|
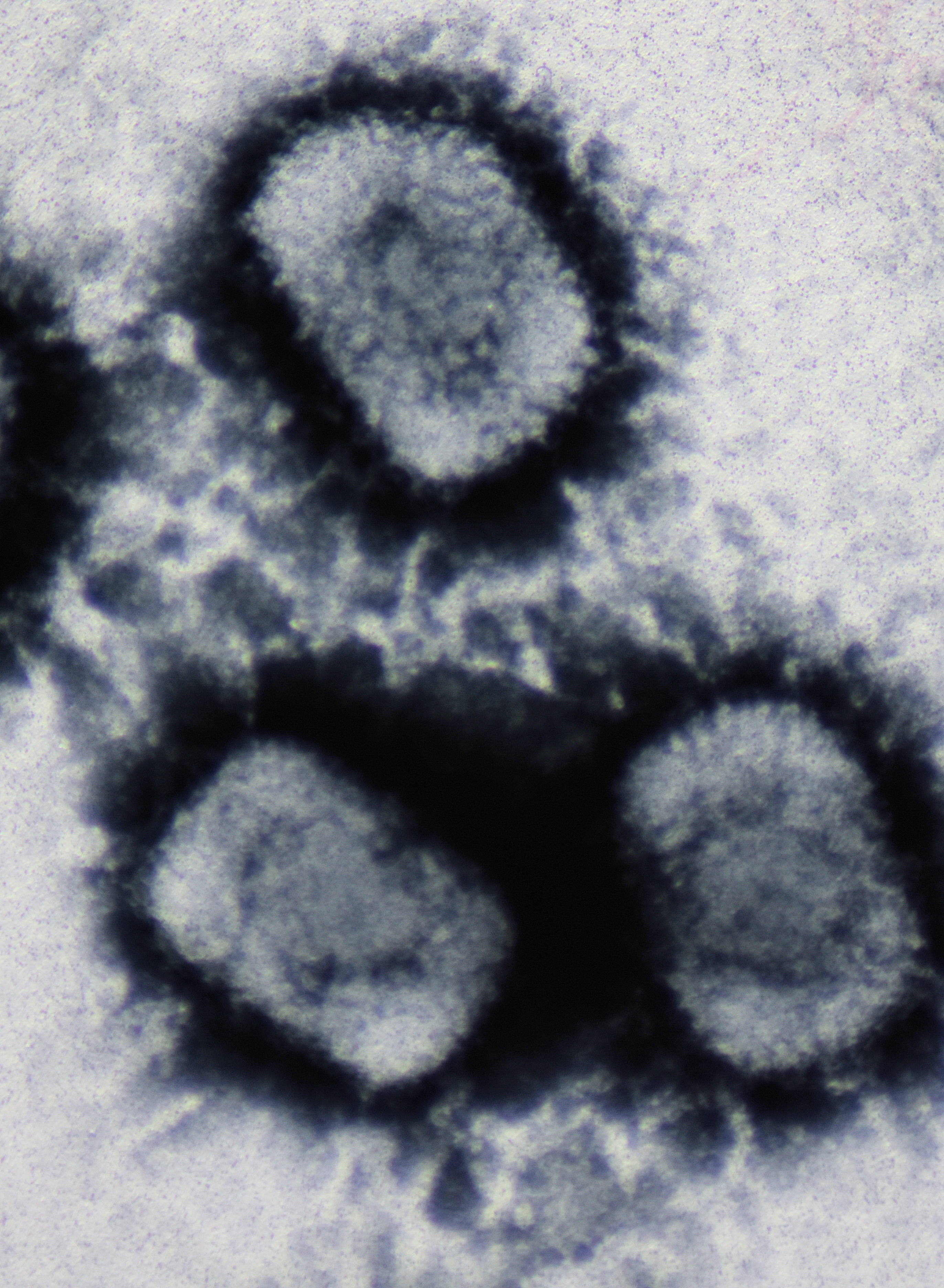
Halorubrum Pleomorphic Virus 1
Halorubrum pleomorphic virus 1 (HRPV-1) is a single stranded DNA virus that infects the species of the archaeal genus '' Halorubrum''.Pietila, M, Laurinavicius S, Sund, J, Roine E & Bamford D (2009) The single-stranded DNA genome of novel archaeal virus Halorubrum pleomorphic virus 1 Is enclosed in the envelope decorated with glycoprotein spikes. J Virol 84 (2) 788-798 It is unlike any other known virus infecting the archaea with a single stranded DNA genome and an external lipid envelope and is classified in the family ''Pleolipoviridae'', genus ''Alphapleolipovirus'', species ''Halorubrum virus HRPV1''. __TOC__ Virology The virons are pleomorphic is shape with an external lipd envelope. There are two main structural proteins (VP3 and VP4) of molecular weights 15 and 53 kiloDaltons respectively. The genome does not appear to be associated with a nucleoprotein. The spike protein (VP4) is glycosylated. The lipid envelope is similar to its host's composition. VP3 is a membrane pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaea
Archaea ( ; singular archaeon ) is a domain of single-celled organisms. These microorganisms lack cell nuclei and are therefore prokaryotes. Archaea were initially classified as bacteria, receiving the name archaebacteria (in the Archaebacteria kingdom), but this term has fallen out of use. Archaeal cells have unique properties separating them from the other two domains, Bacteria and Eukaryota. Archaea are further divided into multiple recognized phyla. Classification is difficult because most have not been isolated in a laboratory and have been detected only by their gene sequences in environmental samples. Archaea and bacteria are generally similar in size and shape, although a few archaea have very different shapes, such as the flat, square cells of '' Haloquadratum walsbyi''. Despite this morphological similarity to bacteria, archaea possess genes and several metabolic pathways that are more closely related to those of eukaryotes, notably for the enzymes invo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. '' Panthera leo'' (lion) and '' Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants of an ancestral taxon are grouped together (i.e. phylogenetic analysis should c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halorubrum
''Halorubrum'' is a genus in the family Halorubraceae. ''Halorubrum'' species areusually halophilic and can be found in waters with high salt concentration such as the Dead Sea or Lake Zabuye. Genetic exchange A population of the haloarchaea ''Halorubrum'' in its natural high salt concentration environment exchanged genetic information frequently by recombination. This population exhibited a degree of linkage equilibrium approaching that of a sexual population. Taxonomy In taxonomy, ''Halorubrum'' is a genus of the Halobacteriaceae. Species ''Halorubrum ejinorense'' was first isolated from Lake Ejinor in Inner Mongolia, China. ''Halorubrum lacusprofundi'' was first isolated in the 1980s from Deep Lake, Antarctica. Its genome, sequenced in 2008, consists of two chromosomes (one 2.74 Mb and the other 0.53 Mb) and one plasmid (0.43 Mb). Its β-galactosidase enzyme has been extensively studied to understand how proteins function in low-temperature, high-saline environments. O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Reading Frame
In molecular biology, open reading frames (ORFs) are defined as spans of DNA sequence between the start and stop codons. Usually, this is considered within a studied region of a Prokaryote, prokaryotic DNA sequence, where only one of the #Six-frame translation, six possible reading frames will be "open" (the "reading", however, refers to the RNA produced by Transcription (biology), transcription of the DNA and its subsequent interaction with the ribosome in Translation (biology), translation). Such an ORF may contain a start codon (usually AUG in terms of RNA) and by definition cannot extend beyond a stop codon (usually UAA, UAG or UGA in RNA). That start codon (not necessarily the first) indicates where translation may start. The transcription terminator, transcription termination site is located after the ORF, beyond the Translation (biology), translation stop codon. If transcription were to cease before the stop codon, an incomplete protein would be made during translation. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ATPase
ATPases (, Adenosine 5'-TriPhosphatase, adenylpyrophosphatase, ATP monophosphatase, triphosphatase, SV40 T-antigen, ATP hydrolase, complex V (mitochondrial electron transport), (Ca2+ + Mg2+)-ATPase, HCO3−-ATPase, adenosine triphosphatase) are a class of enzymes that catalyze the decomposition of ATP into ADP and a free phosphate ion or the inverse reaction. This dephosphorylation reaction releases energy, which the enzyme (in most cases) harnesses to drive other chemical reactions that would not otherwise occur. This process is widely used in all known forms of life. Some such enzymes are integral membrane proteins (anchored within biological membranes), and move solutes across the membrane, typically against their concentration gradient. These are called transmembrane ATPases. Functions Transmembrane ATPases import metabolites necessary for cell metabolism and export toxins, wastes, and solutes that can hinder cellular processes. An important example is the sodium-po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single-stranded DNA Viruses
A DNA virus is a virus that has a genome made of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that is replicated by a DNA polymerase. They can be divided between those that have two strands of DNA in their genome, called double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) viruses, and those that have one strand of DNA in their genome, called single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) viruses. dsDNA viruses primarily belong to two realms: ''Duplodnaviria'' and ''Varidnaviria'', and ssDNA viruses are almost exclusively assigned to the realm ''Monodnaviria'', which also includes some dsDNA viruses. Additionally, many DNA viruses are unassigned to higher taxa. Reverse transcribing viruses, which have a DNA genome that is replicated through an RNA intermediate by a reverse transcriptase, are classified into the kingdom ''Pararnavirae'' in the realm ''Riboviria''. DNA viruses are ubiquitous worldwide, especially in marine environments where they form an important part of marine ecosystems, and infect both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. They a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)