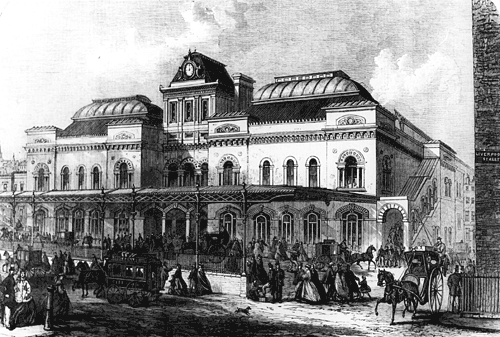|
Haggerston Railway Station
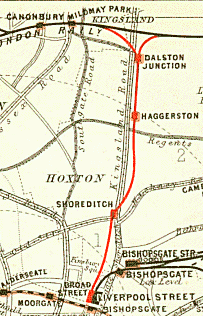
Haggerston is a station on the East London line in Haggerston within the London Borough of Hackney, Greater London. The station is located on the Kingsland Viaduct at the junction of Arbutus Street and Frederick Terrace, near Kingsland Road. The main entrance is in Lee Street. The station was built as part of the East London line extension served by National Rail London Overground under the control of the London Rail division of Transport for London, however there is no standard red National Rail "double arrow" logo signage located at the station, instead only the Overground roundel. The next station north is and the next station south is . It is in Travelcard Zone 2. History Early history (1867-1923) When the East & West India Docks & Birmingham Junction Railway (known as the North London Railway (NLR) from 1853) started operating on 26 September 1850, they shared a London terminus at Fenchurch Street railway station with the London and Blackwall Railway which involved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Overground
London Overground (also known simply as the Overground) is a Urban rail in the United Kingdom, suburban rail network serving London and its environs. Established in 2007 to take over Silverlink Metro routes, (via archive.org). it now serves a large part of Greater London as well as the home counties, home county of Hertfordshire, with 113 stations on nine different routes. The Overground forms part of the United Kingdom's National Rail network but it is under the Rail franchising in Great Britain#Concessions, concession control and branding of Transport for London. Operation has been contracted to Arriva Rail London since 2016. TfL assigned orange as a mode-specific colour for the Overground in branding and publicity including the roundel, on the Tube map, trains and stations. History Pre-1999 Rail services in Rail transport in Great Britain, Great Britain are mostly run under Rail franchising in Great Britain, franchises operated by private train operating companies, marke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hackney Central Railway Station
Hackney Central is a London Overground station on the North London line in Hackney Central, Greater London. It lies between and and is in Travelcard Zone 2. The station and all trains serving it are operated by National Rail services under the control of the London Rail division of Transport for London. However, there is no standard red National Rail "double arrow" logo signage at the station, instead only the Overground roundel. The station is connected to by a direct passenger walkway linking the two stations (replacing an earlier such link) that was opened in July 2015. This walkway means passengers do not have to exit on to the street in order to continue their onward journey. History Early years The North London Railway opened a station named ''Hackney'' on 26 September 1850, to the east of Mare Street, then in the county of Middlesex. It closed on 1 December 1870 and was replaced the same day by a station to the west of Mare Street, designed by Edwin Henry Horne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Holden
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English and French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*karilaz'' (in Latin alphabet), whose meaning was "free man". The Old English descendant of this word was '' Ċearl'' or ''Ċeorl'', as the name of King Cearl of Mercia, that disappeared after the Norman conquest of England. The name was notably borne by Charlemagne (Charles the Great), and was at the time Latinized as ''Karolus'' (as in ''Vita Karoli Magni''), later also as '' Carolus''. Some Germanic languages, for example Dutch and German, have retained the word in two separate senses. In the particular case of Dutch, ''Karel'' refers to the given name, whereas the noun ''kerel'' means "a bloke, fellow, man". Etymology The name's etymology is a Common Germanic noun ''*karilaz'' meaning "free man", which survives in English as churl (< Old English ''ċeorl''), which developed its depr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North London Line
The North London line (NLL) is a railway line which passes through the inner suburbs of west, north-west, north, and east London, England between Richmond in the south-west and Stratford in the east, avoiding central London. Its route is a rough semicircle. Although much of it originated as part of the North London Railway, the current route is the result of a series of amalgamations, closures and reopenings, and has a mix of third-rail and overhead electrical power supply. It remains heavily used by freight services in addition to the main London Overground (LO) service. Between Richmond and Gunnersbury, London Underground's District line shares tracks with London Overground services; the entire route is owned and maintained by Network Rail. TfL took over the line in 2007 and introduced new stock as well as putting the line on the Tube map. It closed for four months in 2010 between and and had a reduced service for another year to allow platform extensions and signalling u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Midland & Scottish Railway
The London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMSIt has been argued that the initials LMSR should be used to be consistent with LNER, GWR and SR. The London, Midland and Scottish Railway's corporate image used LMS, and this is what is generally used in historical circles. The LMS occasionally also used the initials LM&SR. For consistency, this article uses the initials LMS.) was a British railway company. It was formed on 1 January 1923 under the Railways Act of 1921, which required the grouping of over 120 separate railways into four. The companies merged into the LMS included the London and North Western Railway, Midland Railway, the Lancashire and Yorkshire Railway (which had previously merged with the London and North Western Railway on 1 January 1922), several Scottish railway companies (including the Caledonian Railway), and numerous other, smaller ventures. Besides being the world's largest transport organisation, the company was also the largest commercial enterprise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921 (c. 55), also known as the Grouping Act, was an Act of Parliament enacted by the British government and intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, by "grouping" them into four large companies dubbed the " Big Four". This was intended to move the railways away from internal competition, and retain some of the benefits which the country had derived from a government-controlled railway during and after the Great War of 1914–1918. The provisions of the Act took effect from the start of 1923. History The British railway system had been built up by more than a hundred railway companies, large and small, and often, particularly locally, in competition with each other. The parallel railways of the East Midlands and the rivalry between the South Eastern Railway and the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway at Hastings were two examples of such local competition. During the First World War the railways were under st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackwall Railway Station
Blackwall was a railway station in Blackwall, London, that served as the eastern terminus of the Commercial Railway (later the London and Blackwall Railway). It was located on the south side of the East India Docks, near the shore of the River Thames, down-line from the western terminus at . The station was designed by architect William Tite in an ornate Italianate style. It opened on 6 July 1840 with services connecting with a ferry service to Gravesend, Kent. Between 1870 and 1890 the station was also served by some North London Railway trains from Broad Street via Hackney and Bow services to connect to the ferry services. The station was renovated at this time. In March 1926 the London and North Eastern Railway and Port of London Authority announced passenger services would be withdrawn on 30 June 1926. However, with the start of the national general strike services were suspended early on 3 May 1926, and never resumed. John Betjeman (1906-1984) in his book First an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North London Line City Branch
The City Branch was a short spur of the North London Line allowing direct access from the east-west main route of the North London Railway to the terminus at Broad Street in the City of London. History The North London Railway (NLR) was founded in 1850 with the intention of operating a network of railway lines throughout north London that connected to the East India and West India Docks. The company's main headquarters was at Bow, and from there a connection to the London and Blackwall Railway's route allowed the NLR's trains access to a terminus in the City of London, in this case Fenchurch Street. However, this meant that, in order to reach the City, the NLR's trains had to take a fairly circuitous route, and so the company decided to build its own central terminus. In 1861, the North London Railway Act was passed giving permission to the NLR to build an extension from its main line through Hackney to a site at Old Broad Street. The majority of the route was built on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poplar (East India Road) Railway Station
Poplar (East India Road) was a railway station located on the East India Dock Road in Poplar, London. It was opened in 1866 by the North London Railway. It was the southern passenger terminus of the NLR, although goods trains ran on to connect to the London and Blackwall Railway (LBR) for the East India Docks or to the LBR's Millwall Extension Railway for the West India Docks. The station site is now (2021) occupied by All Saints DLR station whilst Poplar DLR station is to the south and west. Description The station building was located on the south side of the East India Dock Road bridge over the railway and was a substantial brick building with some Portland Stone features designed by architect Thomas Matthews. There were four arched windows arranged either side of three arched doors. It had a flat roof. Within the building was a parcels office and ticket office and after passing the ticket inspector the passenger had the choice of the going left for the terminating platfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad Street Railway Station (London)
Broad Street was a major terminal station in the City of London, adjacent to Liverpool Street station. It served as the main terminus of the North London Railway (NLR) network, running from 1865 to 1986. During its lifetime, it catered for mainly local suburban services around London, and over time struggled to compete with other modes of transport, leading to its closure. The station was built as a joint venture by the NLR and the London and North Western Railway (LNWR) in order to have a station serving freight closer to the City. It was immediately successful for both goods and passenger services and saw a significant increase in NLR traffic. Usage peaked in the early 20th century, after which it suffered from competition of London trams,_buses,_and_particularly_the_London_Underground.html" ;"title=""type": ..., buses, and particularly the London Underground">"type": ..., buses, and particularly the London Underground network. Patronage gradually fell and services decreased, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London & North Western Railway
The London and North Western Railway (LNWR, L&NWR) was a British railway company between 1846 and 1922. In the late 19th century, the L&NWR was the largest joint stock company in the United Kingdom. In 1923, it became a constituent of the London, Midland and Scottish (LMS) railway, and, in 1948, the London Midland Region of British Railways: the LNWR is effectively an ancestor of today's West Coast Main Line. History The company was formed on 16 July 1846 by the amalgamation of the Grand Junction Railway, London and Birmingham Railway and the Manchester and Birmingham Railway. This move was prompted, in part, by the Great Western Railway's plans for a railway north from Oxford to Birmingham. The company initially had a network of approximately , connecting London with Birmingham, Crewe, Chester, Liverpool and Manchester. The headquarters were at Euston railway station. As traffic increased, it was greatly expanded with the opening in 1849 of the Great Hall, designed by P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






_&_Poplar_RJD_56.jpg)