|
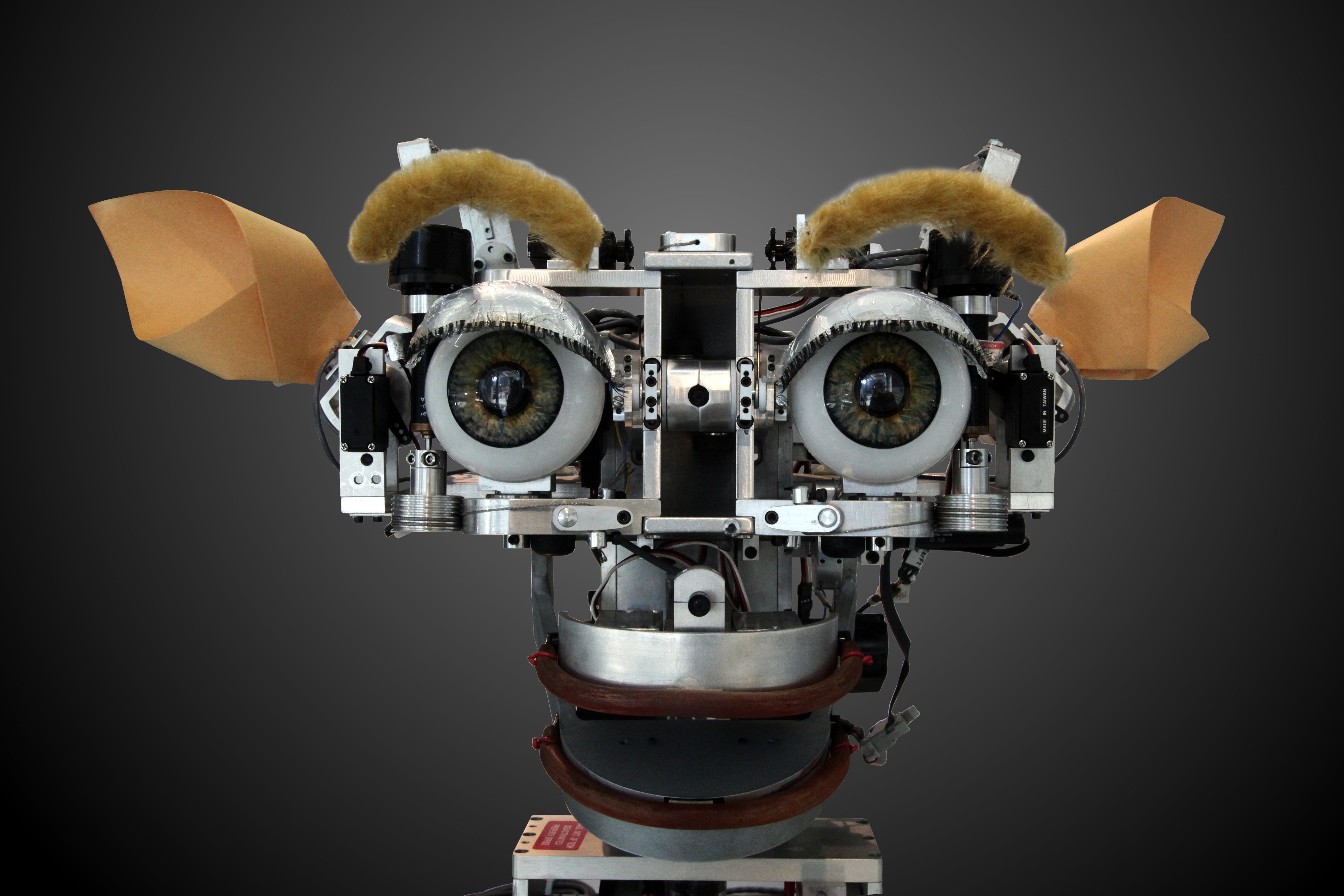
Haile (robot)
Haile (pronounced Hi-lee) is a robot percussionist developed by the Georgia Institute of Technology that listens to music in real time and creates an accompanying beat. The robot was designed in 2006 by Georgia Tech's professor of musical technology, Gil Weinberg. He and one of his graduate students, Scott Driscoll, created the robot to be able to "listen like a human, ndimprovise like a robot" (Weinberg). Haile "listens" through a microphone mounted on the drum and analyzes the sound, separating it into beats, rhythms, pitches and several other qualities. Detecting changes in these qualities helps Haile to assume either a leading or following style of play, roles that define the robot's collaborative abilities. Haile was also the first robot to create an acoustic percussion experience rather than play music through speakers. Its anthropomorphic design, which gives it movable arms that can move in any direction, allow it to create this acoustic music. Goals and purpose Driscoll's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgia Institute Of Technology
The Georgia Institute of Technology, commonly referred to as Georgia Tech or, in the state of Georgia, as Tech or The Institute, is a public research university and institute of technology in Atlanta, Georgia. Established in 1885, it is part of the University System of Georgia and has satellite campuses in Savannah, Georgia; Metz, France; Shenzhen, China; and Singapore. The school was founded as the Georgia School of Technology as part of Reconstruction plans to build an industrial economy in the post-Civil War Southern United States. Initially, it offered only a degree in mechanical engineering. By 1901, its curriculum had expanded to include electrical, civil, and chemical engineering. In 1948, the school changed its name to reflect its evolution from a trade school to a larger and more capable technical institute and research university. Today, Georgia Tech is organized into six colleges and contains about 31 departments/units, with emphasis on science and technology. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gil Weinberg
Gil Weinberg (born 1967) is an Israeli-born American musician and inventor of experimental musical instruments and musical robots. Weinberg is a professor of musical technology at Georgia Tech and founding director of the Georgia Tech Center for Music Technology. Biography Gil Weinberg was born in Jerusalem and began to study the piano at the age of seven. His teachers were disciplinarians who insisted on proper posture and hand position, emphasizing technique and theory at the expense of creativity. When he began composing his own music, they claimed he had no right to do so before mastering the fundamentals. His rebellion against this approach led to much of what he does today. "I'm trying to get children to be creative and expressive long before they have technique and theory," Weinberg says. "They can express themselves by pushing, pulling and other motions. Music is something you can invent and improvise with. I'm sure that this is a much better way into this world than focusin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human–robot Interaction
Human–robot interaction is the study of interactions between humans and robots. It is often referred as HRI by researchers. Human–robot interaction is a multidisciplinary field with contributions from human–computer interaction, artificial intelligence, robotics, natural-language understanding, design, and psychology. Origins Human–robot interaction has been a topic of both science fiction and academic speculation even before any robots existed. Because much of active HRI development depends on natural-language processing, many aspects of HRI are continuations of human communications, a field of research which is much older than robotics. The origin of HRI as a discrete problem was stated by 20th-century author Isaac Asimov in 1941, in his novel ''I, Robot''. He states the Three Laws of Robotics as: # A robot may not injure a human being or, through inaction, allow a human being to come to harm. # A robot must obey the orders by human beings except where such orders would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthropomorphism
Anthropomorphism is the attribution of human traits, emotions, or intentions to non-human entities. It is considered to be an innate tendency of human psychology. Personification is the related attribution of human form and characteristics to abstract concepts such as nations, emotions, and natural forces, such as seasons and weather. Both have ancient roots as storytelling and artistic devices, and most cultures have traditional fables with anthropomorphized animals as characters. People have also routinely attributed human emotions and behavioral traits to wild as well as domesticated animals. Etymology Anthropomorphism and anthropomorphization derive from the verb form ''anthropomorphize'', itself derived from the Greek ''ánthrōpos'' (, "human") and ''morphē'' (, "form"). It is first attested in 1753, originally in reference to the heresy of applying a human form to the Christian God.''Oxford English Dictionary'', 1st ed. "anthropomorphism, ''n.''" Oxford University P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pow Wow
A powwow (also pow wow or pow-wow) is a gathering with dances held by many Native American and First Nations communities. Powwows today allow Indigenous people to socialize, dance, sing, and honor their cultures. Powwows may be private or public, indoors or outdoors. Dancing events can be competitive with monetary prizes. Powwows vary in length from single-day to weeklong events. In mainstream American culture, such as 20th-century Western movies or by military personnel, the term ''powwow'' has been used to refer to any type of meeting. This usage has been considered both offensive and falling under cultural misappropriation. History The word ''powwow'' is derived from the Narragansett word ''powwaw'', meaning "spiritual leader". The term itself has variants including ''Powaw'', ''Pawaw'', ''Powah, Pauwau'' and ''Pawau''. A number of tribes claim to have held the "first" pow wow. Initially, public dances that most resemble what are now known as pow wows were most common ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CNC Wood Router
A CNC wood router is a CNC router tool that creates objects from wood. CNC stands for ''computer numerical control''. The CNC works on the Cartesian coordinate system (X, Y, Z) for 3D motion control. Parts of a project can be designed in the computer with a CAD/CAM program, and then cut automatically using a router or other cutters to produce a finished part. The CNC router is ideal for hobbies, engineering prototyping, product development, art, and production work. Operation A CNC wood router uses CNC (computer numerical control) and is similar to a metal CNC mill with the following differences: *The wood router typically spins faster — with a range of 13,000 to 24,000 RPM *Professional quality machines frequently use surface facing tools up to 3" in diameter or more, and spindle power from 5 to 15 horsepower. Machines capable of routing heavy material at over a thousand inches per minute are common. *Some machines use smaller toolholders MK2 (Morse taper #2 - on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onset (audio)
Onset refers to the beginning of a musical note or other sound. It is related to (but different from) the concept of a transient: all musical notes have an onset, but do not necessarily include an initial transient. Onset detection In signal processing, onset detection is an active research area. For example, the MIREX annual competition features aAudio Onset Detection contest Approaches to onset detection can operate in the time domain, frequency domain, phase domain, or complex domain, and include looking for: * Increases in spectral energy * Changes in spectral energy distribution (spectral flux) or phase * Changes in detected pitch - e.g. using a polyphonic pitch detection algorithm * Spectral patterns recognisable by machine learning techniques such as neural networks. Simpler techniques such as detecting increases in time-domain amplitude can typically lead to an unsatisfactorily high amount of false positives or false negatives. The aim is often to judge onsets similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Motor
A linear motor is an electric motor that has had its stator and rotor "unrolled", thus, instead of producing a torque (rotation), it produces a linear force along its length. However, linear motors are not necessarily straight. Characteristically, a linear motor's active section has ends, whereas more conventional motors are arranged as a continuous loop. A typical mode of operation is as a Lorentz-type actuator, in which the applied force is linearly proportional to the current and the magnetic field (\vec F = I \vec L \times \vec B). Linear motors are by far most commonly found in high accuracy engineering applications. It is a thriving field of applied research with dedicated scientific conferences and engineering text books. Many designs have been put forward for linear motors, falling into two major categories, low-acceleration and high-acceleration linear motors. Low-acceleration linear motors are suitable for maglev trains and other ground-based transportation applicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
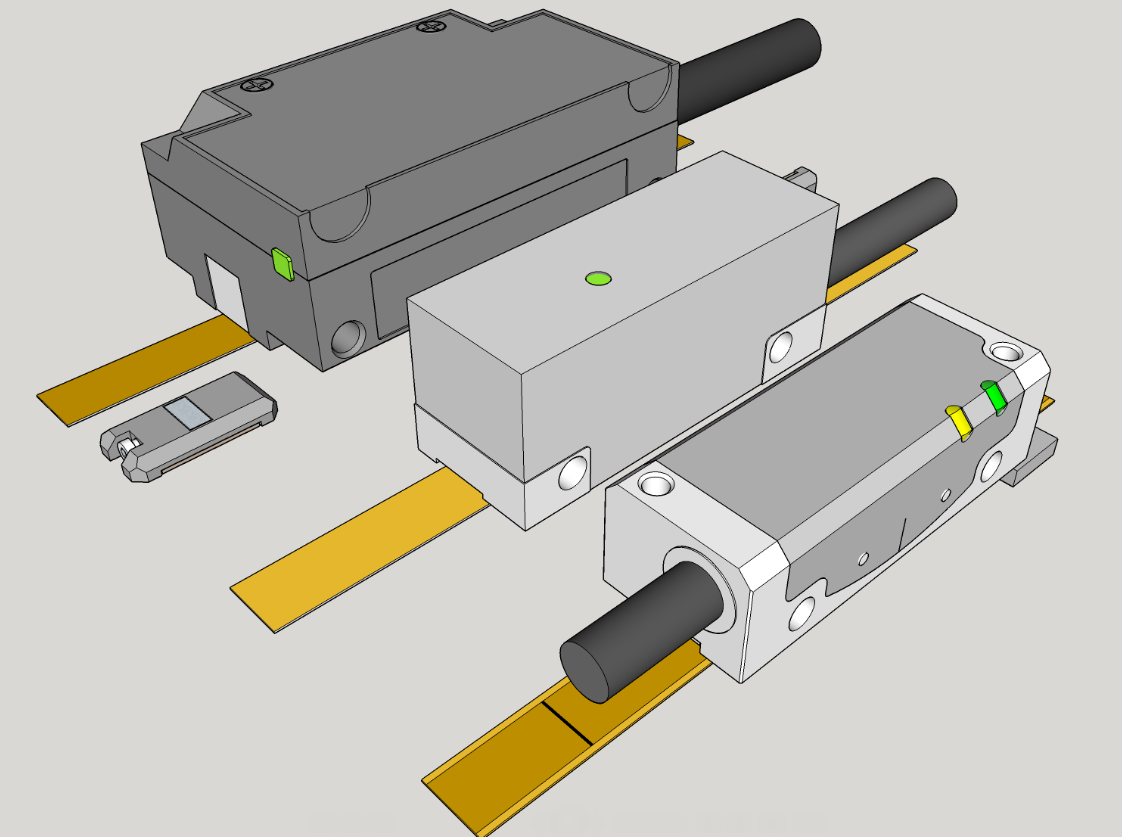
Linear Encoder
A linear encoder is a sensor, transducer or readhead paired with a scale that encodes position. The sensor reads the scale in order to convert the encoded position into an analog or digital signal, which can then be decoded into position by a digital readout (DRO) or motion controller. The encoder can be either ''incremental'' or ''absolute.'' In an incremental system, position is determined by motion over time; in contrast, in an absolute system, motion is determined by position over time. Linear encoder technologies include optical, magnetic, inductive, capacitive and eddy current. Optical technologies include shadow, self imaging and interferometric. Linear encoders are used in metrology instruments, motion systems, inkjet printers and high precision machining tools ranging from digital calipers and coordinate measuring machines to stages, CNC mills, manufacturing gantry tables and semiconductor steppers. Physical principle Linear encoders are transducers that exploit many di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solenoid
upright=1.20, An illustration of a solenoid upright=1.20, Magnetic field created by a seven-loop solenoid (cross-sectional view) described using field lines A solenoid () is a type of electromagnet formed by a helix, helical coil of wire whose length is substantially greater than its diameter, which generates a controlled magnetic field. The coil can produce a uniform magnetic field in a volume of space when an electric current is passed through it. The term ''solenoid'' was coined in 1823 by André-Marie Ampère. The helical coil of a solenoid does not necessarily need to revolve around a straight-line axis; for example, William Sturgeon's electromagnet of 1824 consisted of a solenoid bent into a horseshoe shape (not unlike an arc spring). Solenoids provide magnetic focusing of electrons in vacuums, notably in television camera tubes such as vidicons and image orthicons. Electrons take helical paths within the magnetic field. These solenoids, focus coils, surround nearly th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear-motion Bearing
A linear-motion bearing or linear slide is a bearing designed to provide free motion in one direction. There are many different types of linear motion bearings. Motorized linear slides such as machine slides, X-Y tables, roller tables and some dovetail slides are bearings moved by drive mechanisms. Not all linear slides are motorized, and non-motorized dovetail slides, ball bearing slides and roller slides provide low-friction linear movement for equipment powered by inertia or by hand. All linear slides provide linear motion based on bearings, whether they are ball bearings, dovetail bearings, linear roller bearings, magnetic or fluid bearings. X-Y tables, linear stages, machine slides and other advanced slides use linear motion bearings to provide movement along both X and Y multiple axis. Rolling-element bearing A rolling-element bearing is generally composed of a sleeve-like outer ring and several rows of balls retained by cages. The cages were originally machined from soli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robot Musicians
A robot is a machine—especially one programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the control may be embedded within. Robots may be constructed to evoke human form, but most robots are task-performing machines, designed with an emphasis on stark functionality, rather than expressive aesthetics. Robots can be autonomous or semi-autonomous and range from humanoids such as Honda's ''Advanced Step in Innovative Mobility'' ( ASIMO) and TOSY's ''TOSY Ping Pong Playing Robot'' (TOPIO) to industrial robots, medical operating robots, patient assist robots, dog therapy robots, collectively programmed ''swarm'' robots, UAV drones such as General Atomics MQ-1 Predator, and even microscopic nano robots. By mimicking a lifelike appearance or automating movements, a robot may convey a sense of intelligence or thought of its own. Autonomous things are expected to proliferate i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |