|
Hamilton Astronomical Society Observatory
The Hamilton Astronomical Society Observatory is located next to the Hamilton Zoo in Brymer Road to the west of Hamilton City, New Zealand. The Hamilton Astronomical Society was founded on 3 July 1933 and is one of New Zealand's oldest astronomical societies. The observatory instruments include one 24" Classical cassegrain telescope, a 14" and 8" Schmidt-Cassegrain telescope, a Lunt 60mm Solar telescope, an 8" Dobsonian telescope, and two 12" Dobsonian telescopes. The observatory is open to the public on the first and third Wednesdays of every month at 7:30pm (8:30pm during daylight saving). History The Hamilton Astronomical Society's first dedicated meeting house was the observatory, built at the Hamilton Zoo site in 1984. The observing dome for the 24" Classical Cassegrain telescope was completed in 1997, and opened by Sir Patrick Moore Sir Patrick Alfred Caldwell-Moore (; 4 March 1923 – 9 December 2012) was an English amateur astronomer who attained prominence in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Observatory
An observatory is a location used for observing terrestrial, marine, or celestial events. Astronomy, climatology/meteorology, geophysical, oceanography and volcanology are examples of disciplines for which observatories have been constructed. Historically, observatories were as simple as containing an astronomical sextant (for measuring the distance between stars) or Stonehenge (which has some alignments on astronomical phenomena). Astronomical observatories Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space-based, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Ground-based observatories Ground-based observatories, located on the surface of Earth, are used to make observations in the radio and visible light portions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Most optical telescopes are housed within a dome or similar structure, to protect the delicate instruments from the elements. Telescope domes have a slit or other opening in the roof that can be opened during ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamilton, New Zealand
Hamilton ( mi, Kirikiriroa) is an inland city in the North Island of New Zealand. Located on the banks of the Waikato River, it is the seat and most populous city of the Waikato region. With a territorial population of , it is the country's fourth most-populous city. Encompassing a land area of about , Hamilton is part of the wider Hamilton Urban Area, which also encompasses the nearby towns of Ngāruawāhia, Te Awamutu and Cambridge. In 2020, Hamilton was awarded the title of most beautiful large city in New Zealand. The area now covered by the city was originally the site of several Māori villages, including Kirikiriroa, from which the city takes its Māori name. By the time English settlers arrived, most of these villages, which sat beside the Waikato River, were abandoned as a result of the Invasion of Waikato and land confiscation (''Raupatu'') by the Crown. Initially an agricultural service centre, Hamilton now has a diverse economy and is the third fastest growing urba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
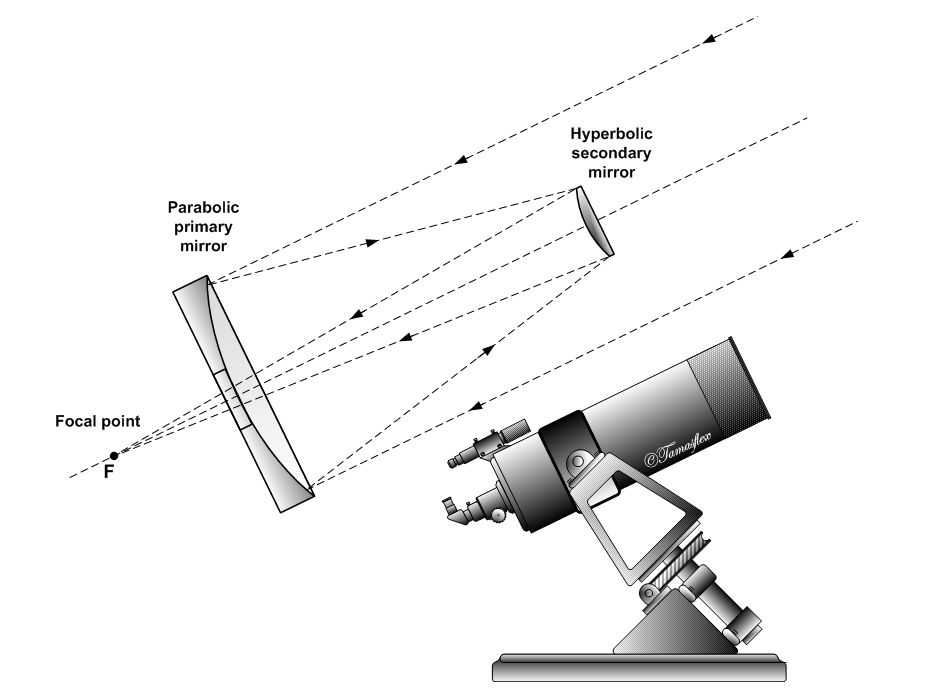
Cassegrain Telescope
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the primary mirror (or both). The classic Cassegrain co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
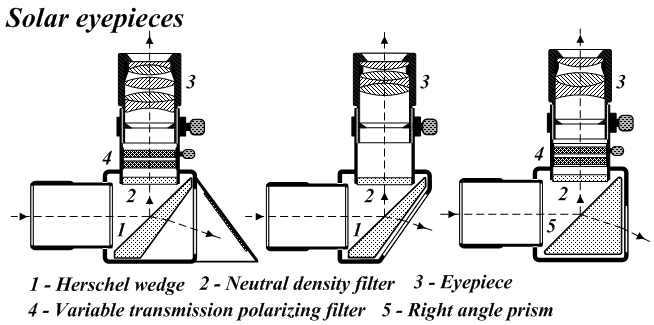
Solar Telescope
A solar telescope is a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun. Solar telescopes usually detect light with wavelengths in, or not far outside, the visible spectrum. Obsolete names for Sun telescopes include heliograph and photoheliograph. Professional solar telescopes Solar telescopes need optics large enough to achieve the best possible diffraction limit but less so for the associated light-collecting power of other astronomical telescopes. However, recently newer narrower filters and higher framerates have also driven solar telescopes towards photon-starved operations. Both the Daniel K. Inouye Solar Telescope as well as the proposed European Solar Telescope (EST) have larger apertures not only to increase the resolution, but also to increase the light-collecting power. Because solar telescopes operate during the day, seeing is generally worse than for night-time telescopes, because the ground around the telescope is heated which causes turbulence and degrades the res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dobsonian Telescope
A Dobsonian telescope is an altazimuth-mounted Newtonian telescope design popularized by John Dobson in 1965 and credited with vastly increasing the size of telescopes available to amateur astronomers. Dobson's telescopes featured a simplified mechanical design that was easy to manufacture from readily available components to create a large, portable, low-cost telescope. The design is optimized for observing faint, deep-sky objects such as nebulae and galaxies. This type of observation requires a large objective diameter (i.e. light-gathering power) of relatively short focal length and portability for travel to less light-polluted locations. Dobsonians are intended to be what is commonly called a "light bucket" operating at low magnification, and therefore the design omits features found in other amateur telescopes such as equatorial tracking. Dobsonians are popular in the amateur telescope making community, where the design was pioneered and continues to evolve. A number o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daylight Saving Time By Country
Daylight is the combination of all direct and indirect sunlight during the daytime. This includes direct sunlight, diffuse sky radiation, and (often) both of these reflected by Earth and terrestrial objects, like landforms and buildings. Sunlight scattered or reflected by astronomical objects is generally not considered daylight. Therefore, daylight excludes moonlight, despite it being reflected indirect sunlight. Definition Daylight is present at a particular location, to some degree, whenever the Sun is above the local horizon. (This is true for slightly more than 50% of the Earth at any given time. For an explanation of why it is not exactly half, see here). However, the outdoor illuminance can vary from 120,000 lux for direct sunlight at noon, which may cause eye pain, to less than 5 lux for thick storm clouds with the Sun at the horizon (even <1 lux for the most extreme case), which may make shadows from distant [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamilton Zoo
Hamilton Zoo ( mi, Rawhi Whakaaturanga o Kirikiriroa) is the main zoological garden of Hamilton, New Zealand. Covering , it is situated on Brymer Road in the Hamilton suburb of Rotokauri, on the outskirts of the metropolitan area towards the northwest. It is owned by the Hamilton City Council with the Department of Recreation and Welfare handling the day-to-day running of the site. Hamilton Zoo is the first zoo in New Zealand to become fully accredited by the Zoo and Aquarium Association. History The park was founded in 1969 as a game farm, the Hilldale Game Farm. It was originally owned by a Mr and Mrs Powell. They mainly raised game birds but there was also a small collection of exotic mammals and birds. The zoo become unprofitable and was facing closure in 1976 before the Hamilton City Council stepped in and brought the site, buildings, and stock. In 1984, the zoo again faced closure but due to public pressure the Council resolved to keep it open. Day-to-day running of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrick Moore
Sir Patrick Alfred Caldwell-Moore (; 4 March 1923 – 9 December 2012) was an English amateur astronomer who attained prominence in that field as a writer, researcher, radio commentator and television presenter. Moore was president of the British Astronomical Association; co-founder and president of the Society for Popular Astronomy; author of over seventy books on astronomy; and presenter of the world's longest-running television series with the same original presenter, BBC's ''The Sky at Night'' (from 1957). He became known as a specialist in Moon observation and for creating the Caldwell catalogue. Idiosyncrasies such as his rapid diction and monocle made him a popular and instantly recognisable figure on British television. Outside his field of astronomy, Moore was known for his role on the video game television show '' GamesMaster''. Moore was also a self-taught xylophonist and pianist, as well as an accomplished composer. He was an amateur cricketer, golfer and chess pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |