|
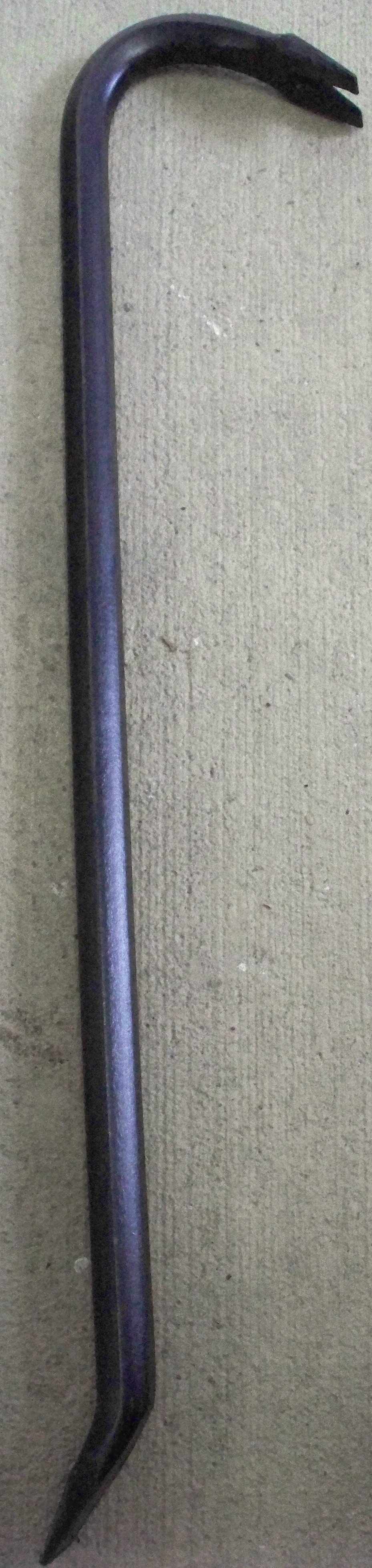
Handspike
A handspike is a metal bar or pipe that is used as a lever for prying or leverage, similar to a crowbar. Handspike is also an archaic term for a bar or lever, generally of wood, used in a windlass or capstan, for heaving anchor, and, in modified forms, for various other purposes.Oxford English Dictionary Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) © Oxford University Press 2009 On the Calder and Hebble Navigation in England, a handspike in the form of a length of 2-by-4-inch (5 by 10 cm) timber shaped at one end to provide a comfortable two-handed grip is used to operate the winding gear of some of the locks Lock(s) may refer to: Common meanings *Lock and key, a mechanical device used to secure items of importance *Lock (water navigation), a device for boats to transit between different levels of water, as in a canal Arts and entertainment * ''Lock .... References Hand tools {{Tool-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
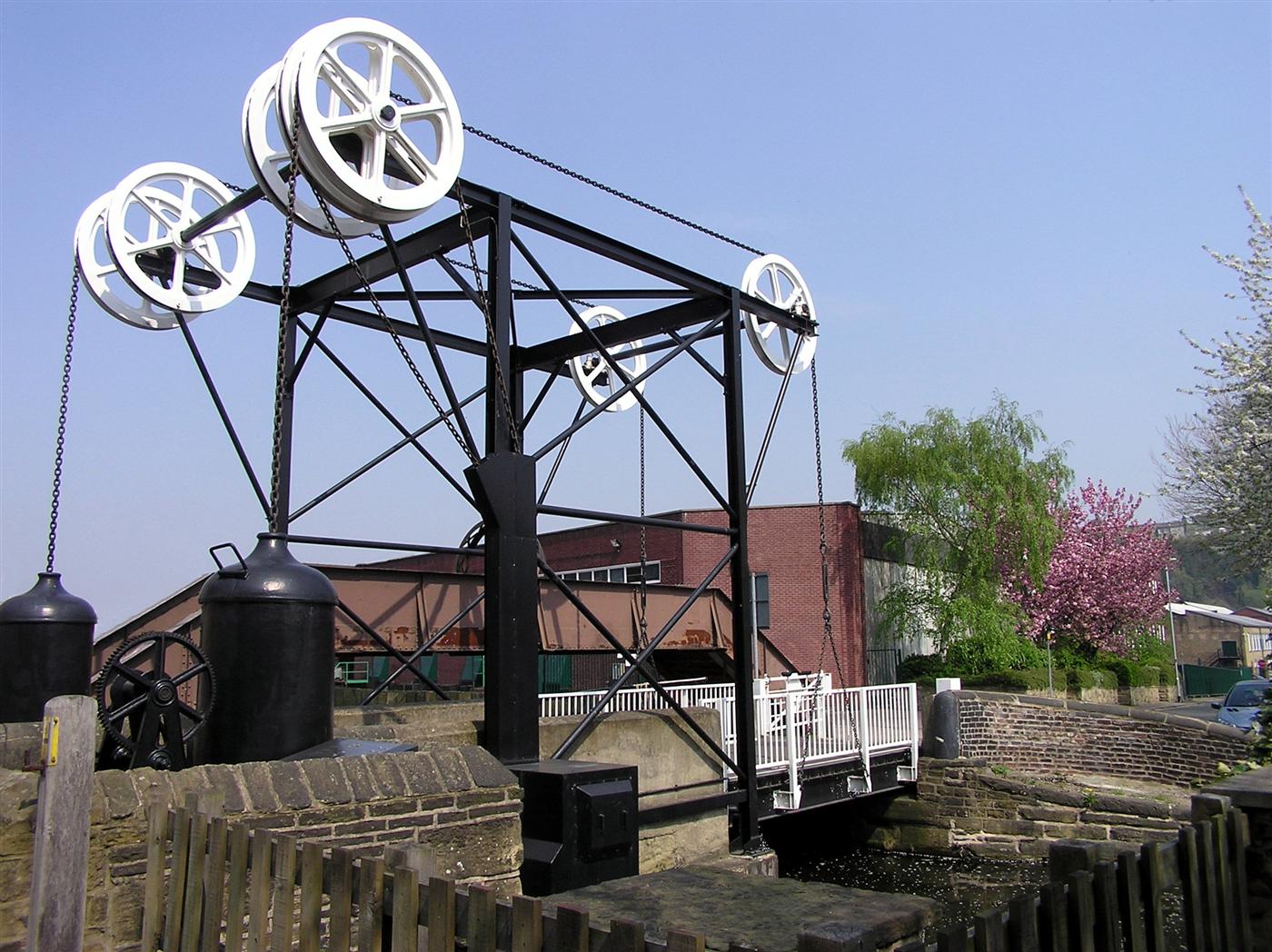
Calder And Hebble Navigation
The Calder and Hebble Navigation is a broad inland waterway, with locks and bridgeholes that are suitable for boats, in West Yorkshire, England. Construction to improve the River Calder and the River Hebble began in 1759, and the initial scheme, which included of new cuts, was completed in 1770 and has remained navigable since it was opened. Significant improvements were made, including the Salterhebble branch to Halifax, opened in 1828, and ever-longer cuts to bypass river sections. Trade was assisted by the opening of the Rochdale Canal in 1804, which provided a through route from Sowerby Bridge to Manchester. There were plans to abandon the river sections completely in the 1830s, but these were modified as the needs of mill owners and other riparian landowners were recognised. With the coming of the railways, the canal was leased to the Manchester and Leeds Railway in 1843, but this was subsequently deemed to be illegal, and the Aire and Calder Navigation with which the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typically ductile (can be drawn into wires) and malleable (they can be hammered into thin sheets). These properties are the result of the ''metallic bond'' between the atoms or molecules of the metal. A metal may be a chemical element such as iron; an alloy such as stainless steel; or a molecular compound such as polymeric sulfur nitride. In physics, a metal is generally regarded as any substance capable of conducting electricity at a temperature of absolute zero. Many elements and compounds that are not normally classified as metals become metallic under high pressures. For example, the nonmetal iodine gradually becomes a metal at a pressure of between 40 and 170 thousand times atmospheric pressure. Equally, some materials regarded as metals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pipe (material)
A pipe is a tubular section or hollow cylinder, usually but not necessarily of circular cross-section, used mainly to convey substances which can flow — liquids and gases (fluids), slurries, powders and masses of small solids. It can also be used for structural applications; hollow pipe is far stiffer per unit weight than solid members. In common usage the words ''pipe'' and ''tube'' are usually interchangeable, but in industry and engineering, the terms are uniquely defined. Depending on the applicable standard to which it is manufactured, pipe is generally specified by a nominal diameter with a constant outside diameter (OD) and a schedule that defines the thickness. Tube is most often specified by the OD and wall thickness, but may be specified by any two of OD, inside diameter (ID), and wall thickness. Pipe is generally manufactured to one of several international and national industrial standards. While similar standards exist for specific industry applicati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
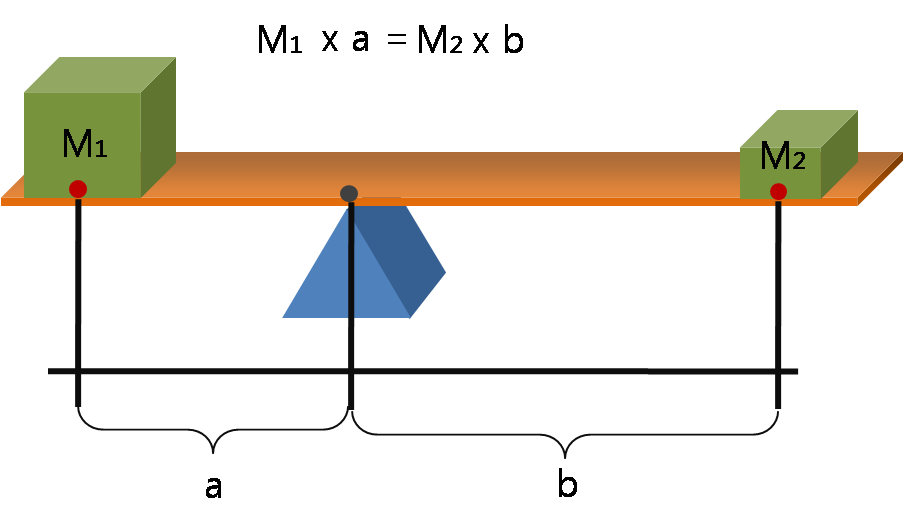
Lever
A lever is a simple machine consisting of a beam or rigid rod pivoted at a fixed hinge, or ''fulcrum''. A lever is a rigid body capable of rotating on a point on itself. On the basis of the locations of fulcrum, load and effort, the lever is divided into three types. Also, leverage is mechanical advantage gained in a system. It is one of the six simple machines identified by Renaissance scientists. A lever amplifies an input force to provide a greater output force, which is said to provide leverage. The ratio of the output force to the input force is the mechanical advantage of the lever. As such, the lever is a mechanical advantage device, trading off force against movement. Etymology The word "lever" entered English around 1300 from Old French, in which the word was ''levier''. This sprang from the stem of the verb ''lever'', meaning "to raise". The verb, in turn, goes back to the Latin ''levare'', itself from the adjective ''levis'', meaning "light" (as in "not heavy"). The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crowbar (tool)
A crowbar, also called a wrecking bar, pry bar or prybar, pinch-bar, or occasionally a prise bar or prisebar, colloquially, in Britain and Australia sometimes called a jemmy or jimmy (also called jemmy bar), gooseneck, or pig foot, is a tool consisting of a metal bar with a single curved end and flattened points, often with a small fissure on one or both ends for removing nails or to force apart two objects. Crowbars are commonly used to open nailed wooden crates or pry apart boards. The design can be used as any of the three lever classes. The curved end is usually used as a first-class lever, and the flat end as a second-class lever. Designs made from thick flat steel bar are often referred to as utility bars. Materials and construction Normally made of medium-carbon steel, crowbars can alternatively be made from titanium, which has the advantage of being lighter. Commonly crowbars are forged from long steel products, either hexagonal or sometimes cylindrical stock. Al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Windlass
The windlass is an apparatus for moving heavy weights. Typically, a windlass consists of a horizontal cylinder (barrel), which is rotated by the turn of a crank or belt. A winch is affixed to one or both ends, and a cable or rope is wound around the winch, pulling a weight attached to the opposite end. The Greek scientist Archimedes was the inventor of the windlass. The oldest depiction of a windlass for raising water can be found in the Book of Agriculture published in 1313 by the Chinese official Wang Zhen of the Yuan Dynasty ( 1290–1333). Uses *Vitruvius, a military engineer writing about 28 BC, defined a machine as "a combination of timber fastened together, chiefly efficacious in moving great weights." About a century later, Hero of Alexandria summarized the practice of his day by naming the "five simple machines" for "moving a given weight by a given force" as the lever, windlass, screw for power, wedge, and tackle block (pulley). Until nearly the end of the nine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capstan (nautical)
A capstan is a vertical- axled rotating machine developed for use on sailing ships to multiply the pulling force of seamen when hauling ropes, cables, and hawsers. The principle is similar to that of the windlass, which has a horizontal axle. History The word, connected with the Old French ''capestan'' or ''cabestan(t)'', from Old Provençal ''cabestan'', from ''capestre'' "pulley cord," from Latin ''capistrum'', -a halter, from ''capere'', to take hold of, seems to have come into English (14th century) from Portuguese or Spanish shipmen at the time of the Crusades. Both device and word are considered Spanish inventions. Early form In its earliest form, the capstan consisted of a timber mounted vertically through a vessel's structure which was free to rotate. Levers, known as bars, were inserted through holes at the top of the timber and used to turn the capstan. A rope wrapped several turns around the drum was thus hauled upon. A rudimentary ratchet was provided to hold t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lock (water Navigation)
A lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a fixed chamber in which the water level can be varied; whereas in a caisson lock, a boat lift, or on a canal inclined plane, it is the chamber itself (usually then called a caisson) that rises and falls. Locks are used to make a river more easily navigable, or to allow a canal to cross land that is not level. Later canals used more and larger locks to allow a more direct route to be taken. Pound lock A ''pound lock'' is most commonly used on canals and rivers today. A pound lock has a chamber with gates at both ends that control the level of water in the pound. In contrast, an earlier design with a single gate was known as a flash lock. Pound locks were first used in China during the Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD), having been pioneered by the Song politician and naval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lock (water Navigation)
A lock is a device used for raising and lowering boats, ships and other watercraft between stretches of water of different levels on river and canal waterways. The distinguishing feature of a lock is a fixed chamber in which the water level can be varied; whereas in a caisson lock, a boat lift, or on a canal inclined plane, it is the chamber itself (usually then called a caisson) that rises and falls. Locks are used to make a river more easily navigable, or to allow a canal to cross land that is not level. Later canals used more and larger locks to allow a more direct route to be taken. Pound lock A ''pound lock'' is most commonly used on canals and rivers today. A pound lock has a chamber with gates at both ends that control the level of water in the pound. In contrast, an earlier design with a single gate was known as a flash lock. Pound locks were first used in China during the Song Dynasty (960–1279 AD), having been pioneered by the Song politician and naval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |