|
Hakea Gilbertii
''Hakea gilbertii'' is a shrub in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to an area in the Wheatbelt region of Western Australia. It is an upright, prickly shrub with greyish needle-shaped leaves and clusters of fragrant flowers from late winter to spring. Description The erect, very prickly, densely branched shrub, typically grows to a height of which short branchlets and does not form a lignotuber. It blooms from August to September and produces sweetly scented white-cream or red-pink flowers in large clusters in upper leaf axils. Grey-blue leaves are fine and terete long by wide ending in a very sharp point. The small fruit are smooth in between warty protuberances ending with a small backward pointed beak. Taxonomy and naming ''Hakea gilbertii'' was first formally described in 1855 by English botanist Richard Kippist and the description was published in ''Hooker's Journal of Botany and Kew Garden Miscellany''. This species was named after John Gilbert, the English nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pingelly, Western Australia
Pingelly is a town and shire located in the Wheatbelt region of Western Australia, from Perth via the Brookton Highway and Great Southern Highway. The town is also located on the Great Southern railway line. The surrounding areas produce wheat and other cereal crops. The town is a receival site for Cooperative Bulk Handling. At the , Pingelly had a population of 809. History The town was originally a railway siding along the Great Southern Railway line, built by the Western Australian Land Company, and opened in 1889. Later the same year the company designed the town and made land available. In 1896 the state government purchased the railway and the land and gazetted the townsite in 1898. Its name is Aboriginal in origin and is the name of the Pingeculling Rocks found to the north of the town. The name was first recorded in 1873, and the original settlers referred to the area as ''Pingegulley'' for years before the town was gazetted. In early 1898 the population of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Gilbert (naturalist)
John Gilbert (14 March 1812 – 28 June 1845) was an English naturalist and explorer. Gilbert is often cited in the earliest descriptions of many Australian animals, many of which were unrecorded in European literature, and some of these are named for him by those authors. Gilbert was sent to the newly founded Swan River Colony and made collections and notes on the unique birds and mammals of the surrounding region. He later joined expeditions to remote parts the country, continuing to make records and collections until he was killed during a violent altercation at Mitchell River (Queensland) on the Cape York Peninsula. Early life John Gilbert was born on 14 March 1812 in Newington Butts, south London, England and was christened on 25 October 1812 at Spa Fields Lady Huntingdons, Clerkenwell, London. His father was William and his mother Ann, who were from nearby villages in Kent. Gilbert was a taxidermist for the Zoological Society of London, where he met John Gould. Gould had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eudicots Of Western Australia
The eudicots, Eudicotidae, or eudicotyledons are a clade of flowering plants mainly characterized by having two seed leaves upon germination. The term derives from Dicotyledons. Traditionally they were called tricolpates or non-magnoliid dicots by previous authors. The botanical terms were introduced in 1991 by evolutionary botanist James A. Doyle and paleobotanist Carol L. Hotton to emphasize the later evolutionary divergence of tricolpate dicots from earlier, less specialized, dicots. Numerous familiar plants are eudicots, including many common food plants, trees, and ornamentals. Some common and familiar eudicots include sunflower, dandelion, forget-me-not, cabbage, apple, buttercup, maple, and macadamia. Most leafy trees of midlatitudes also belong to eudicots, with notable exceptions being magnolias and tulip trees which belong to magnoliids, and ''Ginkgo biloba'', which is not an angiosperm. Description The close relationships among flowering plants with tricolpate po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakea
''Hakea'' ( ) is a genus of about 150 species of plants in the Family ''Proteaceae'', endemic to Australia. They are shrubs or small trees with leaves that are sometimes flat, otherwise circular in cross section in which case they are sometimes divided. The flowers are usually arranged in groups in leaf axils and resemble those of other genera, especially ''Grevillea''. Hakeas have woody fruit which distinguishes them from grevilleas which have non-woody fruit which release the seeds as they mature. Hakeas are found in every state of Australia with the highest species diversity being found in the south west of Western Australia. Description Plants in the genus ''Hakea'' are shrubs or small trees. Some species have flat leaves, whilst others have leaves which are needle-like, in which case they are sometimes divided and sometimes have a groove on the lower surface. The flowers are arranged in groups in leaf axils and are surrounded by bracts when in bud. The flowers have both male ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateritic
Laterite is both a soil and a rock type rich in iron and aluminium and is commonly considered to have formed in hot and wet tropical areas. Nearly all laterites are of rusty-red coloration, because of high iron oxide content. They develop by intensive and prolonged weathering of the underlying parent rock, usually when there are conditions of high temperatures and heavy rainfall with alternate wet and dry periods. Tropical weathering (''laterization'') is a prolonged process of chemical weathering which produces a wide variety in the thickness, grade, chemistry and ore mineralogy of the resulting soils. The majority of the land area containing laterites is between the tropics of Cancer and Capricorn. Laterite has commonly been referred to as a soil type as well as being a rock type. This and further variation in the modes of conceptualizing about laterite (e.g. also as a complete weathering profile or theory about weathering) has led to calls for the term to be abandoned al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
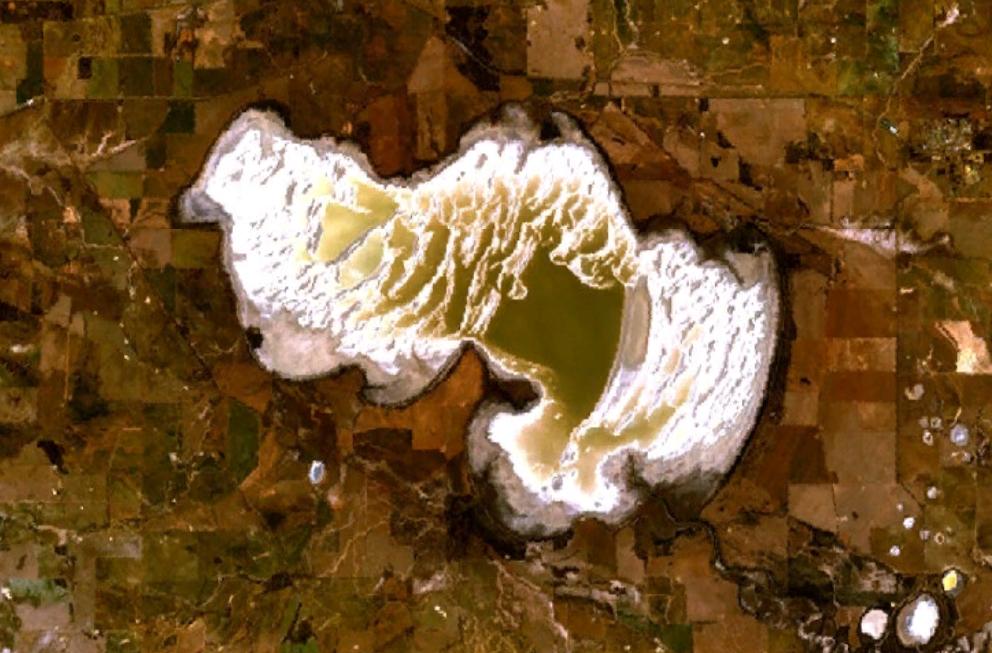
Dumbleyung, Western Australia
Dumbleyung is a town and shire in the Wheatbelt region of Western Australia, south-east of Perth between Wagin and Lake Grace on State Route 107. History Dumbleyung's name is of Noongar origin, coming from "Dambeling" which possibly means "large lake or inland sea" (although another source suggests it came from "dumbung", a game played with bent sticks and a hard piece of fruit. The lake nearby was discovered and named Dambeling Lake by explorers Henry Landor and Henry Maxwell Lefroy in 1843, and the current spelling was used by surveyors in the 1860s and 1870s. Pastoralists and sandalwood cutters moved into the area, initially settling at Nippering, north of Lake Dumbleyung and west of the present town. The first three families to settle in the area were the Cronin, Kersley and Bartram families. George Kersley, Sr. and his future son-in-law Henry Bartram were from pioneer families of the Beverley district and they used to take their sheep flocks from Beverley to Lake Dumbl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheatbelt (Western Australia)
The Wheatbelt is one of nine regions of Western Australia defined as administrative areas for the state's regional development, and a vernacular term for the area converted to agriculture during colonisation. It partially surrounds the Perth metropolitan area, extending north from Perth to the Mid West region, and east to the Goldfields–Esperance region. It is bordered to the south by the South West and Great Southern regions, and to the west by the Indian Ocean, the Perth metropolitan area, and the Peel region. Altogether, it has an area of (including islands). The region has 42 local government authorities, with an estimated population of 75,000 residents. The Wheatbelt accounts for approximately three per cent of Western Australia's population. Ecosystems The area, once a diverse ecosystem, reduced when clearing began in the 1890s with the removal of plant species such as eucalypt woodlands and mallee, is now home to around 11% of Australia's critically end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eneabba, Western Australia
Eneabba is a town on the Brand Highway north of Perth, Western Australia. The area is famous for its spectacular display of wildflowers in the spring. It is also home to the Iluka Resources mineral sands facility. The first European visit to the area was in 1839 by the second disastrous George Grey expedition along the west coast. Grey and his party were forced to walk through the area after their boats were lost. On 11 April, Grey discovered and named the Arrowsmith River, after John Arrowsmith the English cartographer. The next Europeans in the area were government Assistant Surveyor Augustus Charles Gregory and Francis Thomas Gregory (both attached to the department of the Surveyor-General) and their brother Henry Churchman Gregory, on a public-private funded expedition to search for new agricultural land beyond the settled areas. They camped at Eneabba Springs, east of Eneabba on 14 September 1846, while returning to Perth from the Irwin River. In 1870 the first settl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hooker's Journal Of Botany And Kew Garden Miscellany
''Hooker's Journal of Botany and Kew Garden Miscellany'' was a scientific journal In academic publishing, a scientific journal is a periodical publication intended to further the progress of science, usually by reporting new research. Content Articles in scientific journals are mostly written by active scientists such as s ... edited by Sir William Hooker that was published in nine volumes between 1849 and 1857. External links ''Hooker's Journal of Botany and Kew Garden Miscellany'' London : Reeve, Benham, and Reeve, 1849–1857. (9 volumes) Biodiversity Heritage Library profileScan of journal pages {{botany-journal-stub Botany journals Publications established in 1849 Publications disestablished in 1857 English-language journals 1849 establishments in England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Kippist
Richard Kippist (1812–1882) was an English botanist and librarian. Life Kippist was born in Stoke Newington, London, on 11 June 1812. He worked as a clerk in the office of Joseph Woods, F.L.S., architect, with whom he shared an interest in botany. He was employed by the Linnean Society from 1830, holding the position of librarian from 1842 to 1881. His special interest was Australian flora, and he advised George Bentham, Ferdinand von Mueller and others on this subject. His published works include "On ''Jansonia'', a new genus of Leguminosae from Western Australia" and "On ''Acradenia'', a new genus of Diosmae" in the ''Transactions'' of the society, describing the genera ''Jansonia'' (''Gastrolobium'') and '' Acradenia''. He assisted with the editing of Wood's ''The Tourists Flora'', published in 1830. His important papers include one on the discovery of spiral cells in the seeds of the family Acanthaceae. Kippist was a founding member of The Microscopical Society of Londo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terete
Terete is a term in botany used to describe a cross section that is circular, or like a distorted circle, with a single surface wrapping around it.Lichen Vocabulary, Lichens of North America Information, Sylvia and Stephen Sharnoff/ref> This is usually contrasted with cross-sections that are flattened, with a distinct upper surface that is different from the lower surface. The cross-section of a branch in a tree is somewhat round, so the branch is terete. The cross section of a normal leaf has an upper surface, and a lower surface, so the leaf is not terete. However, the fleshy leaves of succulents are sometimes terete. Fruticose lichens are terete, with a roughly circular cross section and a single wrap-around skin-like surface called the cortex, compared to foliose lichens and crustose lichens Crustose lichens are lichens that form a crust which strongly adheres to the substrate (soil, rock, tree bark, etc.), making separation from the substrate impossible without destruction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lignotuber
A lignotuber is a woody swelling of the root crown possessed by some plants as a protection against destruction of the plant stem, such as by fire. Other woody plants may develop basal burls as a similar survival strategy, often as a response to coppicing or other environmental stressors. However, lignotubers are specifically part of the normal course of development of the plants that possess them, and often develop early on in growth. The crown contains buds from which new stems may sprout, as well as stores of starch that can support a period of growth in the absence of photosynthesis. The term "lignotuber" was coined in 1924 by Australian botanist Leslie R. Kerr. Plants possessing lignotubers include many species in Australia: ''Eucalyptus marginata'' (Jarrah), ''Eucalyptus brevifolia'' (snappy gum) and ''Eucalyptus ficifolia'' (scarlet gum) all of which can have lignotubers wide and deep, as well as most mallees (where it is also known as a mallee root) and many ''Banksia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |