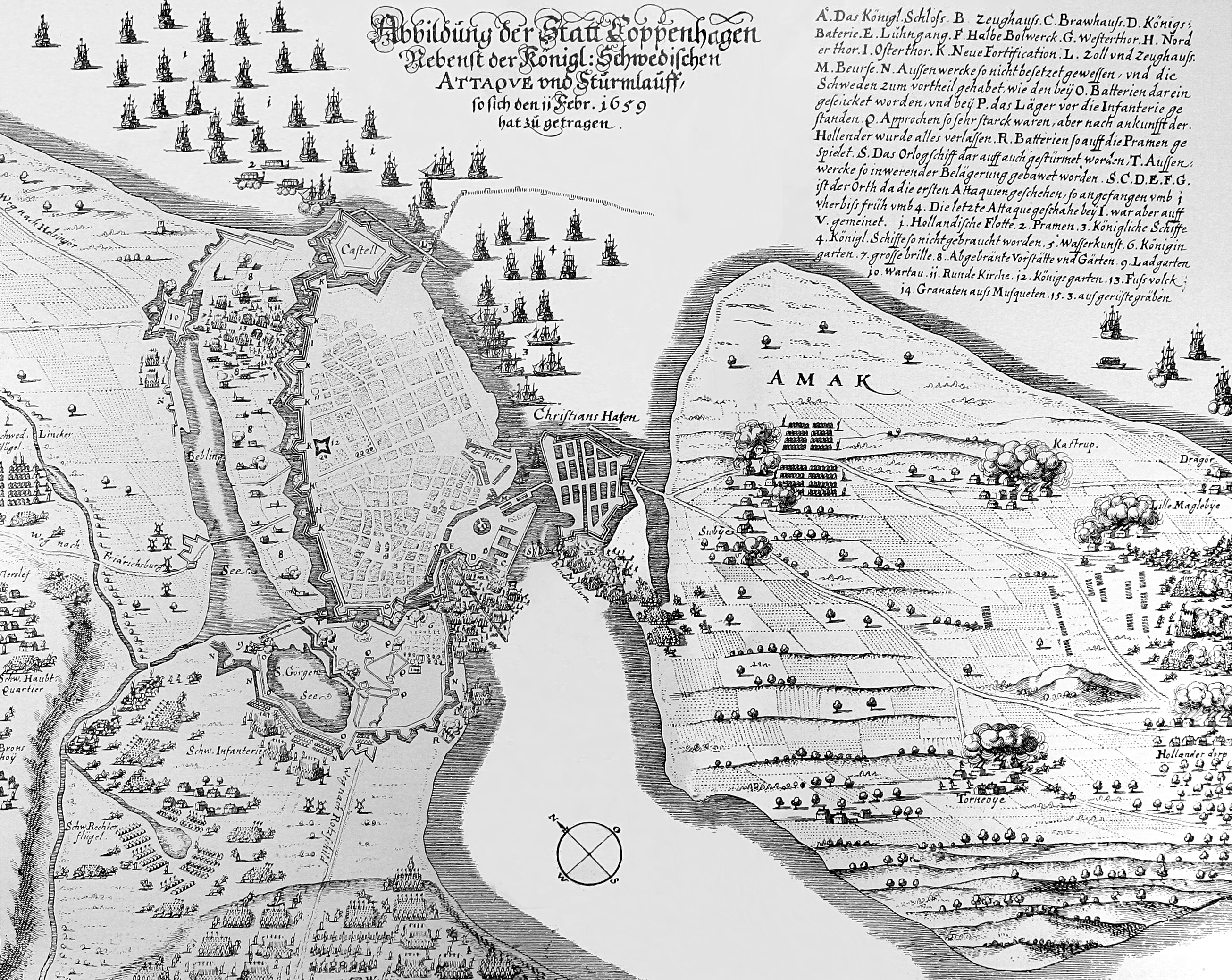
Assault On Copenhagen (1659)
The Battle of Copenhagen also known as the Assault on Copenhagen on 11 February 1659 was a major battle during the Second Northern War, taking place during the siege of Copenhagen by the Swedish army. Background During the Northern Wars, the Swedish army under Charles X Gustav of Sweden, after invading the Danish mainland of Jutland, swiftly crossed the frozen straits and occupied most of the Danish island of Zealand, with the invasion beginning on 11 February 1658. This forced the Danes to sue for peace. A preliminary treaty, the Treaty of Taastrup, was signed on 18 February 1658, with the final treaty, the Treaty of Roskilde, signed on 26 February 1658, granting Sweden major territorial gains. The Swedish king, however, was not content with his stunning victory, and at the Privy Council held at Gottorp on 7 July Charles X Gustav resolved to wipe his inconvenient rival from the map of Europe. Without any warning, in defiance of international treaty, he ordered his troops to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
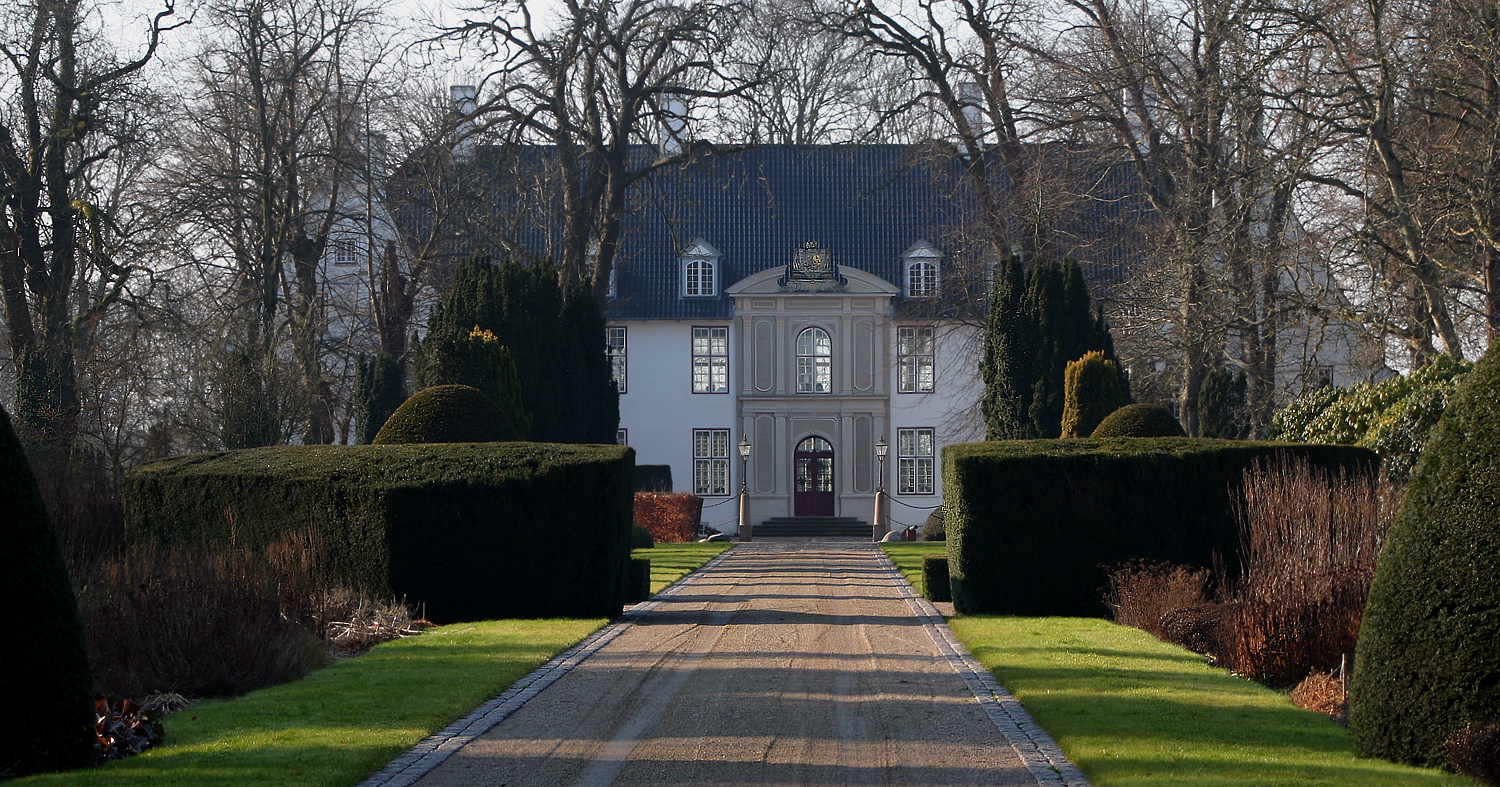
Schackenborg Castle
Schackenborg Castle ( da, Schackenborg Slot, ) is a château located in Møgeltønder, Southern Jutland. From 1993 until 2014, it was the private residence of Prince Joachim of Denmark, the second son of Queen Margrethe II of Denmark. History Originally called Møgeltønderhus (Møgeltønder House), the former stronghold on the site was the property of the Roman Catholic bishops of Ribe. It served as protection against the Frisians in the south, and guarded the waterway that joined Vidå to Tønder. During the Reformation in Denmark, the mansion was confiscated from the Church by the Danish crown. Count Hans von Schack, a Schleswig nobleman and soldier, was given Møgeltønderhus as a token of King Frederick III of Denmark's gratitude for his military achievements in the Northern Wars. Schack demolished most of the mansion in 1661 due to its bad condition, building the more impressive, baroque style "Schackenborg Castle". In 1680, a street was laid out from the manor hou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Møgeltønder
Møgeltønder () is a small town in Denmark, located in Møgeltønder Parish and Tønder Municipality in the southwestern corner of the Danish peninsula of Jutland 5 kilometres north of the Danish-German border and 4 kilometres west of Tønder. Møgeltønder is known for its picturesque main street, the large 12th-century church, and Schackenborg Castle. As of 2022, it has a population of 799. Møgeltønder Church Møgeltønder Church is one of the largest village churches in southern Jutland. The church was built in c. 1180 but had the nave extended and a larger choir added c1275. The tower with the tall spire was added in the 15th century. The church was owned by the counts Schack of Schackenborg castle from 1661 to 1970, and has a rich interior e.g. a gothic altarpiece from c.1 450, 17th pulpit and pews, and the oldest church organ in Denmark. As a manor church, it shows many references to the Schack family. Apart from the large burial chapel of the Schack family, the med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Life Tenancy
In common law and statutory law, a life estate (or life tenancy) is the ownership of immovable property for the duration of a person's life. In legal terms, it is an estate in real property that ends at death when ownership of the property may revert to the original owner, or it may pass to another person. The owner of a life estate is called a "life tenant". In the combined jurisdiction of England and Wales since 1925 a freehold estate intended to be 'held' as a life interest takes effect only as an interest enjoyed in equity, specifically as an interest in possession trust. The other type of land ownership is leasehold and although most long leases are for a period of between 99 and 999 years 'leases for life' will be interpreted in often unpredictable ways as either as a licence or a lease. Principles The ownership of a life estate is of limited duration because it ends at the death of a person. Its owner is the life tenant (typically also the 'measuring life') and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Estate (land)
An estate is a large parcel of land under single ownership, which would historically generate income for its owner. British context In the UK, historically an estate comprises the houses, outbuildings, supporting farmland, and woods that surround the gardens and grounds of a very large property, such as a country house, mansion, palace or castle. It is the modern term for a manor, but lacks a manor's now-abolished jurisdiction. The "estate" formed an economic system where the profits from its produce and rents (of housing or agricultural land) sustained the main household, formerly known as the manor house. Thus, "the estate" may refer to all other cottages and villages in the same ownership as the mansion itself, covering more than one former manor. Examples of such great estates are Woburn Abbey in Bedfordshire, England, and Blenheim Palace, in Oxfordshire, England, built to replace the former manor house of Woodstock. In a more urban context are the "Great Estates" in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobility
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy (class), aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below Royal family, royalty. Nobility has often been an Estates of the realm, estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The characteristics associated with nobility may constitute substantial advantages over or relative to non-nobles or simply formal functions (e.g., Order of precedence, precedence), and vary by country and by era. Membership in the nobility, including rights and responsibilities, is typically Hereditary title, hereditary and Patrilinearity, patrilineal. Membership in the nobility has historically been granted by a monarch or government, and acquisition of sufficient power, wealth, ownerships, or royal favour has occasionally enabled commoners to ascend into the nobility. There are often a variety of ranks within the noble class. Legal recognition of nobility has been much more common in monarchies, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturalization
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-citizen of a country may acquire citizenship or nationality of that country. It may be done automatically by a statute, i.e., without any effort on the part of the individual, or it may involve an application or a motion and approval by legal authorities. The rules of naturalization vary from country to country but typically include a promise to obey and uphold that country's laws and taking and subscribing to an oath of allegiance, and may specify other requirements such as a minimum legal residency and adequate knowledge of the national dominant language or culture. To counter multiple citizenship, some countries require that applicants for naturalization renounce any other citizenship that they currently hold, but whether this renunciation actually causes loss of original citizenship, as seen by the host country and by the original country, will depend on the laws of the countries involved. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lieutenant General
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the battlefield, who was normally subordinate to a captain general. In modern armies, lieutenant general normally ranks immediately below general and above major general; it is equivalent to the navy rank of vice admiral, and in air forces with a separate rank structure, it is equivalent to air marshal. A lieutenant general commands an army corps, made up of typically three army divisions, and consisting of around 60 000 to 70 000 soldiers (U.S.). The seeming incongruity that a lieutenant general outranks a major general (whereas a major outranks a lieutenant) is due to the derivation of major general from sergeant major general, which was a rank subordinate to lieutenant general (as a lieutenant outranks a sergeant major). In contrast, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxe-Lauenburg
The Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg (german: Herzogtum Sachsen-Lauenburg, called ''Niedersachsen'' (Lower Saxony) between the 14th and 17th centuries), was a '' reichsfrei'' duchy that existed from 1296–1803 and again from 1814–1876 in the extreme southeast region of what is now Schleswig-Holstein. Its territorial center was in the modern district of Herzogtum Lauenburg and originally its eponymous capital was Lauenburg upon Elbe, though in 1619 the capital moved to Ratzeburg. Former territories not part of today's district of Lauenburg In addition to the core territories in the modern district of Lauenburg, at times other territories, mostly south of the river Elbe, belonged to the duchy: * The tract of land along the southern Elbe bank (german: Marschvogtei), reaching from Marschacht to the ''Amt Neuhaus'', territorially connecting the core of the duchy with these more southeastern Lauenburgian areas. This land was ceded to the Kingdom of Hanover in 1814. It is now part of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |