|
Hallesches Tor (Berlin U-Bahn)
Hallesches Tor is a Berlin U-Bahn station in the central Kreuzberg quarter, served by lines U1, U3, and U6. It is named after the historic ''Hallsches Tor'' (Halle Gate) of the Berlin Customs Wall, erected in the 18th century. Overview The historic gate of the Customs Wall, laid out from 1737 onwards to replace the medieval city fortifications, marked the southern tip of the Friedrichstadt neighbourhood. It was located at the southern end of Friedrichstraße and the ''Rondell'' (renamed '' Belle-Alliance-Platz'' in 1815 and Mehringplatz in 1946). Neighbouring gates were on Potsdamer Platz in the west and on Wassertorplatz (Water Gate) in the east, where the present course of the U1 viaduct roughly corresponds to the former city wall. South of the gate, a wooden bridge led across the Landwehr Canal; from here the road ran via Tempelhof to the city of Halle, part of Brandenburg-Prussia since 1680. The present-day stone bridge was built between 1874 and 1876. The U1 and U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kreuzberg
Kreuzberg () is a district of Berlin, Germany. It is part of the Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg borough located south of Mitte. During the Cold War era, it was one of the poorest areas of West Berlin, but since German reunification in 1990 it has become more gentrified and known for its arts scene. The borough is known for its large percentage of immigrants and descendants of immigrants, many of whom are of Turkish ancestry. As of 2006, 31.6% of Kreuzberg's inhabitants did not have German citizenship. Kreuzberg is noted for its diverse cultural life and experimental alternative lifestyles, and is an attractive area for many, however, some parts of the district are still characterized by higher levels of unemployment. The counterculture tradition of Kreuzberg led to a plurality of votes for the Green Party, which is unique among all Berlin boroughs. Geography Layout Kreuzberg is bounded by the river Spree in the east. The Landwehrkanal flows through Kreuzberg from east to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wassertorplatz
Wassertorplatz is a neighbourhood in Berlin, Germany Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe .... References Friedrichshain-Kreuzberg {{Berlin-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U1 (Berlin U-Bahn) Stations
U1, U.I or U-1 may refer to: Mathematics *U(1), the degree one ''unitary group'' Military *U-1, the USAF and US Military's designation for the De Havilland Canada DHC-3 Otter light transport aircraft *U-1, Soviet designation for Avro 504 trainer. *Multiple German U-boats named ''U-1'' *Oberursel U.I, an early German aircraft engine *HDMS U-1, a Danish submarine * SM U-1, an Austro-Hungarian submarine, lead ship of the U-1 class Entertainment *U1 Technology, a game and software developing company *'' Ultima I: The First Age of Darkness'', a 1981 video game People * U1, alias for Yuvan Shankar Raja (born 1979), a Tamil musician and film composer *U-1, the main character in the video game ''Gitaroo Man'' for the PlayStation 2/PlayStation Portable Railways * LNER Class U1, a 1924 British solitary 2-8-0+0-8-2 Beyer-Garratt locomotive *SR U1 class, a class of 2-6-0 locomotives developed from the U Class U-Bahn lines *U1 (Berlin U-Bahn) *U1 (Frankfurt U-Bahn) *U1 (Hamburg U-Bahn) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
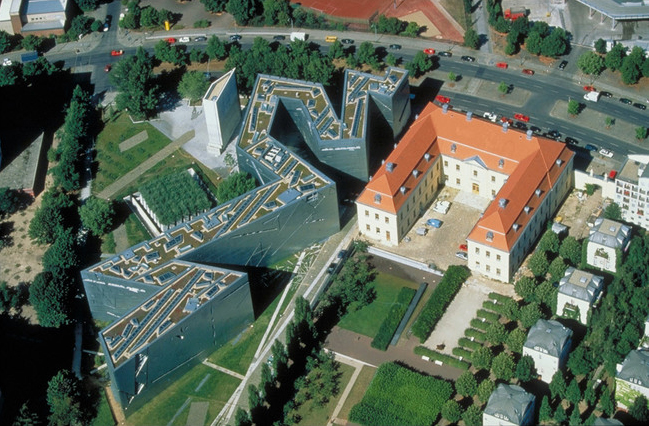
Daniel Libeskind
Daniel Libeskind (born May 12, 1946) is a Polish–American architect, artist, professor and set designer. Libeskind founded Studio Daniel Libeskind in 1989 with his wife, Nina, and is its principal design architect. He is known for the design and completion of the Jewish Museum in Berlin, Germany, that opened in 2001. On February 27, 2003, Libeskind received further international attention after he won the competition to be the master plan architect for the reconstruction of the World Trade Center site in Lower Manhattan. Other buildings that he is known for include the extension to the Denver Art Museum in the United States, the Grand Canal Theatre in Dublin, the Imperial War Museum North in Greater Manchester, England, the Michael Lee-Chin Crystal at the Royal Ontario Museum in Toronto, Canada, the Felix Nussbaum Haus in Osnabrück, Germany, the Danish Jewish Museum in Copenhagen, Denmark, Reflections in Singapore and the Wohl Centre at the Bar-Ilan University in Ramat Gan, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Museum Berlin
The Jewish Museum Berlin (''Jüdisches Museum Berlin'') was opened in 2001 and is the largest Jewish museum in Europe. On of floor space, the museum presents the history of Jews in Germany from the Middle Ages to the present day, with new focuses and new scenography. It consists of three buildings, two of which are new additions specifically built for the museum by architect Daniel Libeskind. German-Jewish history is documented in the collections, the library and the archive, and is reflected in the museum's program of events. From its opening in 2001 to December 2017, the museum had over eleven million visitors and is one of the most visited museums in Germany. Opposite the building ensemble, the W. Michael Blumenthal Academy of the Jewish Museum Berlin was built – also after a design by Libeskind – in 2011/2012 in the former flower market hall. The archives, library, museum education department, a lecture hall and the Diaspora Garden can all be found in the academy. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amerika-Gedenkbibliothek
The Amerika-Gedenkbibliothek (AGB; en, America Memorial Library) is one of the largest public libraries in Berlin, Germany. It was co-financed by a donation from the United States. The building was designed by American and German architects, including Fritz Bornemann and Willy Kreuer. It was opened on September 17, 1954, and was originally planned to become the Central Library of Berlin. History In 1950 the American people had donated $5 million (= DM 21 million; so-called McCloy Grant) for cultural purposes in recognition of the West Berliners' keeping up during the Berlin Blockade, which took place in 1948/1949. With DM 5.4 million (=$1.285 million) from the grant, and additionally the same sum from its own funds, the Senate of Berlin built the new library on Blücherplatz in Kreuzberg. On 10 September 1954 it opened to become Berlin's central public library.Frauke Mahrt-Thomsen, ''150 Jahre: Von den Berliner Volksbibliotheken zur Stadtbibliothek Kreuzberg; eine Chronik'', B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
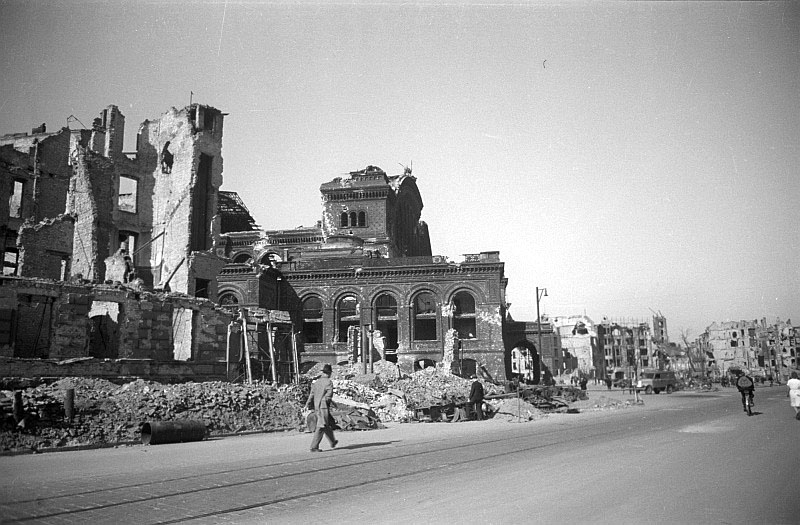
Bombing Of Berlin In World War II
A bomb is an explosive weapon that uses the exothermic reaction of an explosive material to provide an extremely sudden and violent release of energy. Detonations inflict damage principally through ground- and atmosphere-transmitted mechanical stress, the impact and penetration of pressure-driven projectiles, pressure damage, and explosion-generated effects. Bombs have been utilized since the 11th century starting in East Asia. The term bomb is not usually applied to explosive devices used for civilian purposes such as construction or mining, although the people using the devices may sometimes refer to them as a "bomb". The military use of the term "bomb", or more specifically aerial bomb action, typically refers to airdropped, unpowered explosive weapons most commonly used by air forces and naval aviation. Other military explosive weapons not classified as "bombs" include shells, depth charges (used in water), or land mines. In unconventional warfare, other names can refer t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berlin Potsdamer Platz Station
Berlin Potsdamer Platz is a railway station in Berlin. It is completely underground and situated under Potsdamer Platz in central Berlin. Regional and S-Bahn services call at the station, and it is also served by U-Bahn line U2. History S-Bahn The first station at Potsdamer Platz was the Potsdamer Bahnhof terminus, which was closed on 27 September 1945 due to war damage. In 1939 the S-Bahn, or ''Stadtbahn'' (City Railway), arrived. The idea for a North-South Link rapid transit rail line from Unter den Linden to Yorckstraße, via Potsdamer Platz and Anhalter Bahnhof, had first been mooted in 1914, but it was not planned in detail until 1928, and then approval had to wait until 1933. Begun in 1934, it was plagued with disasters. Determination to have it finished in time for the Berlin Olympic Games in 1936 meant vital safety measures were ignored: on 20 August 1935, a tunnel collapse just south of the Brandenburg Gate buried 23 workmen of whom only four survived; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stralauer Tor (Berlin U-Bahn)
Stralauer Tor (''Osthafen'' as of 1924) was a Berlin U-Bahn station in Berlin-Friedrichshain. It operated between Warschauer Straße and Schlesisches Tor stations on today's U1. Following its destruction in World War II it was never rebuilt and is one of three Berlin U-Bahn stations (the others being Nürnberger Platz, which was closed and demolished in 1961 and Französische Straße, which was closed in 2020) to have been abandoned after having previously been in service. History ''Stralauer Tor'' was an elevated station built into the north-eastern part of the Oberbaumbrücke viaduct, which featured a barrel-shaped roof and two street level stairwell entrances accommodating opposing platform sides.berliner-untergrundbahn.de ''Berlins U-Bahnstrecken'' It was constructed by German engineering co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
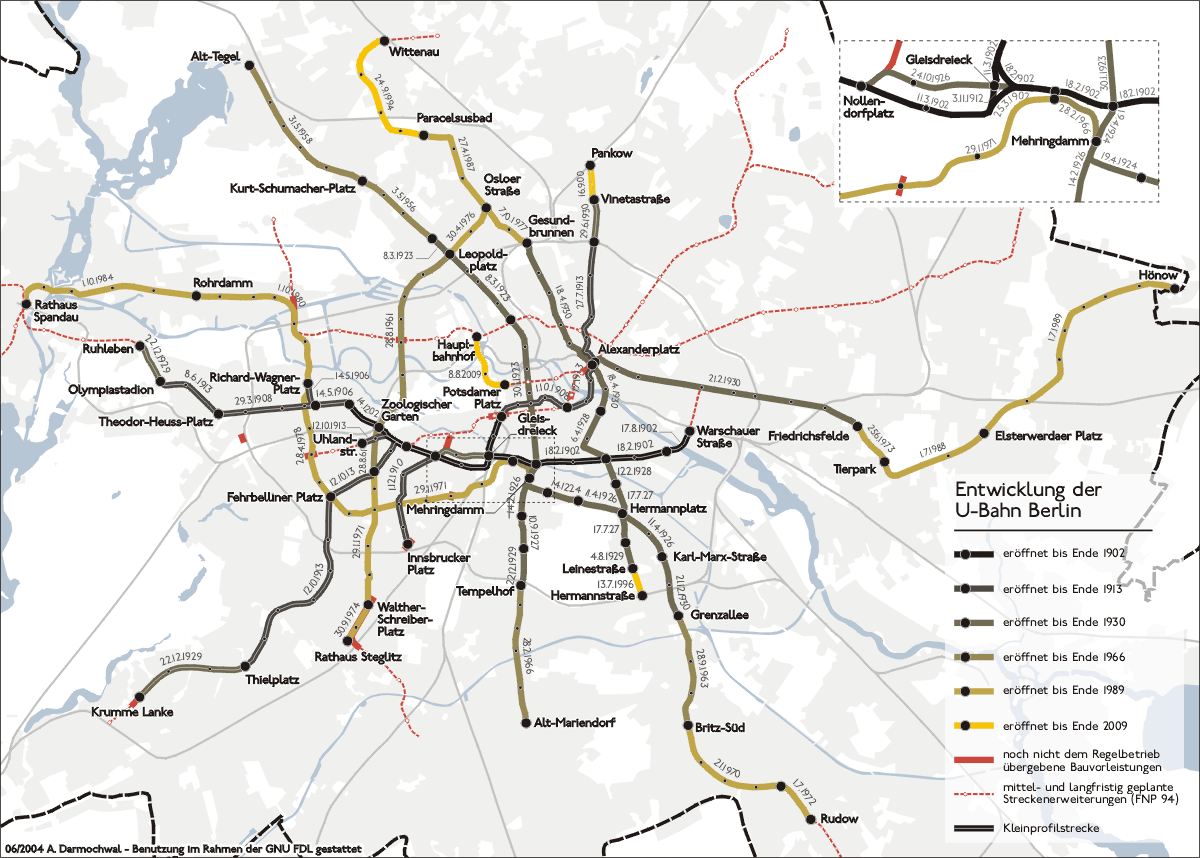
History Of The Berlin U-Bahn
The Berlin U-Bahn originated in 1880 with Werner Siemens' idea to build an urban railway in Berlin. During the nine years after the German Empire was founded, the city's population grew by over one-third and traffic problems increased. In 1896, Siemens & Halske began to construct the first stretch of overhead railway. On 1 April 1897, the company began construction of an electric underground railway. The Berliner Verkehrs Aktiengesellschaft (BVG) was formed in 1928, and took over further construction and operation of the network. In 1938, the company was renamed Berlin Transport Company; the original acronym, however, remained. Since 1994, the BVG has been a public company. The line between Stralauer Tor and Potsdamer Platz (the present-day U1 line) was the first to open, on 18 February 1902. Four additional lines were built before the First World War. In the Weimar Republic, hyperinflation initially prevented further expansion of the system. A new line with a wider car, kno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elevated Railway
An elevated railway or elevated train (also known as an el train for short) is a rapid transit railway with the tracks above street level on a viaduct or other elevated structure (usually constructed from steel, cast iron, concrete, or bricks). The railway may be broad-gauge, standard-gauge or narrow-gauge railway, light rail, monorail, or a suspension railway. Elevated railways are normally found in urban areas where there would otherwise be multiple level crossings. Usually, the tracks of elevated railways that run on steel viaducts can be seen from street level. History The earliest elevated railway was the London and Greenwich Railway on a brick viaduct of 878 arches, built between 1836 and 1838. The first of the London and Blackwall Railway (1840) was also built on a viaduct. During the 1840s there were other plans for elevated railways in London that never came to fruition. From the late 1860s onward, elevated railways became popular in US cities. The New York West ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |