|
Handheld Computer
A mobile device (or handheld computer) is a computer small enough to hold and operate in the hand. Mobile devices typically have a flat LCD or OLED screen, a touchscreen interface, and digital or physical buttons. They may also have a physical keyboard. Many such devices can connect to the Internet and connect with other devices such as car entertainment systems or headsets via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks or near field communication (NFC). Integrated cameras, the ability to place and receive voice and video telephone calls, video games, and Global Positioning System (GPS) capabilities are common. Power is typically provided by a lithium-ion battery. Mobile devices may run mobile operating systems that allow third-party applications to be installed and run. Early smartphones were joined in the late 2000s by larger tablets. Input and output is usually via a touch-screen interface. Phones/tablets and personal digital assistants may provide much of the functionality of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IPad & IPhone
The iPad is a brand of iOS and iPadOS-based tablet computers that are developed by Apple Inc. The iPad was conceived before the related iPhone but the iPhone was developed and released first. Speculation about the development, operating system, and release of the original iPad began in 2002 prior to its introduction on January 20, 2010. The iPad range consists of the original iPad lineup and the flagship products iPad Mini, iPad Air, and iPad Pro. The iPhone's iOS operating system (OS) was initially used for the iPad but in September 2019, its OS was switched to a fork of iOS called iPadOS that has better support for the device's hardware and its user interface is customized for the tablets' larger screens. The iPad's App Store is subject to application and content approval. Many older devices are susceptible to jailbreaking, which circumvents these restrictions. The original iPad was well-received for its software and was recognized as one of the most-influential inven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Touch User Interface
A touch user interface (TUI) is a computer-pointing technology based upon the sense of touch ( haptics). Whereas a graphical user interface (GUI) relies upon the sense of sight, a TUI enables not only the sense of touch to innervate and activate computer-based functions, it also allows the user, particularly those with visual impairments, an added level of interaction based upon tactile or Braille input. Technology Generally, the TUI requires pressure or presence with a switch located outside of the printed paper. Not to be confused with electronic paper endeavors, the TUI requires the printed pages to act as a template or overlay to a switch array. By interacting with the switch through touch or presence, an action is innervated. The switching sensor cross-references with a database. The database retains the correct pathway to retrieve the associated digital content or launch the appropriate application. TUI icons may be used to indicate to the reader of the printed page what ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fingerprint Recognition
A fingerprint is an impression left by the friction ridges of a human finger. The recovery of partial fingerprints from a crime scene is an important method of forensic science. Moisture and grease on a finger result in fingerprints on surfaces such as glass or metal. Deliberate impressions of entire fingerprints can be obtained by ink or other substances transferred from the peaks of friction ridges on the skin to a smooth surface such as paper. Fingerprint records normally contain impressions from the pad on the last joint of fingers and thumbs, though fingerprint cards also typically record portions of lower joint areas of the fingers. Human fingerprints are detailed, nearly unique, difficult to alter, and durable over the life of an individual, making them suitable as long-term markers of human identity. They may be employed by police or other authorities to identify individuals who wish to conceal their identity, or to identify people who are incapacitated or deceased and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Face Recognition
A facial recognition system is a technology capable of matching a human face from a digital image or a video frame against a database of faces. Such a system is typically employed to authenticate users through ID verification services, and works by pinpointing and measuring facial features from a given image. Development began on similar systems in the 1960s, beginning as a form of computer application. Since their inception, facial recognition systems have seen wider uses in recent times on smartphones and in other forms of technology, such as robotics. Because computerized facial recognition involves the measurement of a human's physiological characteristics, facial recognition systems are categorized as biometrics. Although the accuracy of facial recognition systems as a biometric technology is lower than iris recognition and fingerprint recognition, it is widely adopted due to its contactless process. Facial recognition systems have been deployed in advanced human–compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biometrics
Biometrics are body measurements and calculations related to human characteristics. Biometric authentication (or realistic authentication) is used in computer science as a form of identification and access control. It is also used to identify individuals in groups that are under surveillance. Biometric identifiers are the distinctive, measurable characteristics used to label and describe individuals. Biometric identifiers are often categorized as physiological characteristics which are related to the shape of the body. Examples include, but are not limited to fingerprint, palm veins, face recognition, DNA, palm print, hand geometry, iris recognition, retina, odor/scent, voice, shape of ears and gait. Behavioral characteristics are related to the pattern of behavior of a person, including but not limited to mouse movement, typing rhythm, gait, signature, behavioral profiling, and credentials. Some researchers have coined the term behaviometrics to describe the latter class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyroscopes
A gyroscope (from Ancient Greek γῦρος ''gŷros'', "round" and σκοπέω ''skopéō'', "to look") is a device used for measuring or maintaining orientation and angular velocity. It is a spinning wheel or disc in which the axis of rotation (spin axis) is free to assume any orientation by itself. When rotating, the orientation of this axis is unaffected by tilting or rotation of the mounting, according to the conservation of angular momentum In physics, angular momentum (rarely, moment of momentum or rotational momentum) is the rotational analog of linear momentum. It is an important physical quantity because it is a conserved quantity—the total angular momentum of a closed system .... Gyroscopes based on other operating principles also exist, such as the microchip-packaged Vibrating structure gyroscope#MEMS gyroscopes, MEMS gyroscopes found in electronic devices (sometimes called gyrometers), solid-state ring laser gyroscope, ring lasers, fibre optic gyroscopes, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, one that measures the direction of an ambient magnetic field, in this case, the Earth's magnetic field. Other magnetometers measure the magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic material such as a ferromagnet, for example by recording the effect of this magnetic dipole on the induced current in a coil. The first magnetometer capable of measuring the absolute magnetic intensity at a point in space was invented by Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1833 and notable developments in the 19th century included the Hall effect, which is still widely used. Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field, in geophysical surveys, to detect magnetic anomalies of various types, and to determine the dipole moment of magnetic materials. In an air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
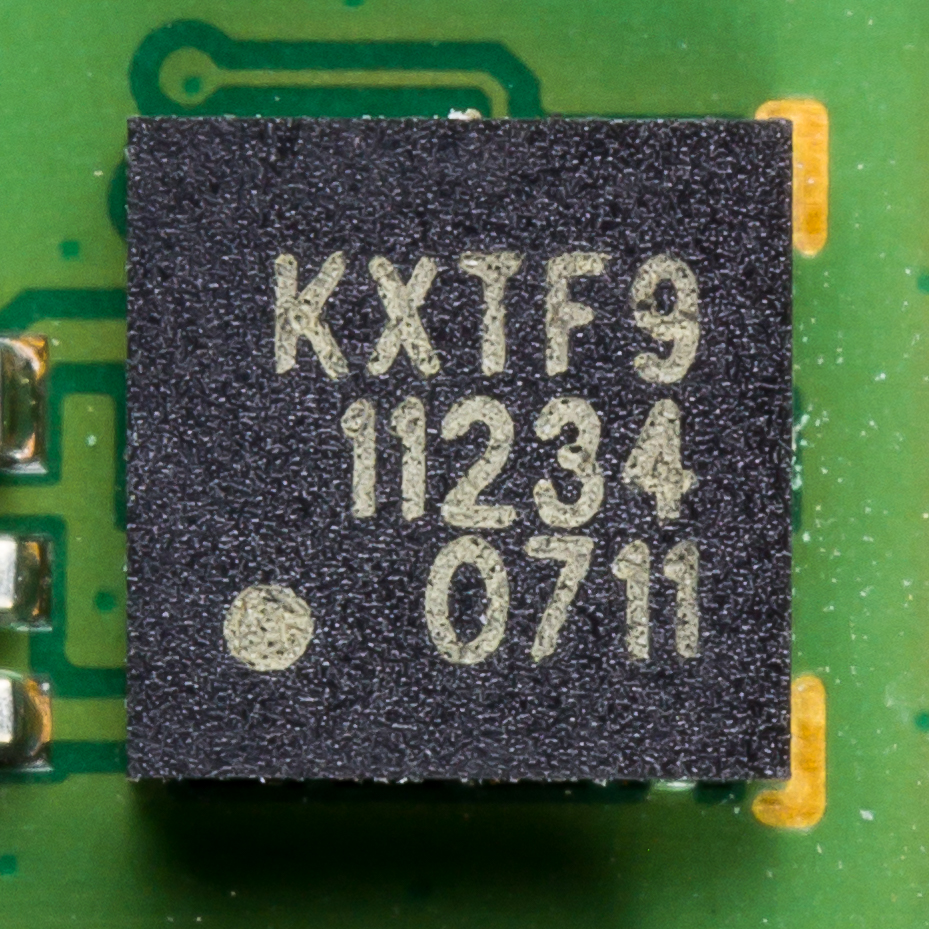
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smart Card
A smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC or IC card) is a physical electronic authentication device, used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart cards include a pattern of metal contacts to electrically connect to the internal chip. Others are contactless, and some are both. Smart cards can provide personal identification, authentication, data storage, and application processing. Applications include identification, financial, mobile phones (SIM), public transit, computer security, schools, and healthcare. Smart cards may provide strong security authentication for single sign-on (SSO) within organizations. Numerous nations have deployed smart cards throughout their populations. The universal integrated circuit card, or SIM card, is also a type of smart card. , 10.5billion smart card IC chips are manufactured annually, including 5.44billion SIM card IC chips. Hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio-frequency Identification
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder, a radio receiver and transmitter. When triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device, the tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader. This number can be used to track inventory goods. Passive tags are powered by energy from the RFID reader's interrogating radio waves. Active tags are powered by a battery and thus can be read at a greater range from the RFID reader, up to hundreds of meters. Unlike a barcode, the tag does not need to be within the line of sight of the reader, so it may be embedded in the tracked object. RFID is one method of automatic identification and data capture (AIDC). RFID tags are used in many industries. For example, an RFID tag attached to an automobile during production can be used to track ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barcode Scanner (application)
The application Barcode Scanner is an Android app, from the open-source project ZXing (short for Zebra Crossing), that allows an Android device with imaging hardware (a built-in camera) to scan barcodes or 2D barcodes and retrieve the data encoded. Information encoded often includes web addresses, geographical coordinates, and small pieces of text, in addition to commercial product codes. This Android-based system has similar functionality to a hardware barcode reader. This application supports many different types of barcodes, including those used to identify products in commerce. The Barcode Scanner can automatically search the Web to identify a product with a barcode and use, for example, price-comparison information between vendors. The application can decode several 2D barcodes including the widely used QR Code and Data Matrix. QR codes are often embedded in websites; Barcode Scanner can open a browser at the encoded site, for example, facilitating the download of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enterprise Digital Assistant
A portable data terminal, or shortly PDT, is an electronic device that is used to enter or retrieve data via wireless transmission (WLAN or WWAN). They have also been called enterprise digital assistants (EDA), data capture mobile devices, batch terminals or just portables. They can also serve as barcode readers, and they are used in large stores, warehouses, hospitals, or in the field, to access a database from a remote location. Others have a touch screen, IrDA, Bluetooth, a memory card slot, or one or more data capture devices. PDT's frequently run wireless device management software that allows them to interact with a database or software application hosted on a server or mainframe computer.List oBitpipewhitepapers on wireless device management. Boundaries among PDA, smartphone and EDA can be blurred when comparing the wide array of common features and functions. EDAs attempt to distinguish themselves with a pre-defined requirement for long term constant daily operation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)

